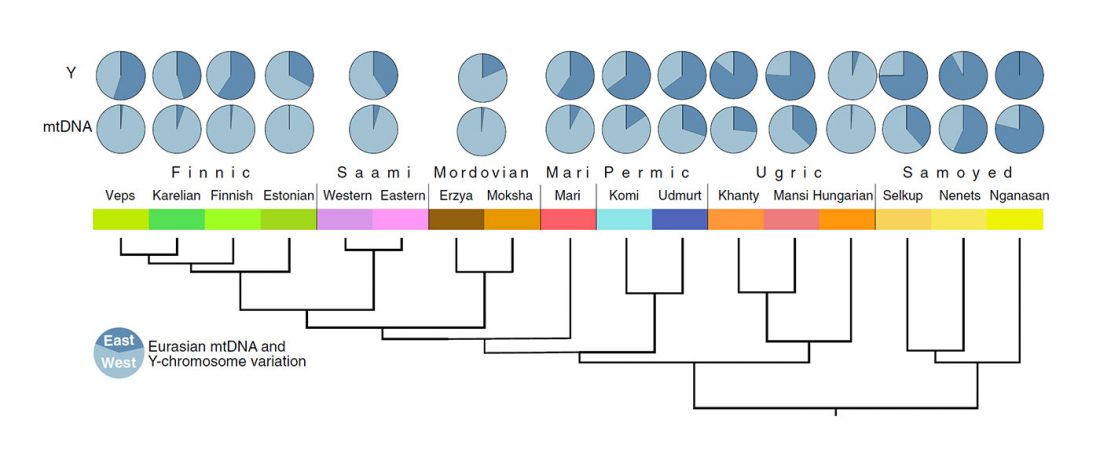
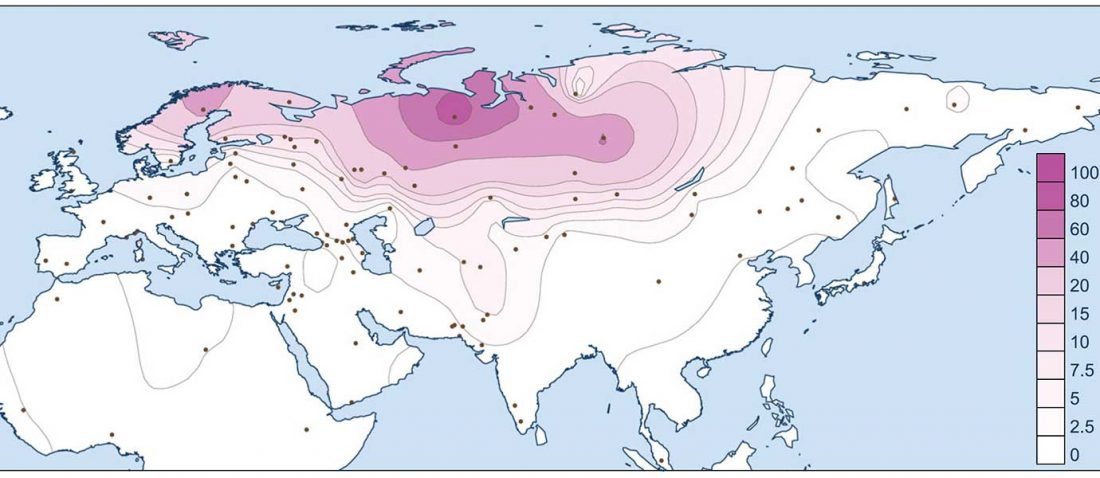
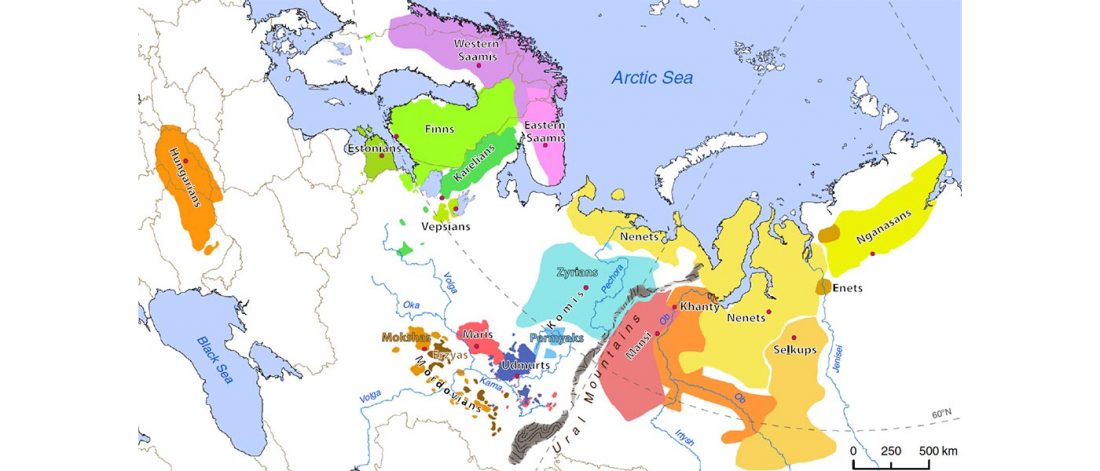
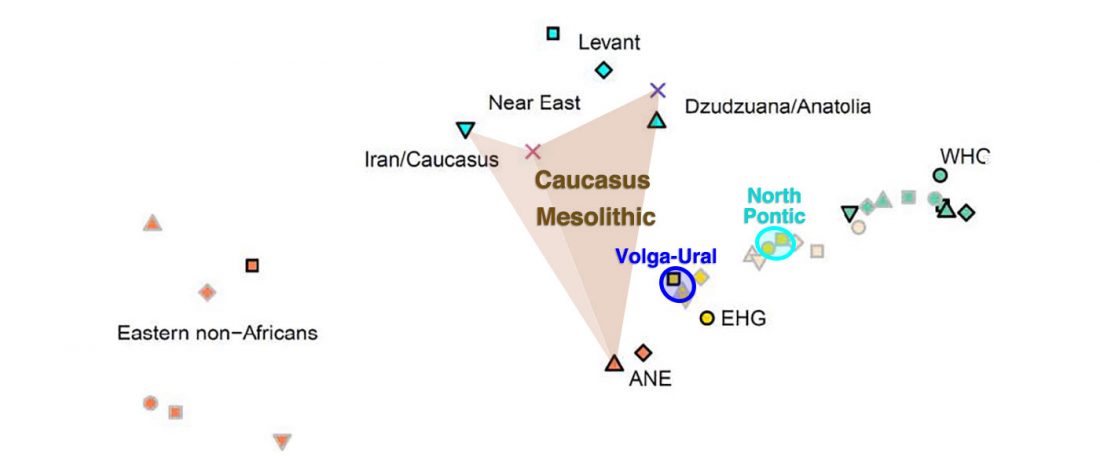
Corded Ware—Uralic (IV): Hg R1a and N in Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic expansions
This is the fourth of four posts on the Corded Ware—Uralic identification:
- Corded Ware—Uralic (I): Differences and similarities with Yamna
- Corded Ware—Uralic (II): Finno-Permic and the expansion of N-L392/Siberian ancestry
