Open access preprint at bioRxiv, Ancient Fennoscandian genomes reveal origin and spread of Siberian ancestry in Europe, by Lamnidis et al. (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
European history has been shaped by migrations of people, and their subsequent admixture. Recently, evidence from ancient DNA has brought new insights into migration events that could be linked to the advent of agriculture, and possibly to the spread of Indo-European languages. However, little is known so far about the ancient population history of north-eastern Europe, in particular about populations speaking Uralic languages, such as Finns and Saami. Here we analyse ancient genomic data from 11 individuals from Finland and Northwest Russia. We show that the specific genetic makeup of northern Europe traces back to migrations from Siberia that began at least 3,500 years ago. This ancestry was subsequently admixed into many modern populations in the region, in particular populations speaking Uralic languages today. In addition, we show that ancestors of modern Saami inhabited a larger territory during the Iron Age than today, which adds to historical and linguistic evidence for the population history of Finland.
Interesting excerpts (edited):
While the Siberian genetic component described here was previously described in modern-day populations from the region, we gain further insights into its temporal depth. Our data suggest that this fourth genetic component found in modern-day north-eastern Europeans arrived in the area around 4,000 years ago at the latest, as illustrated by ALDER dating using the ancient genome-wide data from Bolshoy Oleni Ostrov. The upper bound for the introduction of this component is harder to estimate. The component is absent in the Karelian hunter-gatherers (EHG) 3 dated to 8,300-7,200 yBP as well as Mesolithic and Neolithic populations from the Baltics from 8,300 yBP and 7,100-5,000 yBP respectively. While this suggests an upper bound of 5,000 yBP for the arrival of Siberian ancestry, we cannot exclude the possibility of its presence even earlier, yet restricted to more northern regions, as suggested by its absence in populations in the Baltic during the Bronze Age. Our study also presents the earliest occurrence of the Y-chromosomal haplogroup N1c in Fennoscandia. N1c is common among modern Uralic speakers, and has also been detected in Hungarian individuals dating to the 10th century, yet it is absent in all published Mesolithic genomes from Karelia and the Baltics.
The large Siberian component in the Bolshoy individuals from the Kola Peninsula provides the earliest direct genetic evidence for an eastern migration into this region. Such contact is well documented in archaeology, with the introduction of asbestos-mixed Lovozero ceramics during the second millenium BC, and the spread of even-based arrowheads in Lapland from 1,900 BCE. Additionally, the nearest counterparts of Vardøy ceramics, appearing in the area around 1,600-1,300 BCE, can be found on the Taymyr peninsula, much further to the east. Finally, the Imiyakhtakhskaya culture from Yakutia spread to the Kola Peninsula during the same period. Contacts between Siberia and Europe are also recognised in linguistics. The fact that the Siberian genetic component is consistently shared among Uralic-speaking populations, with the exceptions of Hungarians and the non-Uralic speaking Russians, would make it tempting to equate this component with the spread of Uralic languages in the area. However, such a model may be overly simplistic. First, the presence of the Siberian component on the Kola Peninsula at ca. 4000 yBP predates most linguistic estimates of the spread of Uralic languages to the area. Second, as shown in our analyses, the admixture patterns found in historic and modern Uralic speakers are complex and in fact inconsistent with a single admixture event. Therefore, even if the Siberian genetic component partly spread alongside Uralic languages, it likely presented only an addition to populations carrying this component from earlier.
