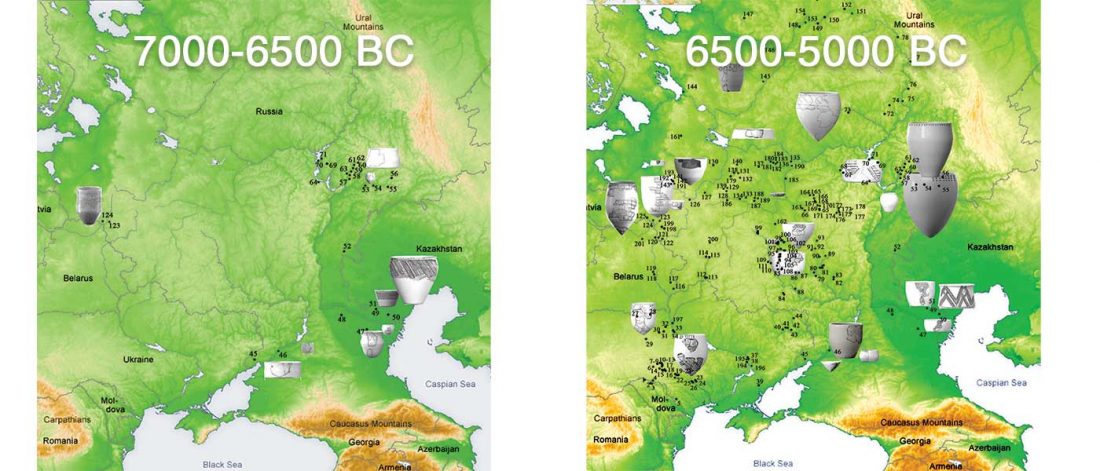
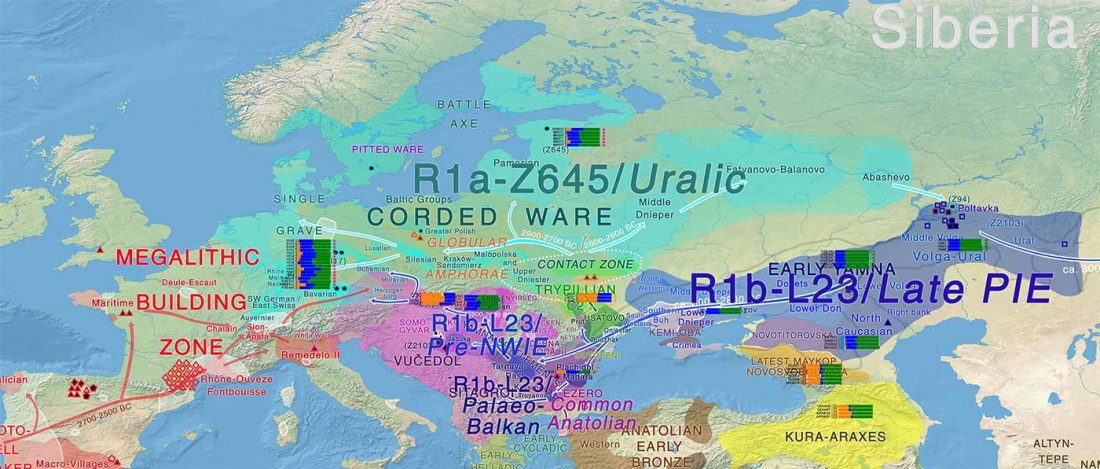
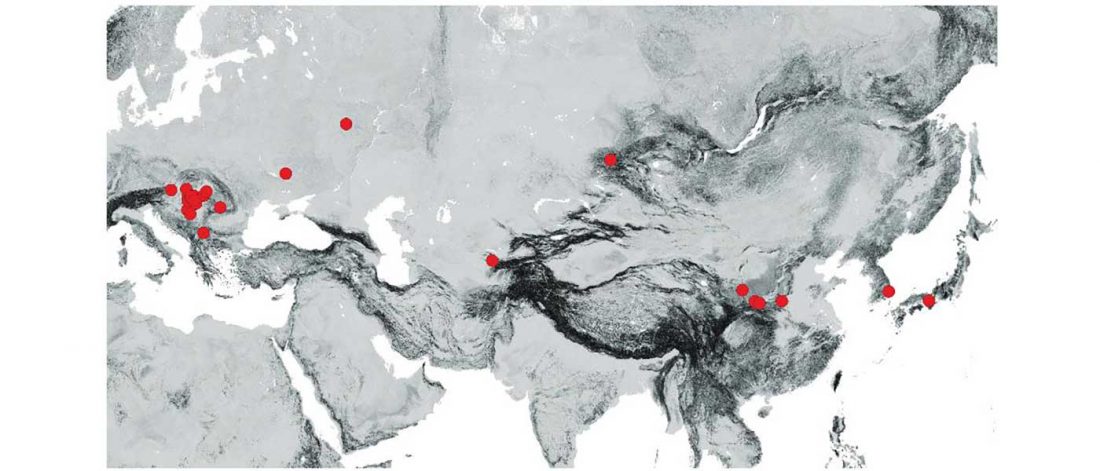
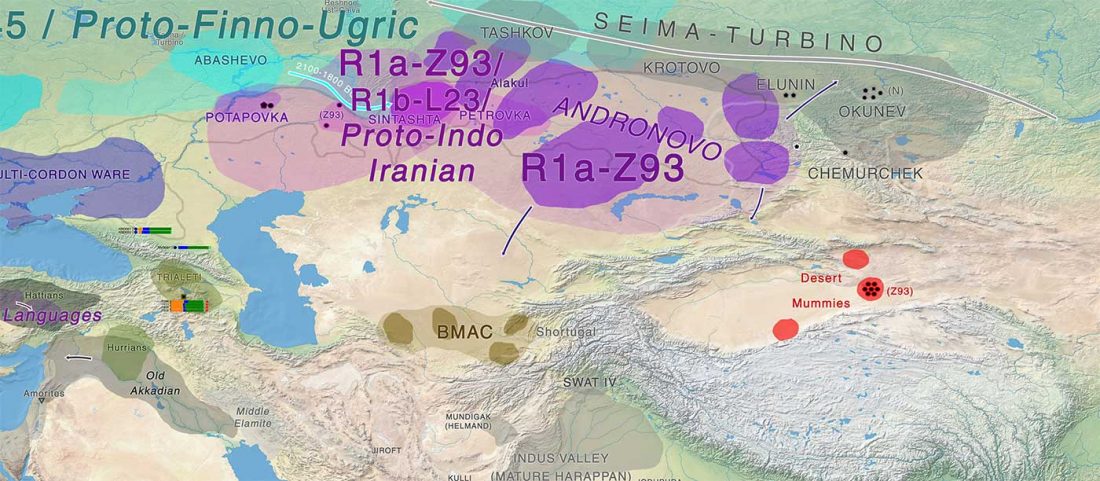
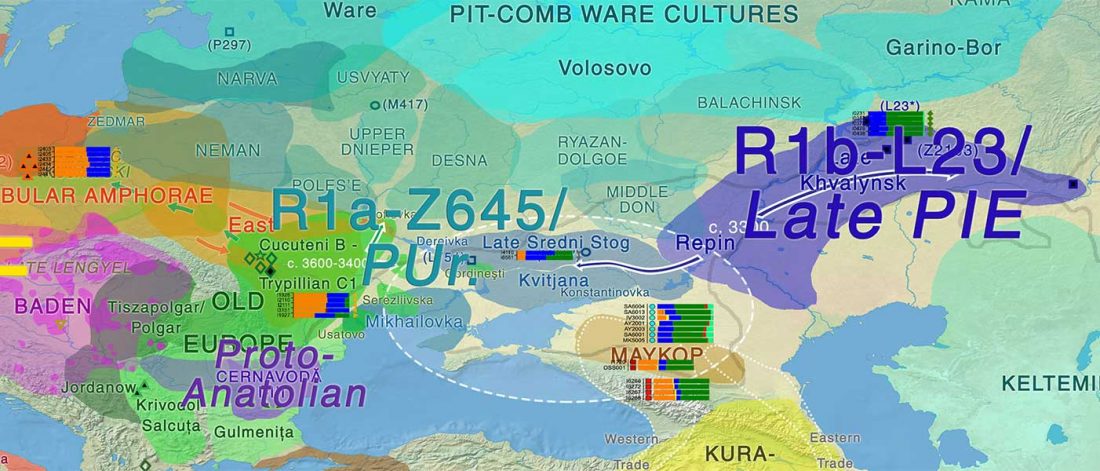
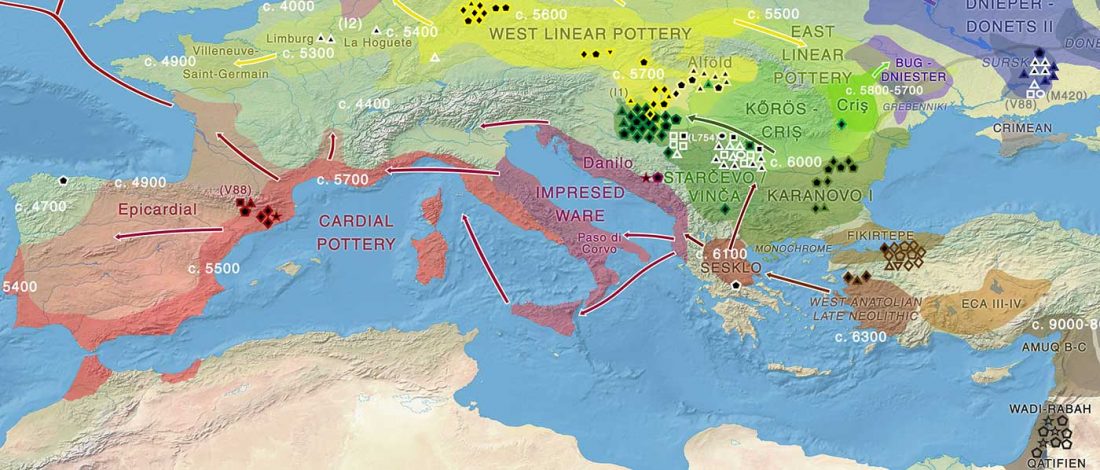
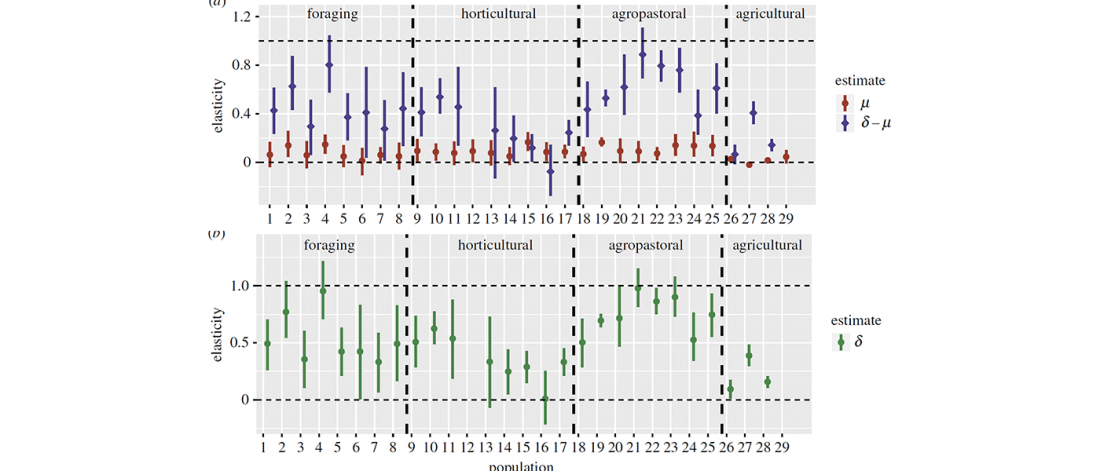
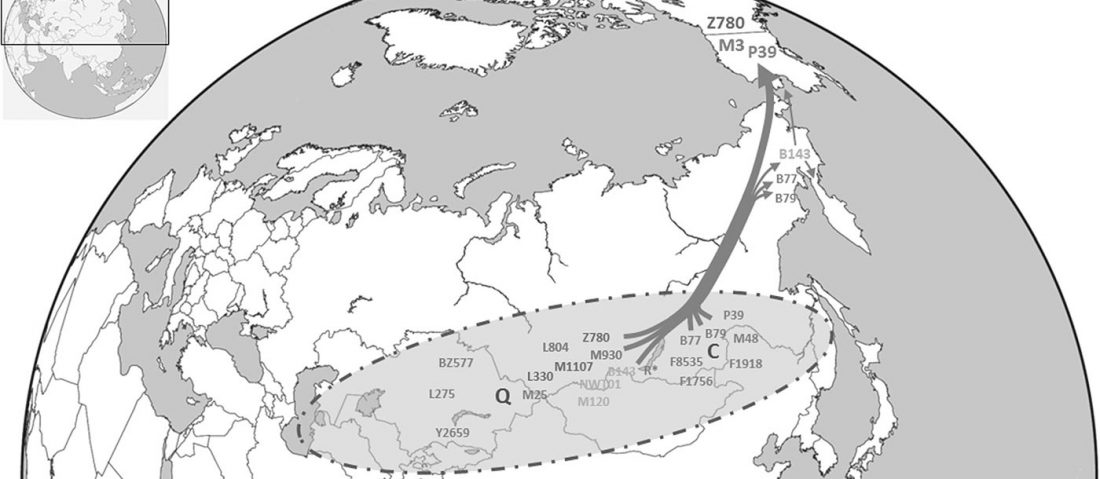
It has been known for a long time that the Caucasus must have hosted many (at least partially) isolated populations, probably helped by geographical boundaries, setting it apart from open Eurasian areas.
David Reich writes in his book the following about India:
… Read the rest “Dzudzuana, Sidelkino, and the Caucasus contribution to the Pontic-Caspian steppe”The genetic data told a clear story. Around a third of Indian groups experienced population bottlenecks as strong or stronger than the ones that occurred among Finns or Ashkenazi Jews. We later confirmed this finding in an even larger dataset that we collected working with Thangaraj: genetic data from more than 250 jati groups spread throughout India (…)