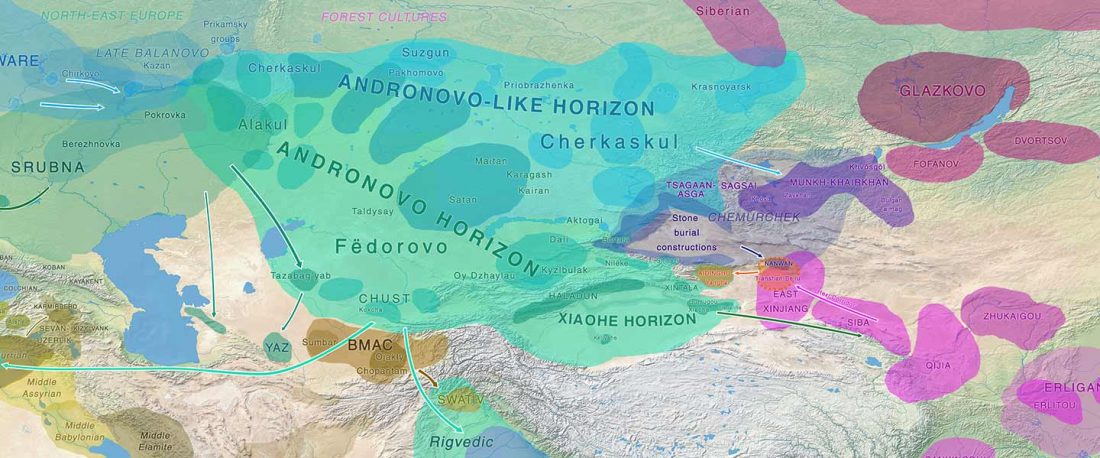
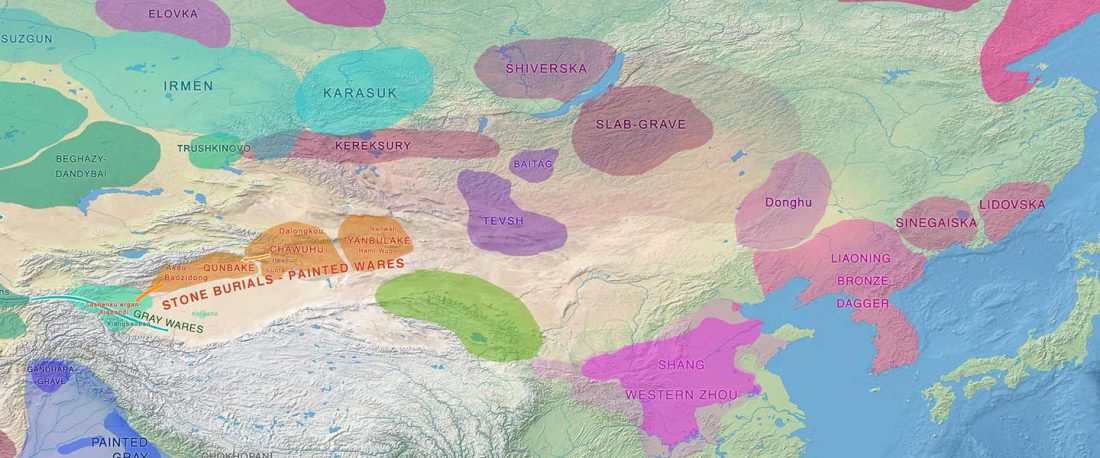
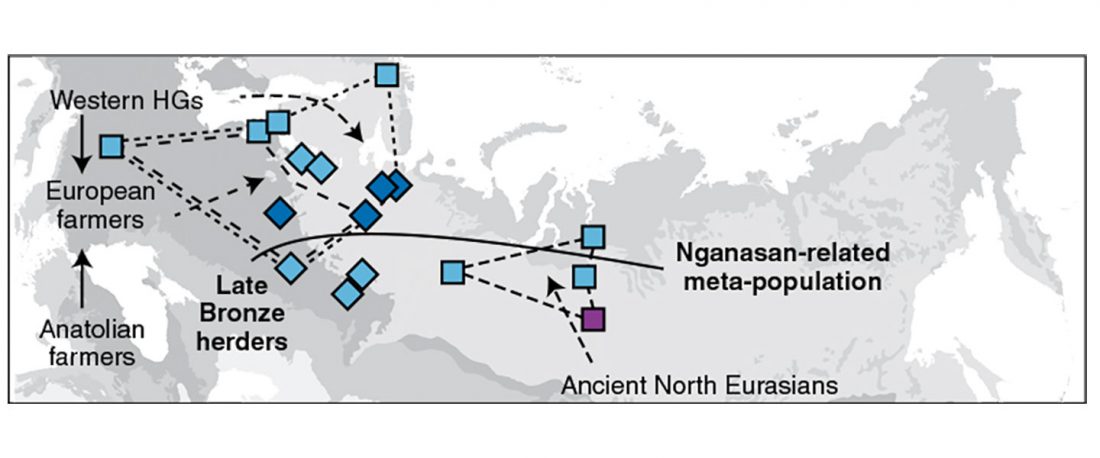
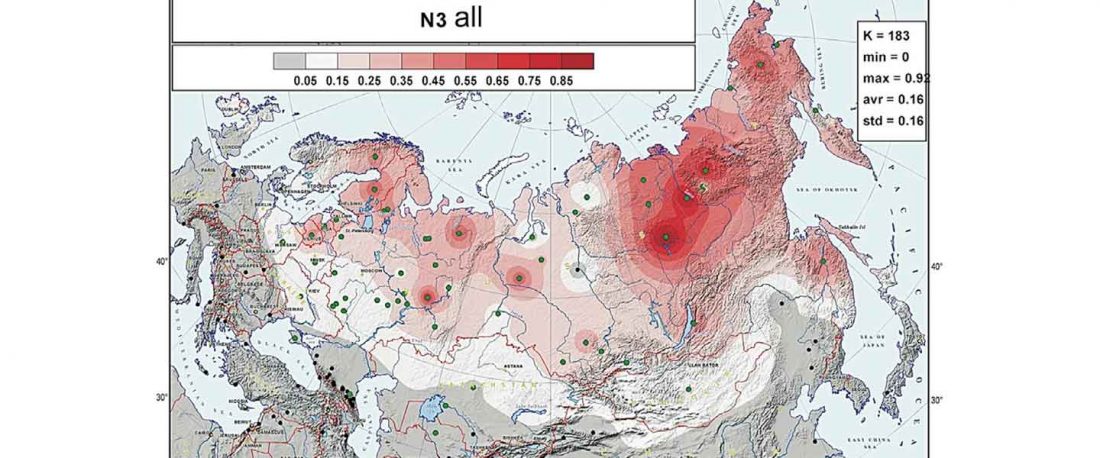
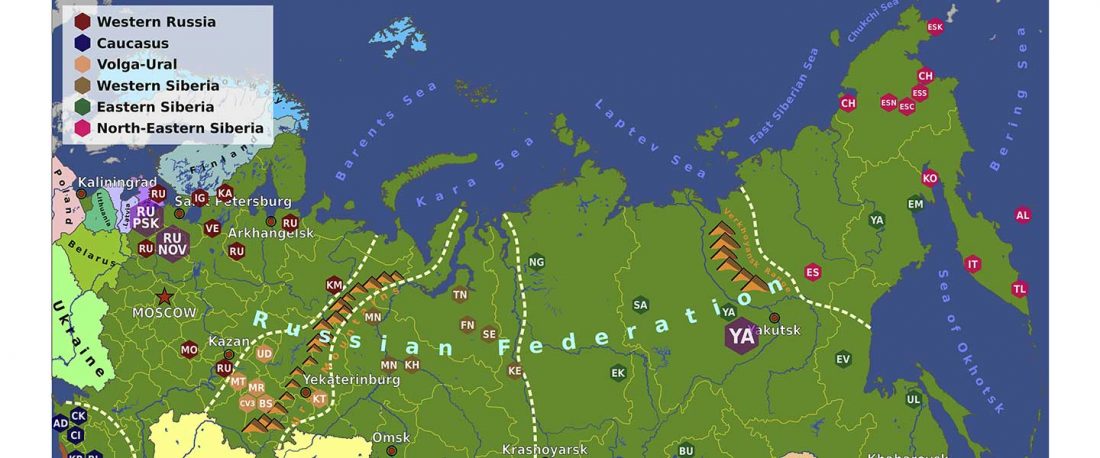
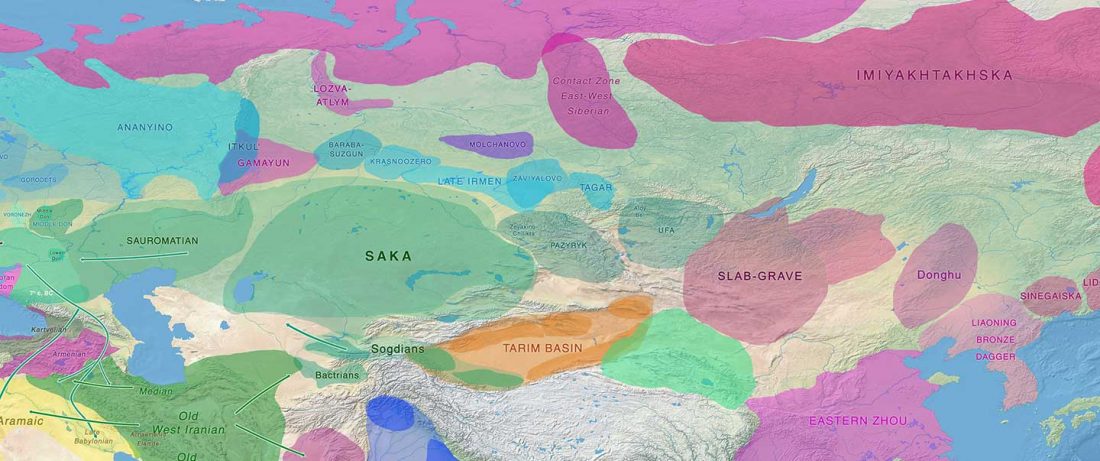
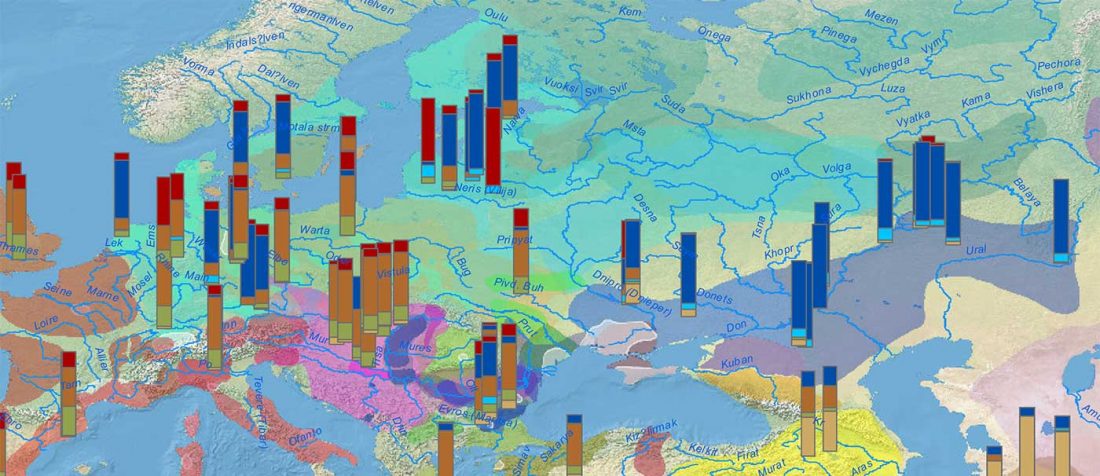
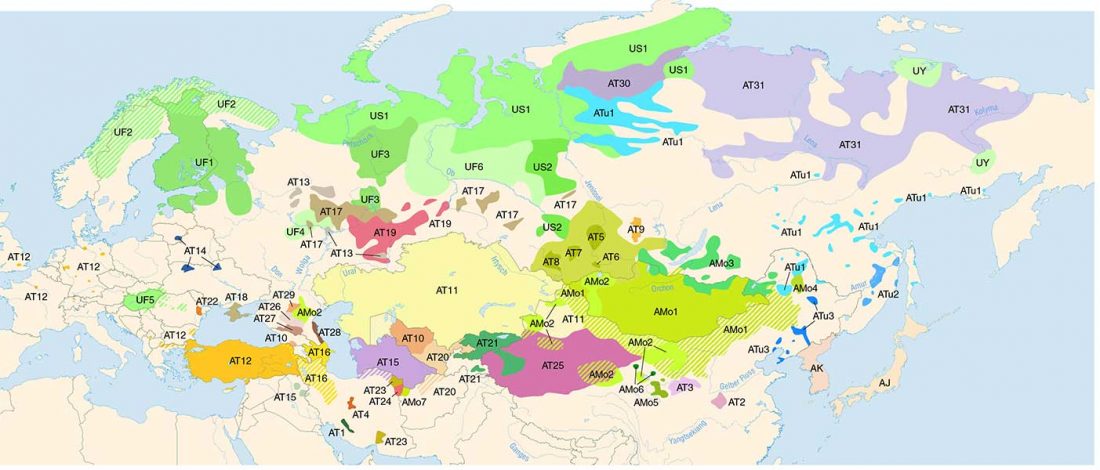
Another preprint came out at the same time as Wang et al. (2020), from the Jena Lab of the Max Planck Society: A dynamic 6,000-year genetic history of Eurasia’s Eastern Steppe, by Jeong, Warinner, et al. bioRxiv (2020).
NOTE. I have now updated the Ancient DNA Dataset, the Prehistory Atlas – with PDF and GIS files including Y-DNA and mtDNA of all newly reported samples (starting with the Neolithic) – as well as the PCA files with those from Wang et al. (2020).
The conclusions are similar, but with some interesting twists. Relevant excerpts (emphasis mine), … Read the rest “R1b-rich Proto-Indo-Europeans show genetic continuity in Asia”