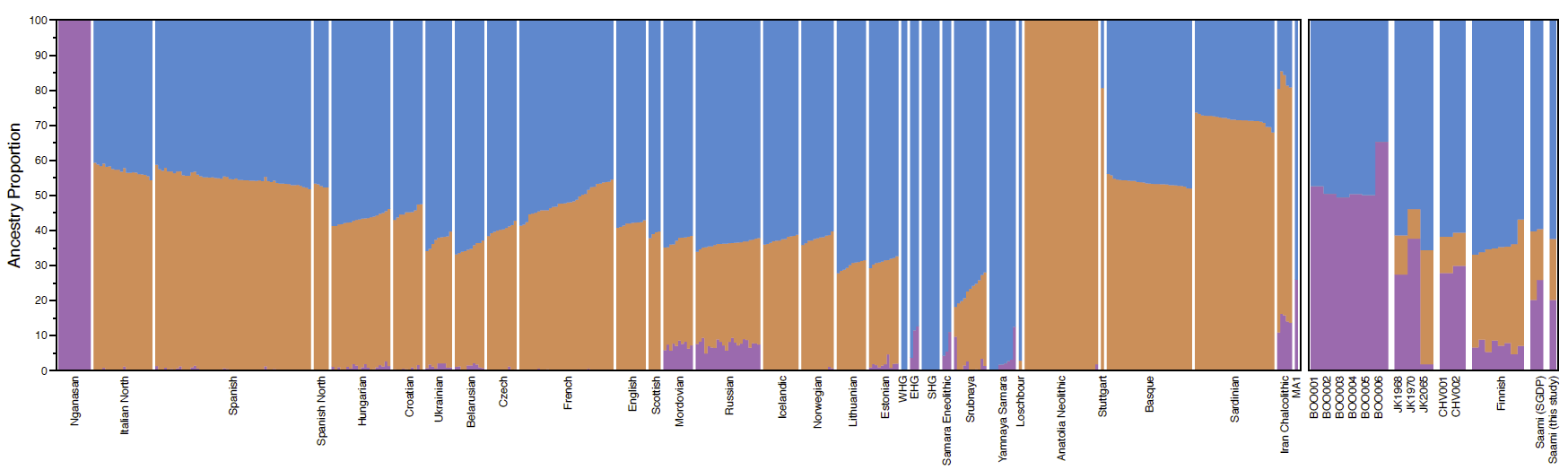
The novel genome-wide data here presented from ancient individuals from Finland opens new insights into Finnish population history. Two of the three higher coverage individuals and all six low coverage individuals from Levänluhta showed low genetic affinity to modern-day Finnish speakers of the area. Instead, an increased affinity was observed to modern-day Saami speakers, now mostly residing in the north of the Scandinavian Peninsula. These results suggest that the geographic range of the Saami extended further south in the past, and hints at a genetic shift at least in the western Finnish region during the Iron Age. The findings are in concordance with the noted linguistic shift from Saami languages to early Finnish. Further ancient DNA from Finland is needed to conclude to what extent these signals of migration and admixture are representative of Finland as a whole.

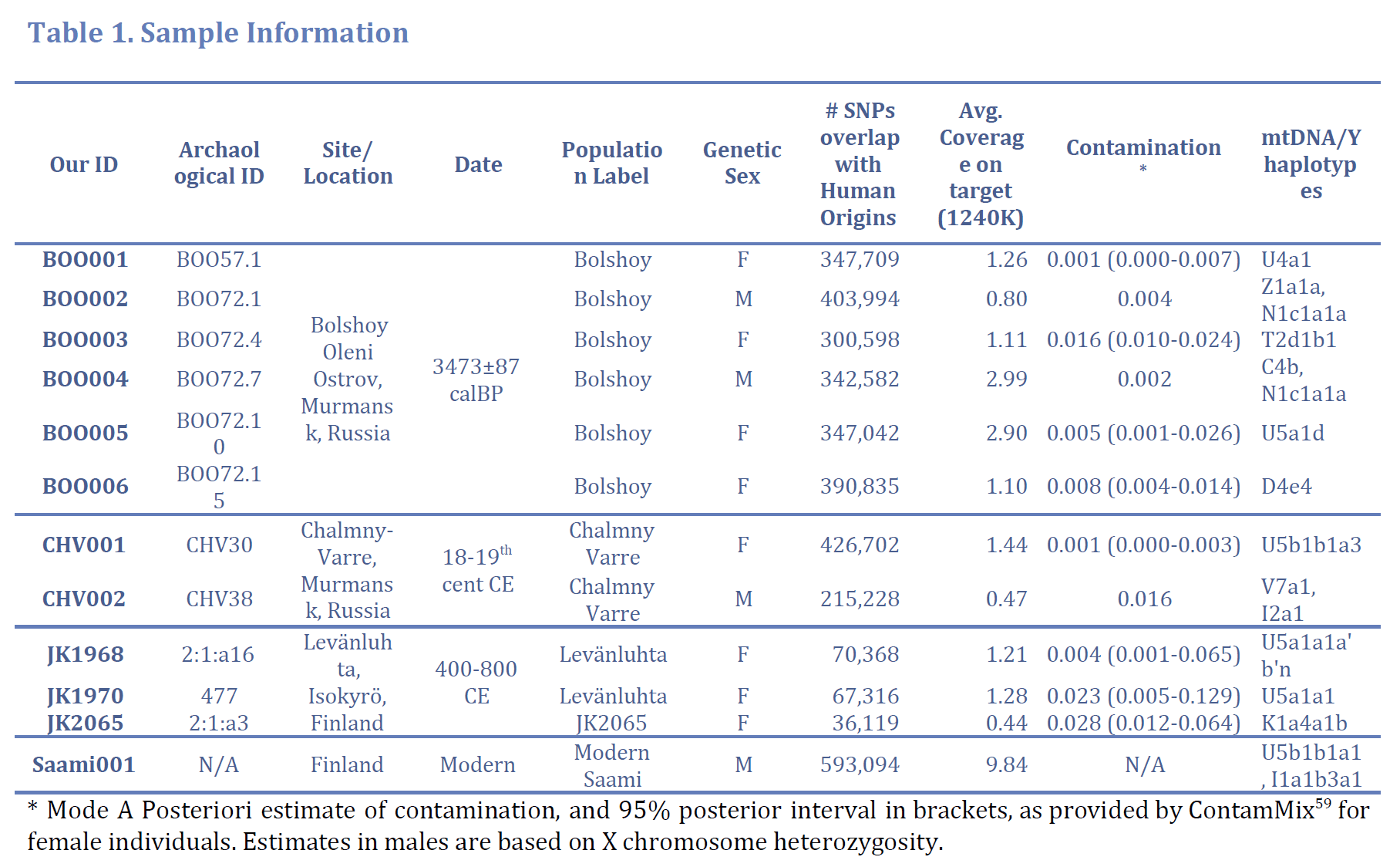
The two samples of haplogroup N1c1a1a-L392/L1026, dated ca. 1500 BC, come from the site Bolshoy Oleniy Ostrov, in the Kola Peninsula.
Bolshoy Oleniy Ostrov (Great Reindeer Island), situated in the Kola Bay of the Barents Sea and separated from the mainland by Yekarerininsky Island and two straits, harbors the ancient cemetery of an unknown Early Metal Age culture. The preservation of artifacts made from bone and antler, wooden structures, as well as human remains is remarkable for the location and age this site represents. Altogether 19 skeletons of adults and children have been recognized from both single and collective burials of the site, together with more than 250 artifacts. (…) Apart from these excavations, approximately 25 burials were revealed in 1934 during the construction of fortifications. (…) Radiocarbon dates are provided by Moiseyev and Khartanovich in their 2012 study, placing the site in middle to the late 2nd millennium BC (…)
After seing how Late Indo-European languages spread with Yamna and (mainly) R1b-L23 lineages, we are now obtaining proof of how Siberian ancestry – likely accompanying N1c-L392 lineages – was probably related to an early archaeological Siberian influence in the easternmost region of North-East Europe, seen also probably in linguistics.
