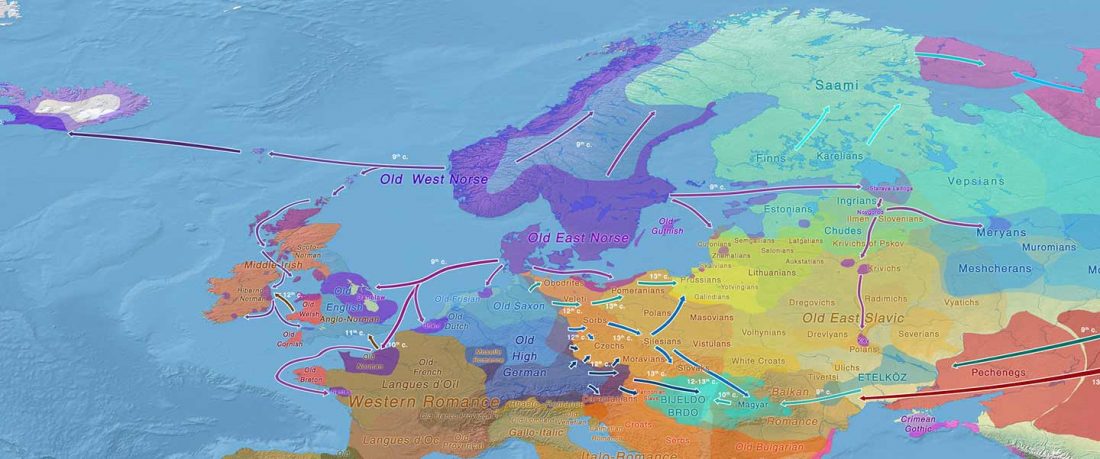
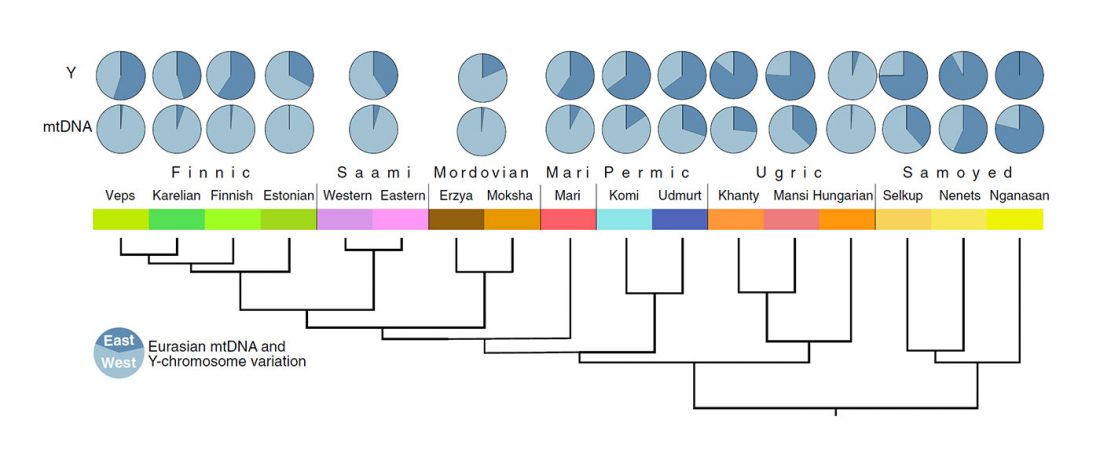
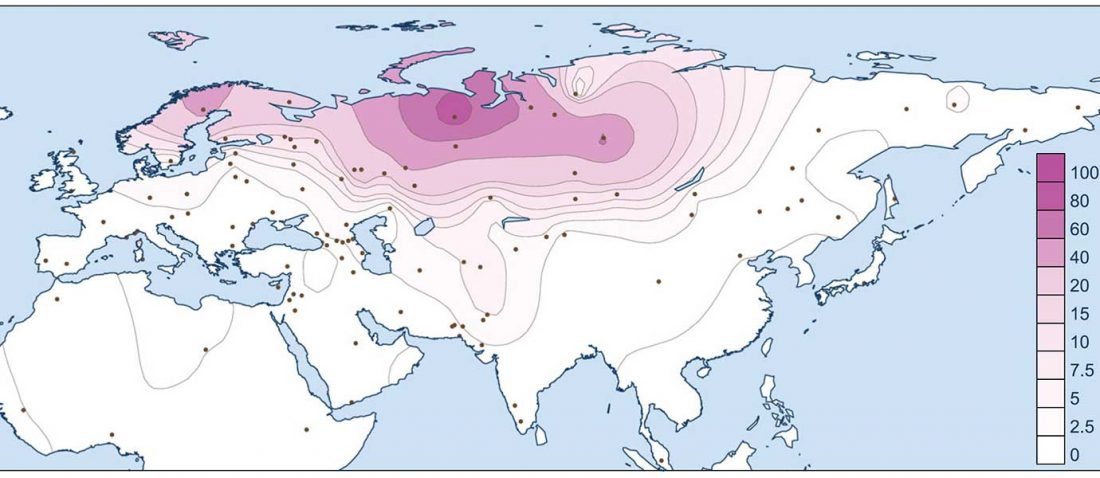
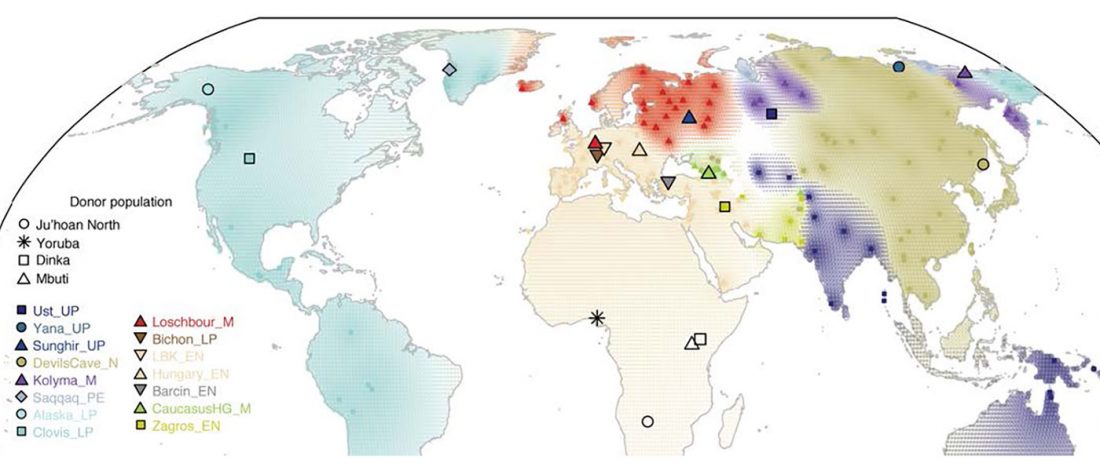
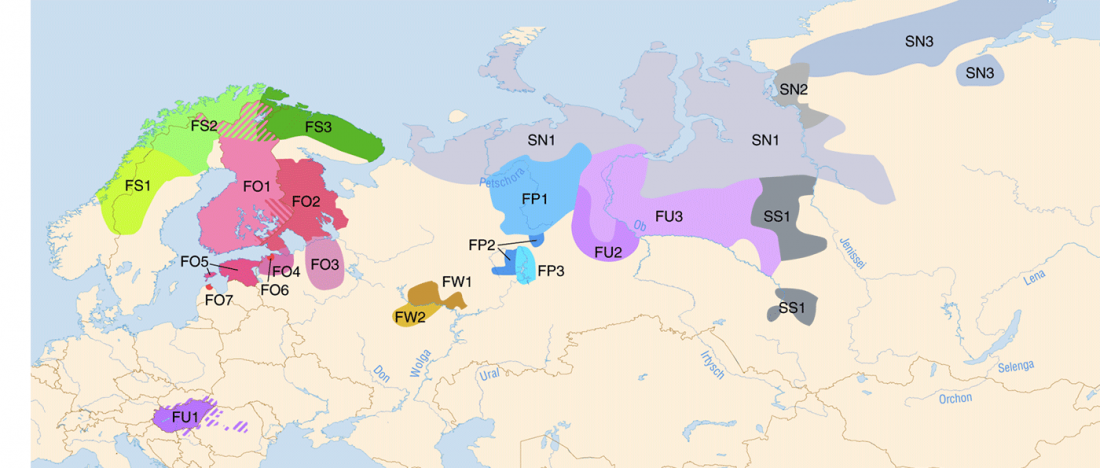
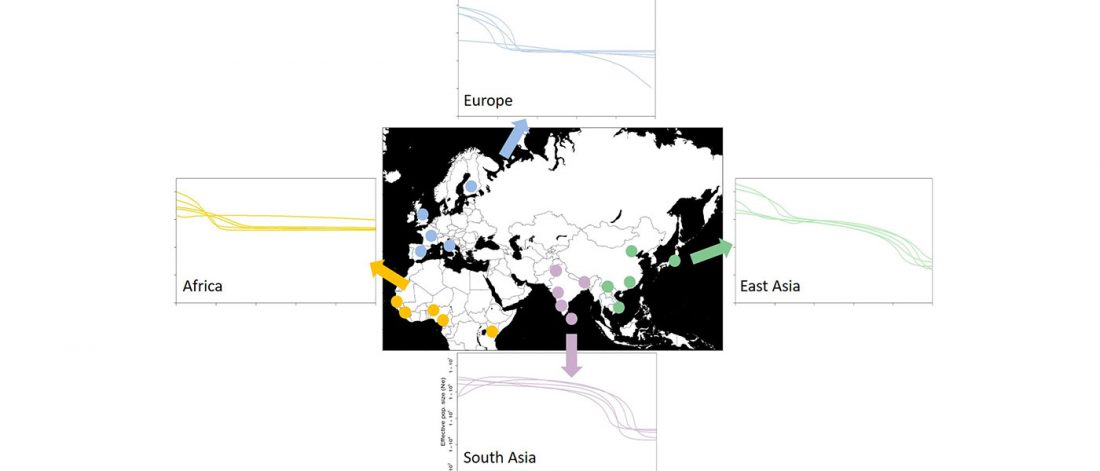
Open access Population genomics of the Viking world, by Margaryan et al. bioRxiv (2019), with a huge new sampling from the Viking Age.
#EDIT (16 SEP 2020): The paper has been published in Nature.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine, modified for clarity):
… Read the rest “Vikings, Vikings, Vikings! “eastern” ancestry in the whole Baltic Iron Age”To understand the genetic structure and influence of the Viking expansion, we sequenced the genomes of 442 ancient humans from across Europe and Greenland ranging from the Bronze Age (c. 2400 BC) to the early Modern period (c. 1600 CE), with particular emphasis on the Viking Age. We find that the period preceding the Viking Age was