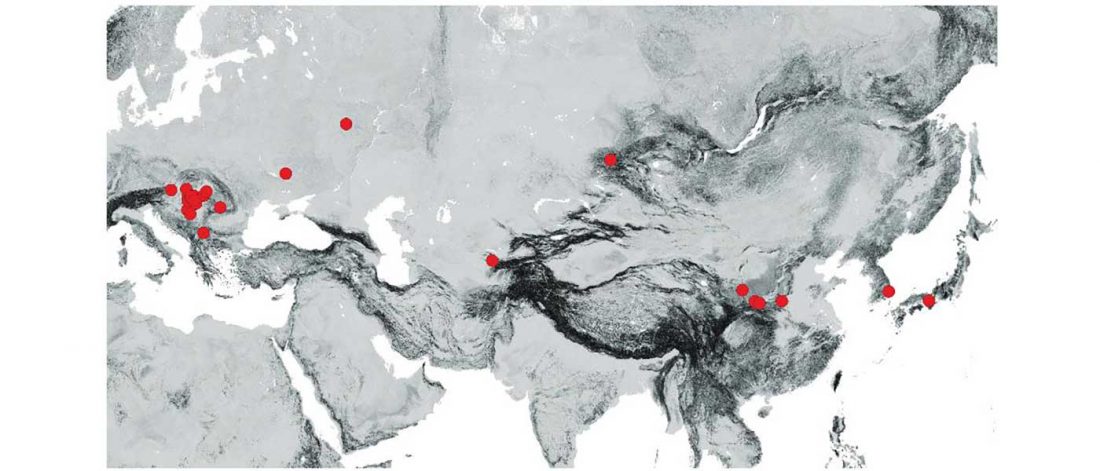
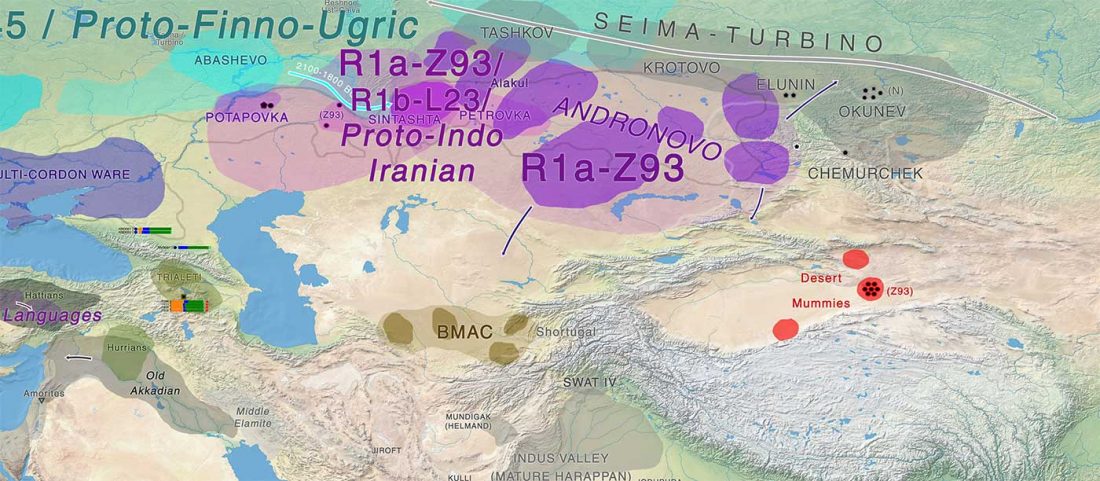
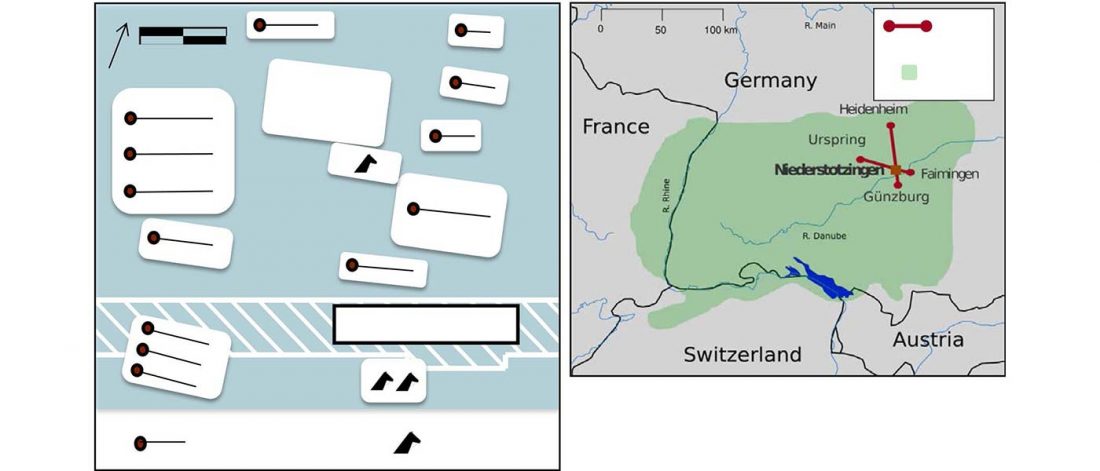
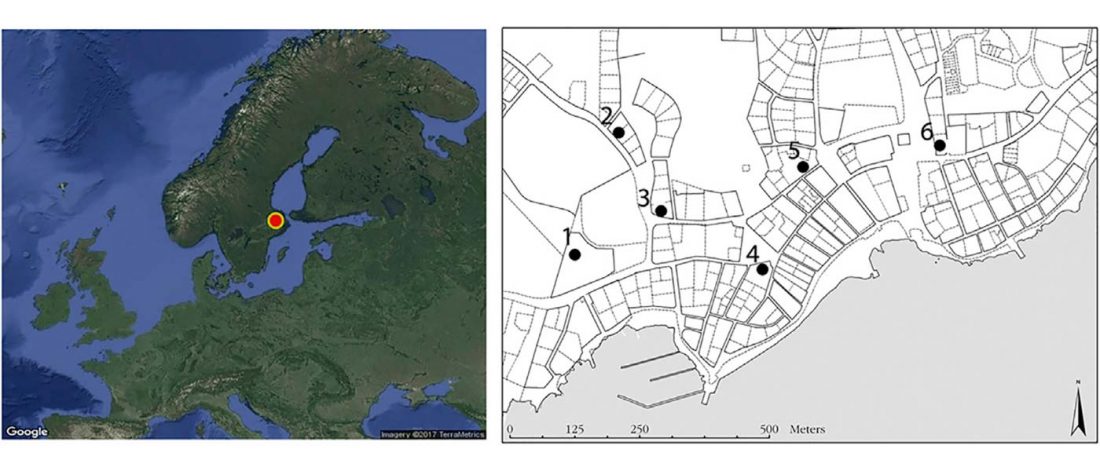
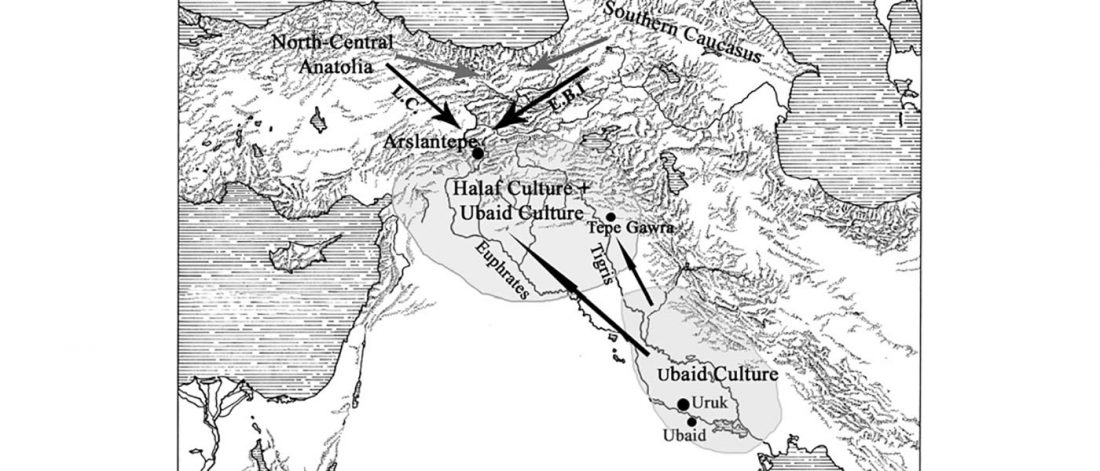
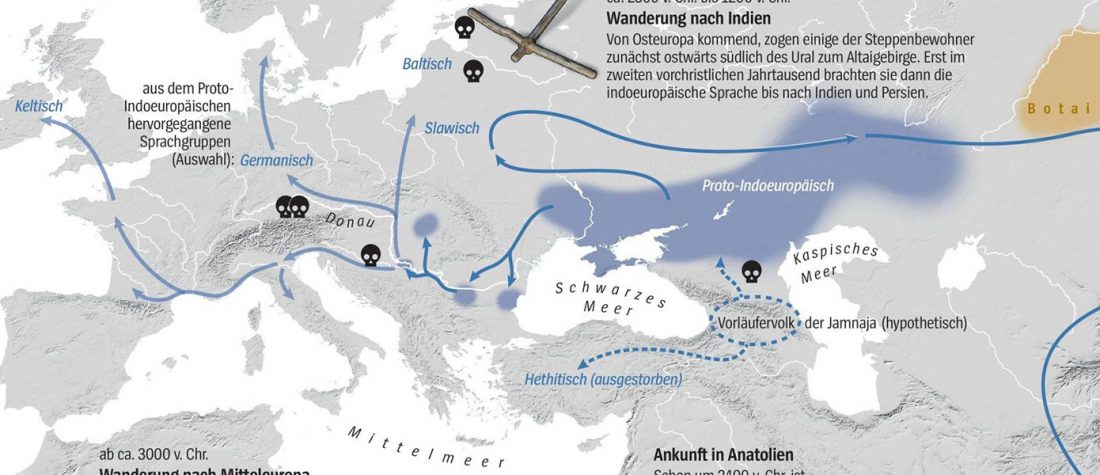
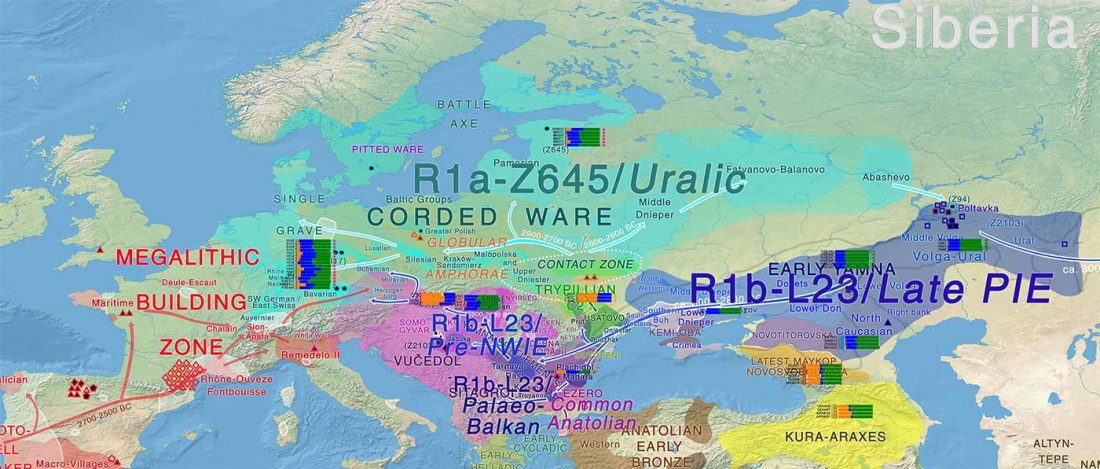
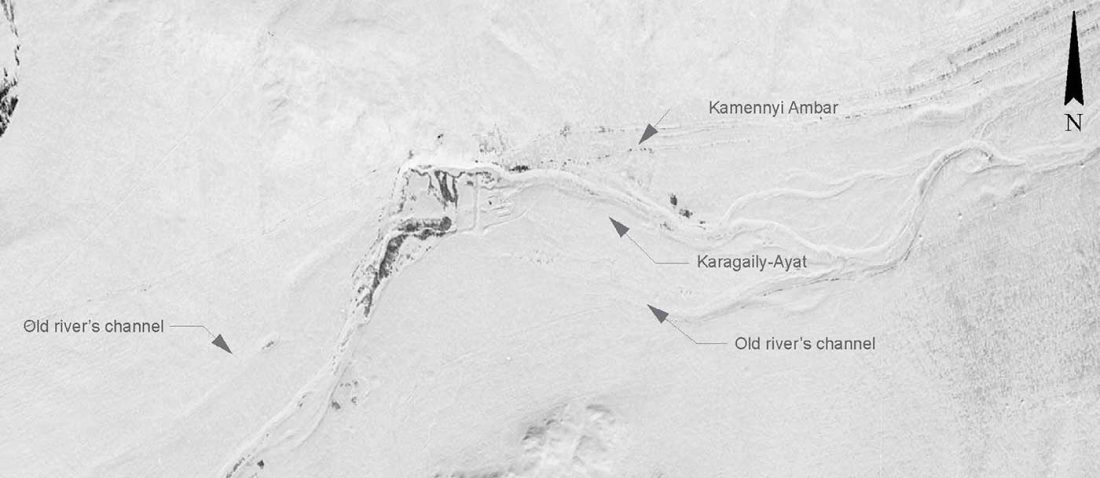
Evolution of Steppe, Neolithic, and Siberian ancestry in Eurasia (ISBA 8, 19th Sep)
Some information is already available from ISBA 8 (see programme in PDF), thanks to the tweets from Alexander M. Kim.
Official abstracts are listed first (emphasis mine), then reports and images with link to Kim’s tweets. Here is the list for quick access:
- Turkic and Hunnic expansions
- Central Asia and Indo-Iranian
- British Isles
- MN Atlantic / Megalithic cultures
- Central European Bronze Age
Updates (17:00 CET):
- Finland AD 5th-8th c.
- Russian Far East populations
- Dairying in ancient Mongolia
- Neolithic transition in Northeast Asia
Turkic and Hunnic expansions
Tracing the origin and expansion of the Turkic and … Read the rest “Evolution of Steppe, Neolithic, and Siberian ancestry in Eurasia (ISBA 8, 19th Sep)”