NOTE. Whereas I proposed – based mainly on common guesstimates – that R1a-M417 and EHG ancestry might have signaled the arrival of an early Yukaghir substratum to NE Europe, later acquired by Uralic spreading over this territory, while N1c1a1a lineages with the Seima-Turbino phenomenon might have given Uralic its later Altaic traits, it is indeed possible – and more likely with the findings in this paper – that N1c1a1a lineages may have in fact spread Yukaghir languages, especially if (like the Leiden school) one supports an Indo-Uralic community.
The linguistic effect of this migration may depend on one’s preferred model for Proto-Uralic and its strata, and especially on one’s position in the Proto-Uralic vs. Proto-Uralo-Yukaghir controversy. Although I really didn’t have a strong opinion on this matter, it is clear from my texts that (unlike Kortlandt) I didn’t consider Yukaghir to share a common ancestor with Uralic languages. What genomics is showing right now seems to me directly translatable to a linguistic model, and we should therefore reject an original Proto-Uralo-Yukaghir community.
Also, it seems that the Finnish population peak which expanded today’s prevalent N1c-L392 lineages – after the Iron Age bottleneck which likely reduced its haplogroup diversity – may have been associated with the event that displaced the Saami population from Finland after ca. 1000 AD.
I think it is becoming still clearer where Uralic languages came from.
Related:
- Uralic as a Corded Ware substrate of Indo-Iranian, and loanwords in Finno-Ugric
- North Pontic steppe Eneolithic cultures, and an alternative Indo-Slavonic model
- The concept of “Outlier” in Human Ancestry (III): Late Neolithic samples from the Baltic region and origins of the Corded Ware culture
- Genetic prehistory of the Baltic Sea region and Y-DNA: Corded Ware and R1a-Z645, Bronze Age and N1c
- Another hint at the role of Corded Ware peoples in spreading Uralic languages into north-eastern Europe, found in mtDNA analysis of the Finnish population
- Recent archaeological finds near Indo-European and Uralic homelands
- New Ukraine Eneolithic sample from late Sredni Stog, near homeland of the Corded Ware culture