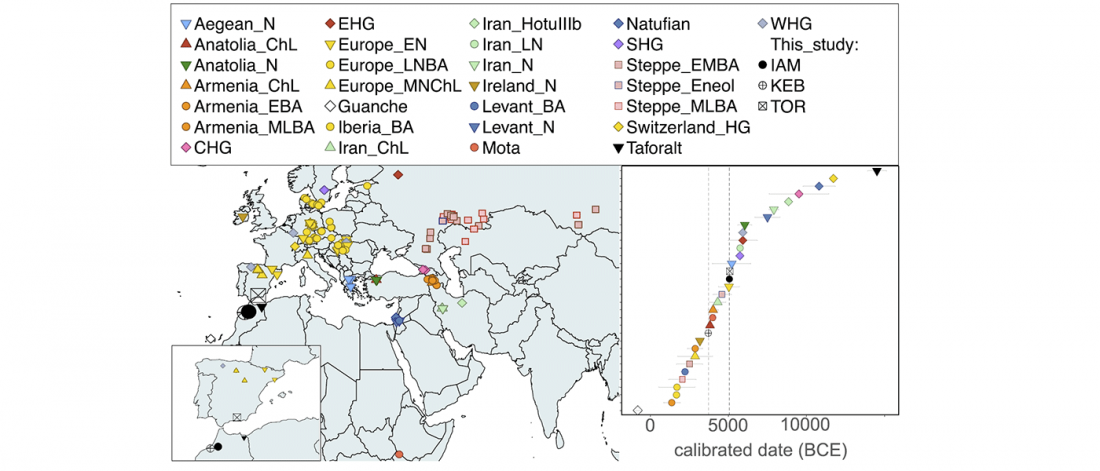
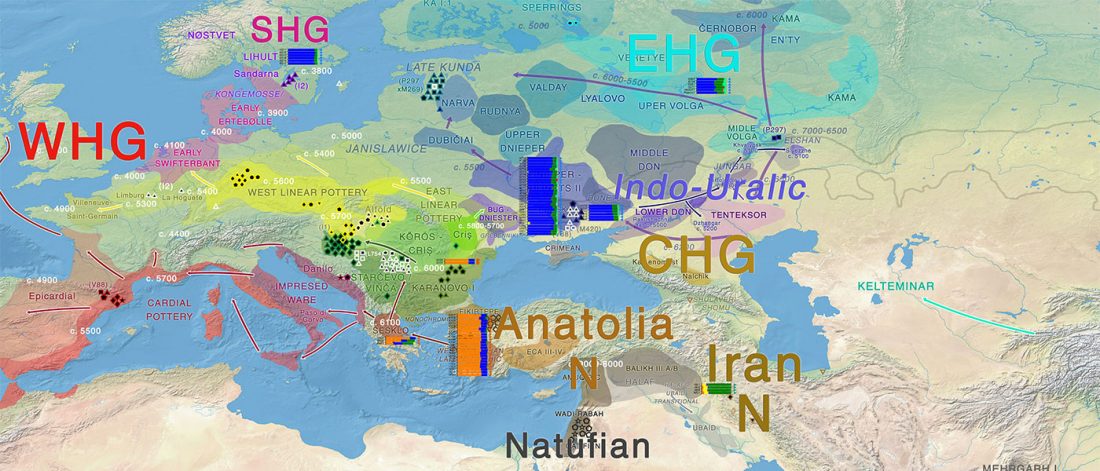
Ancient genomes from North Africa evidence Neolithic migrations to the Maghreb
BioRxiv preprint now published (behind paywall) Ancient genomes from North Africa evidence prehistoric migrations to the Maghreb from both the Levant and Europe, by Fregel et al., PNAS (2018).
NOTE. I think one of the important changes in this version compared to the preprint is the addition of the recent Iberomaurusian samples.
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Ancient genomes from North Africa evidence Neolithic migrations to the Maghreb”The extent to which prehistoric migrations of farmers influenced the genetic pool of western North Africans remains unclear. Archaeological evidence suggests that the Neolithization process may have happened through the adoption of innovations by local Epipaleolithic communities or by demic diffusion from the