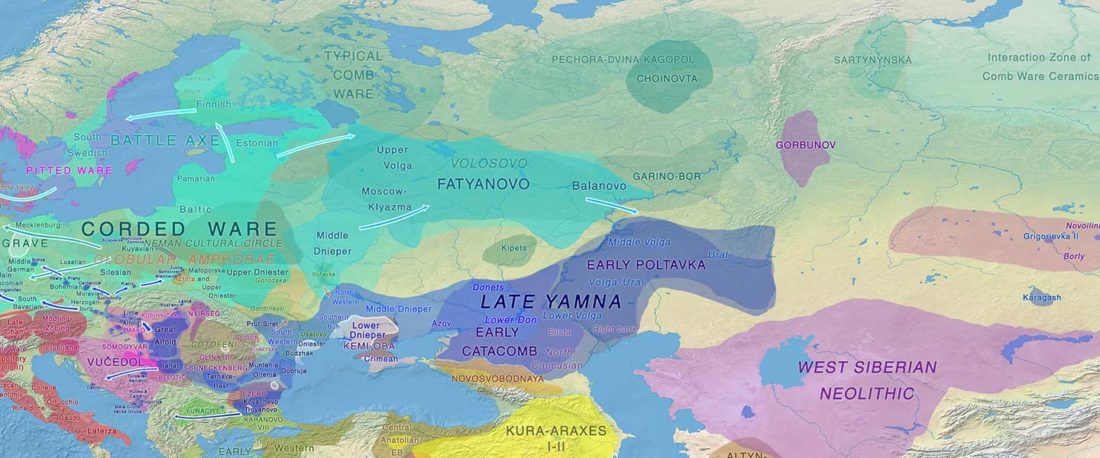
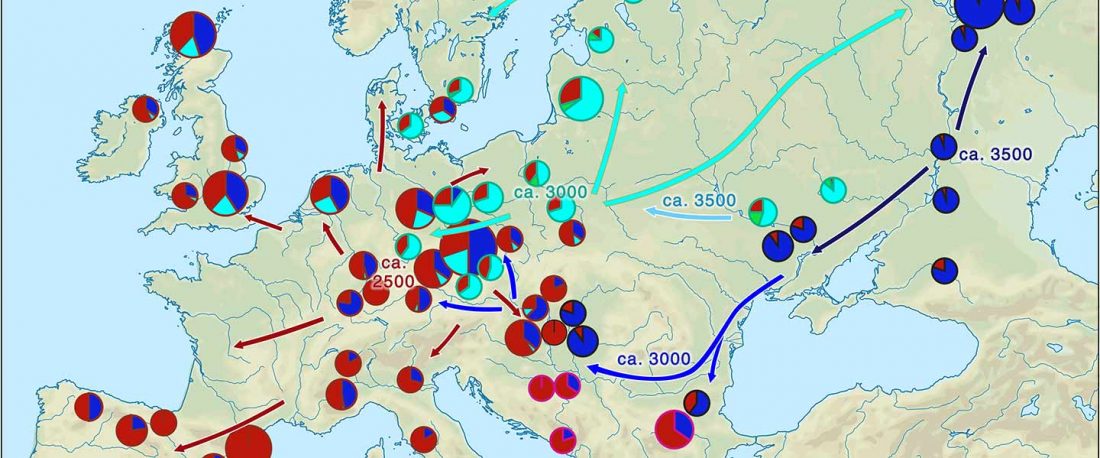
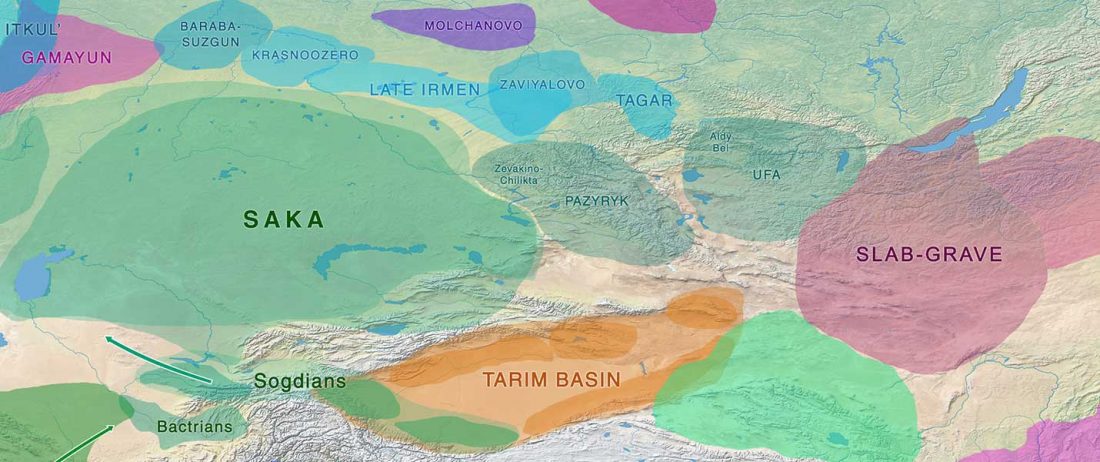
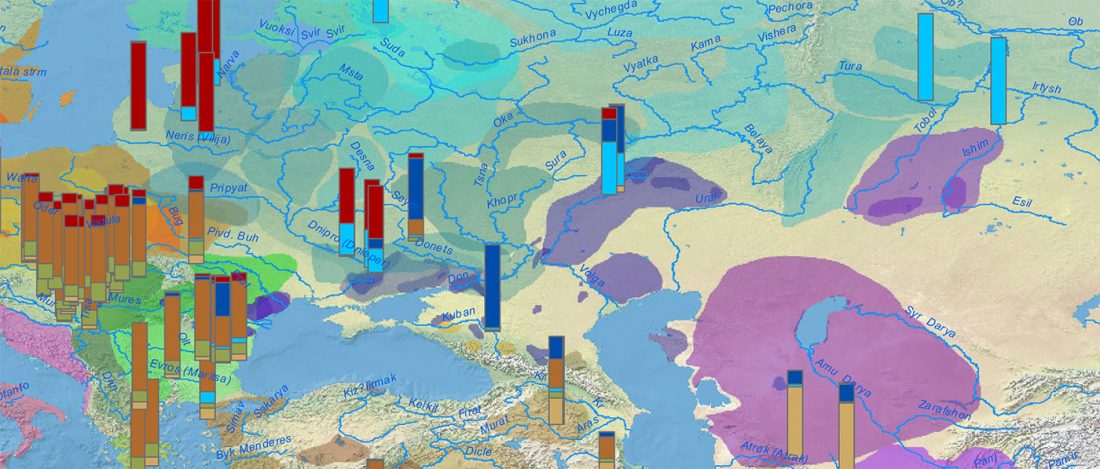
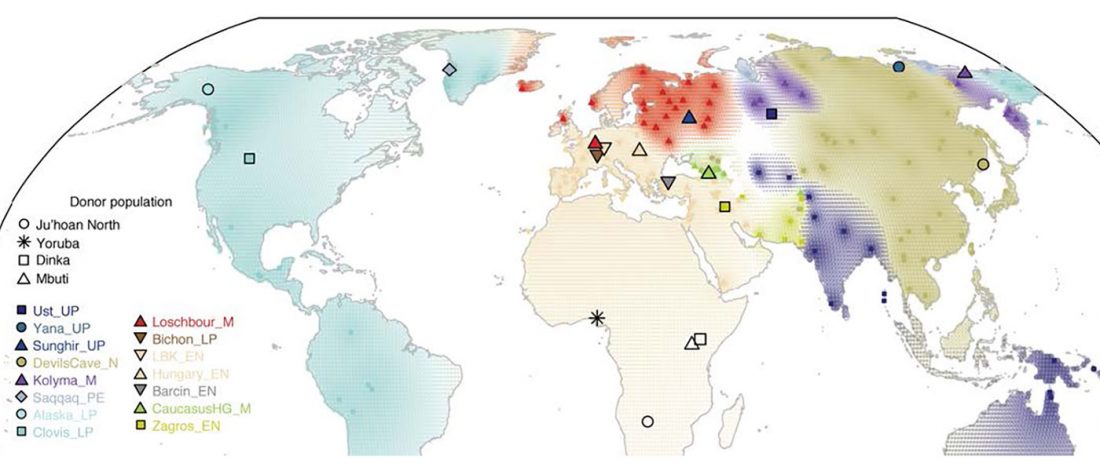
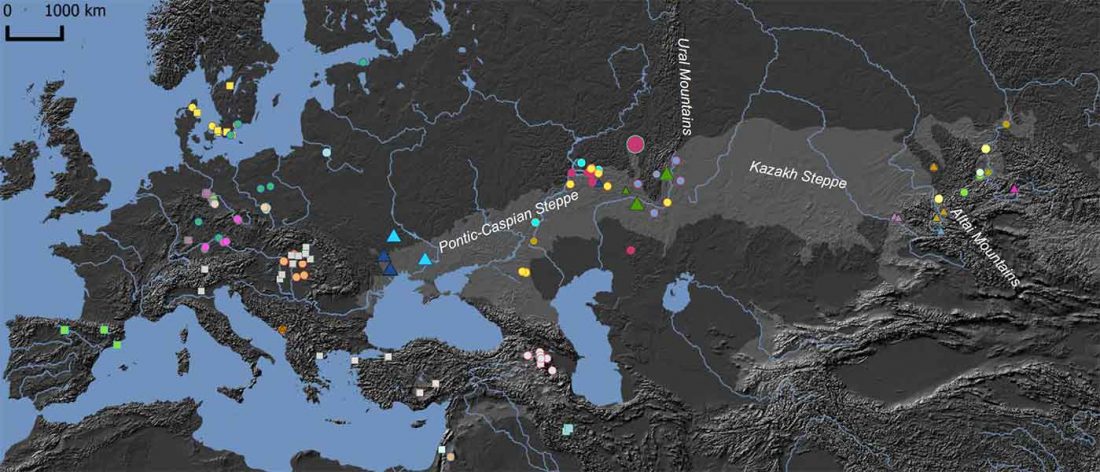
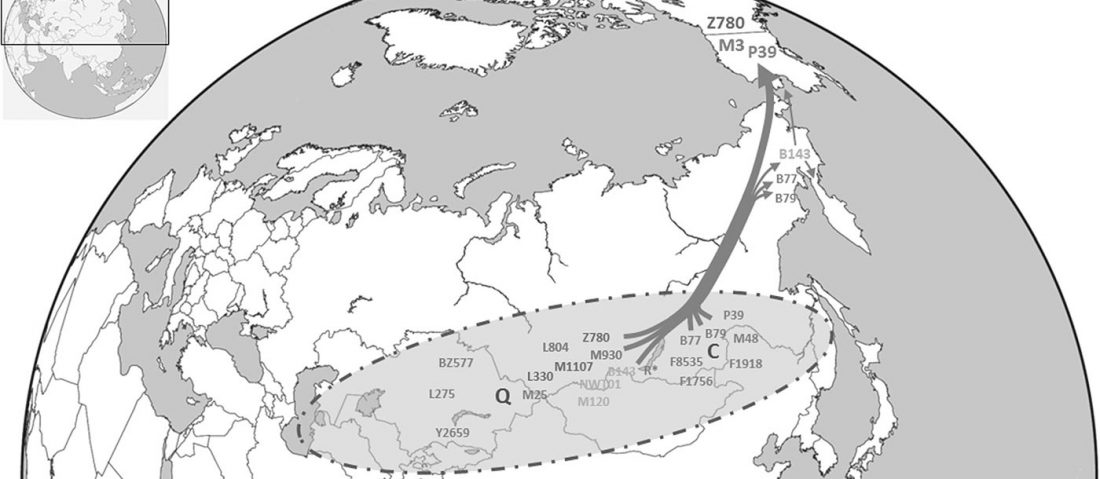
