New open source paper, Dynamic changes in genomic and social structures in third millennium BCE central Europe, by Papac et al., Science Advances (2021).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
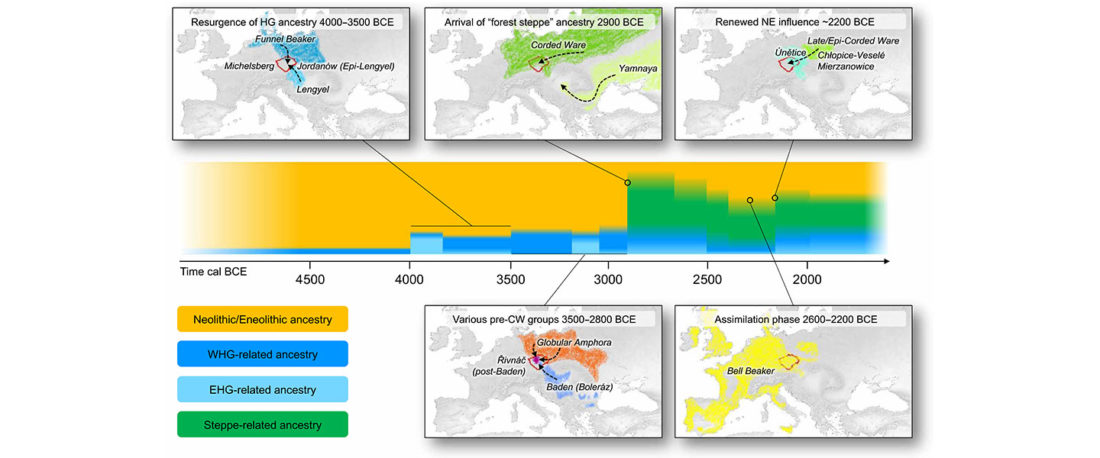
We report genomic data from the earliest CW individuals to date [show] that CW was widespread across Bohemia by 2900 BCE. The early radiocarbon dates are also supported by these individuals’ genetic profiles, who occupy the most extreme positions on PC2, as expected under a scenario of the earliest CW being migrants from the east who mixed with locals, resulting in intermediate PC2 positions in later generations.
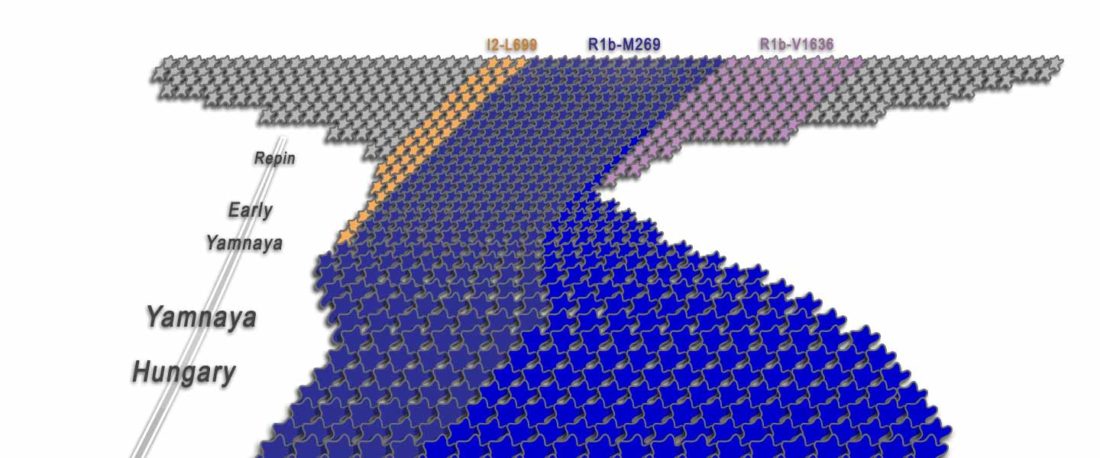
… Read the rest “R1b-rich earliest Corded Ware, a Yamnaya-related vector of Indo-European languages”(…)We found poor statistical