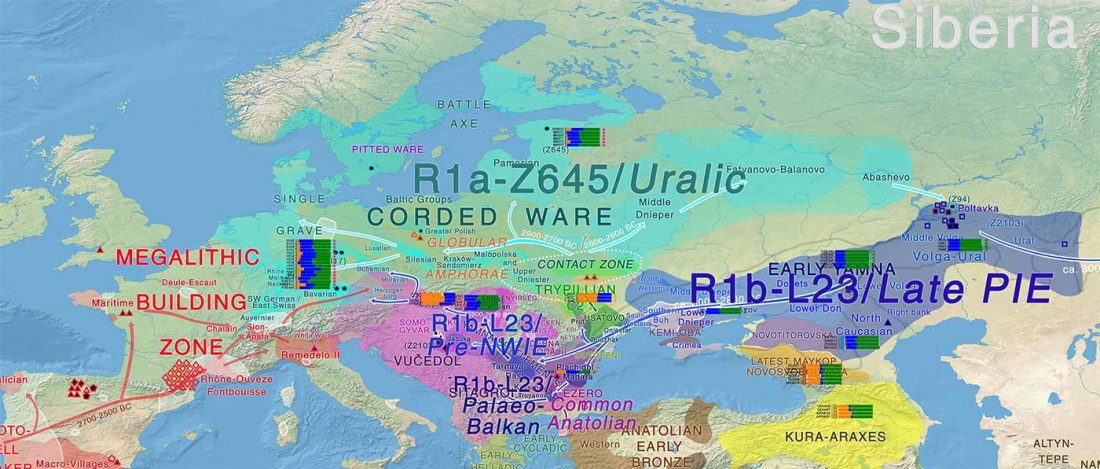
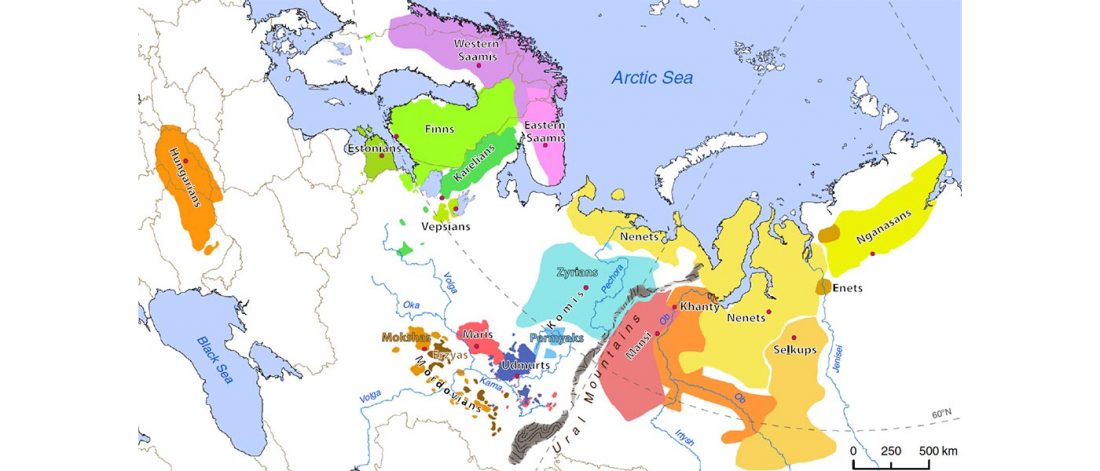
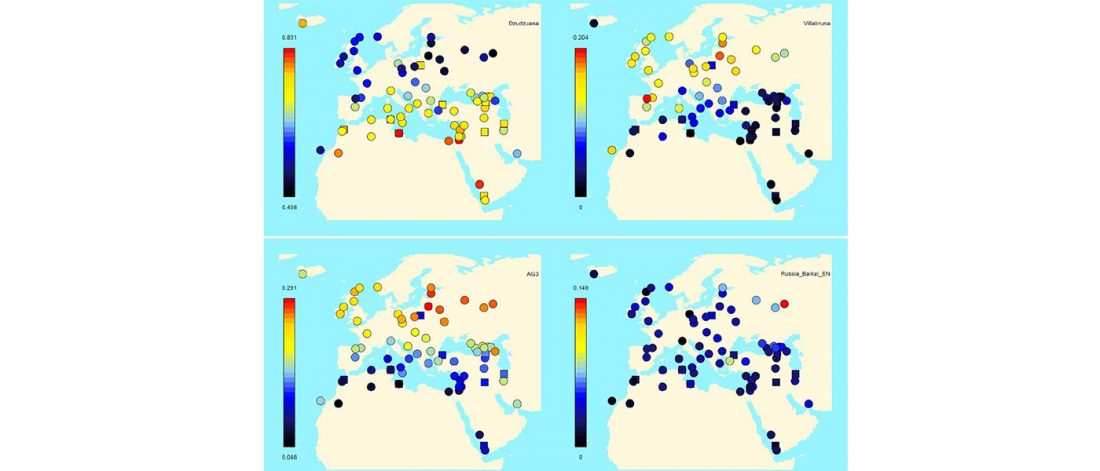
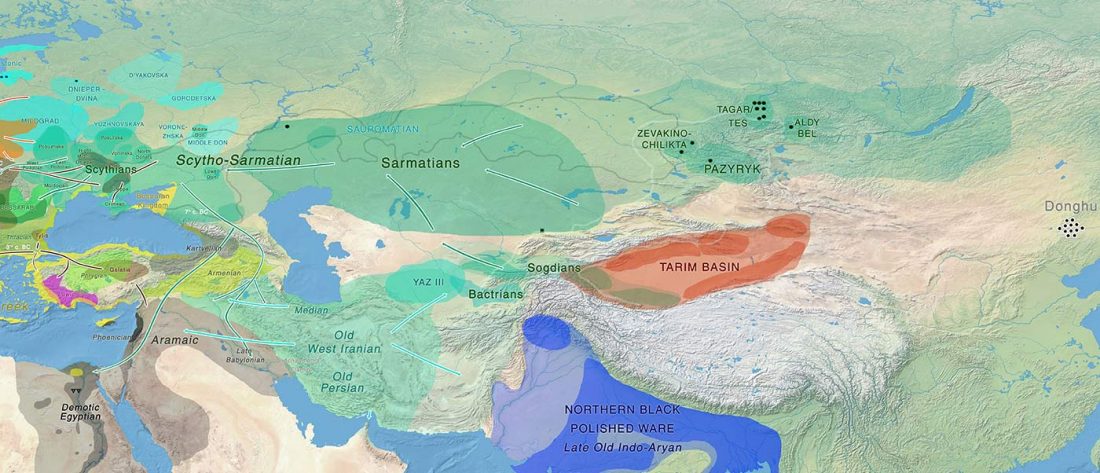
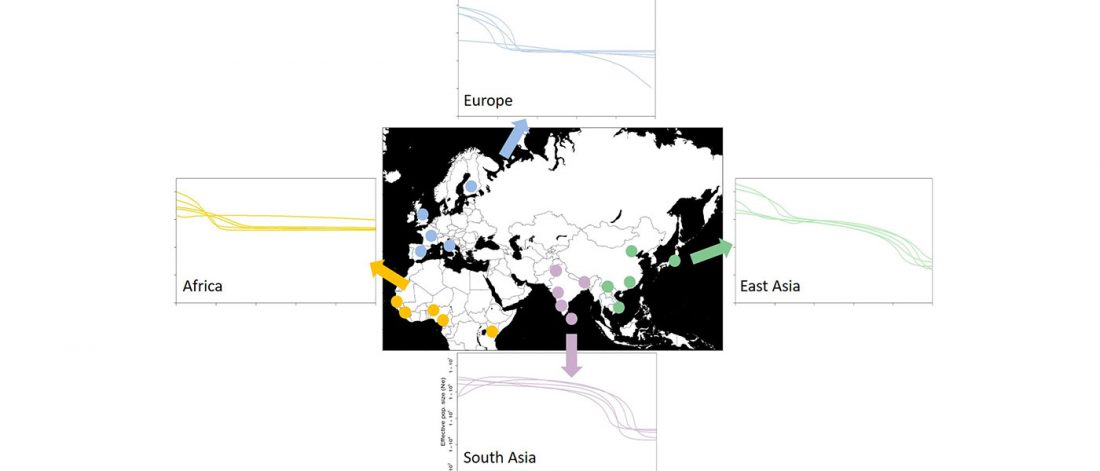
R1a-Z280 lineages in Srubna; and first Palaeo-Balkan R1b-Z2103?
Scythian samples from the North Pontic area are far more complex than what could be seen at first glance. From the new Y-SNP calls we have now thanks to the publications at Molgen (see the spreadsheet) and in Anthrogenica threads, I think this is the basis to work with:
NOTE. I understand that writing a paper requires a lot of work, and probably statistical methods are the main interest of authors, editors, and reviewers. But it is difficult to comprehend how any user of open source tools can instantly offer a more complex assessment of the samples’ Y-SNP … Read the rest “R1a-Z280 lineages in Srubna; and first Palaeo-Balkan R1b-Z2103?”