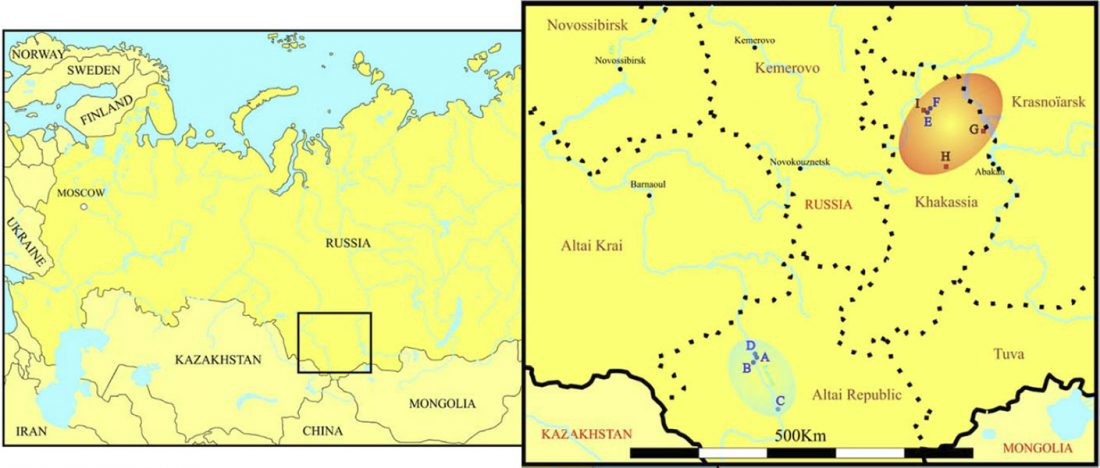
The recent preprint on ancient DNA from Veretye, Lyalovo/Volosovo and Fatyanovo from Saag et al. (2020) has been published in Science Advances Vol. 7, no. 4, eabd6535, and with it the BAM files.
Here are the Y-SNP calls from the files, following the FTDNA Haplotree standard, with Fatyanovo individuals in alphabetical order:
- Veretye PES001 from Peschanitsa (ca. 10785–10626 calBC), mtDNA U4a1, Y-DNA R1aM459YP1301(pre-YP1272?), with 2 SNPs derived – YP1306 (T-C, 5 reads) and Y12474 (T-A, 6 reads) – and 46 SNPs ancestral at the YP1272 level. A sample with 5× coverage that