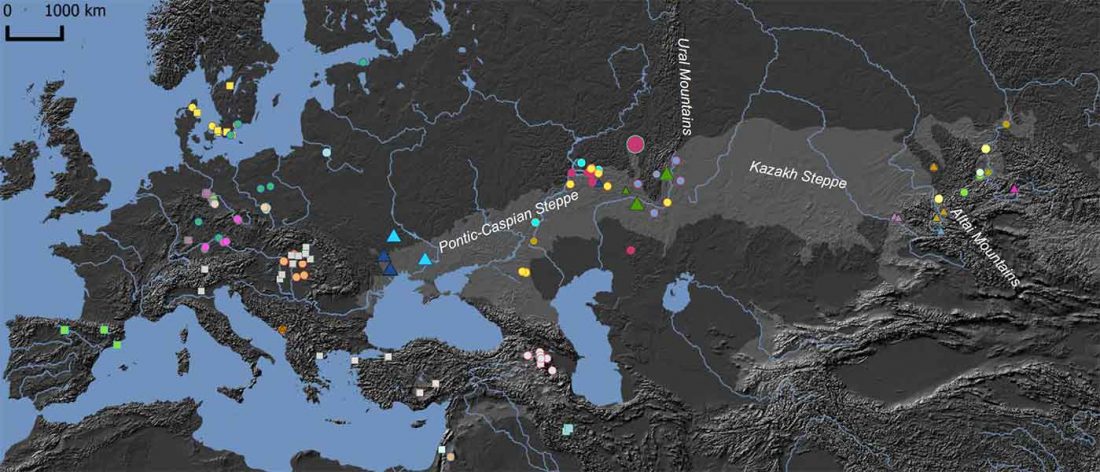
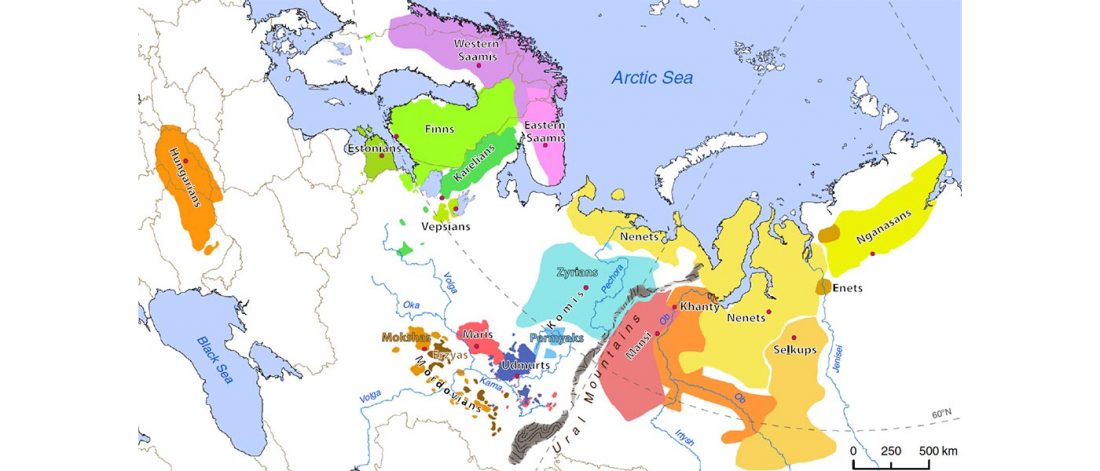
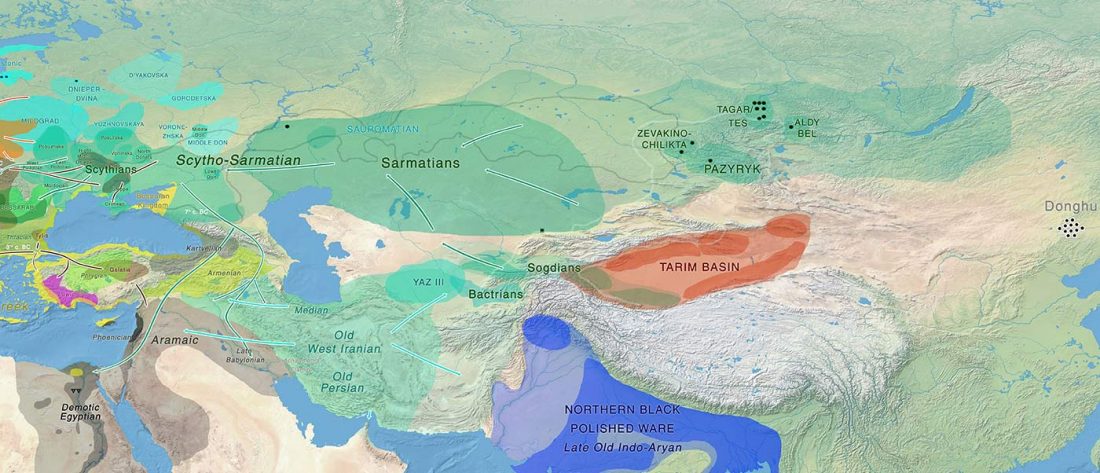
New paper (behind paywall) Ancient genomes suggest the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe as the source of western Iron Age nomads, by Krzewińska et al. Science (2018) 4(10):eaat4457.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine, some links to images and tables deleted for clarity):
… Read the rest “Early Iranian steppe nomadic pastoralists also show Y-DNA bottlenecks and R1b-L23”Late Bronze Age (LBA) Srubnaya-Alakulskaya individuals carried mtDNA haplogroups associated with Europeans or West Eurasians (17) including H, J1, K1, T2, U2, U4, and U5 (table S3). In contrast, the Iron Age nomads (Cimmerians, Scythians, and Sarmatians) additionally carried mtDNA haplogroups associated with Central Asia and the Far East (A, C, D, and M). The absence of East Asian mitochondrial