- Corded Ware—Uralic (III): “Siberian ancestry” and Ugric-Samoyedic expansions
- Corded Ware—Uralic (IV): Haplogroups R1a and N in Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic
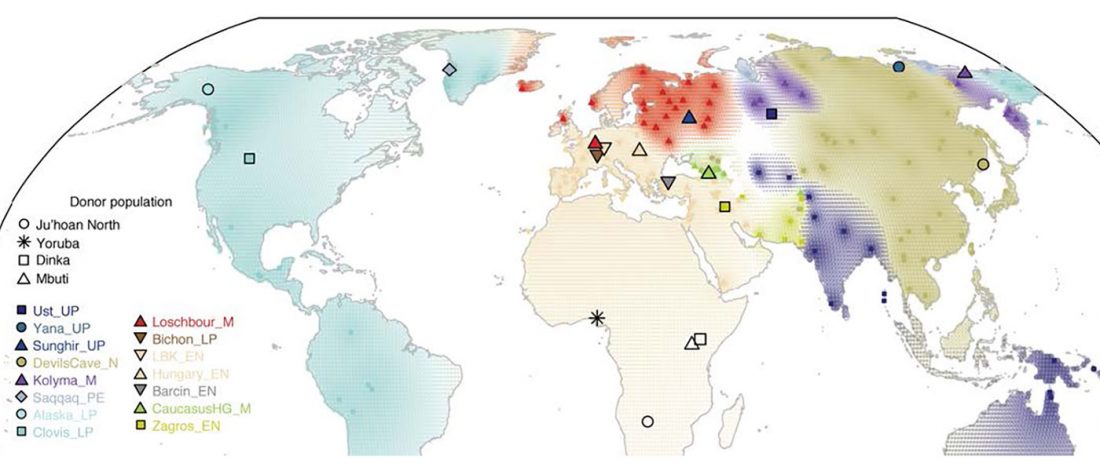
Let me begin this final post on the Corded Ware—Uralic connection with an assertion that should be obvious to everyone involved in ethnolinguistic identification of prehistoric populations but, for one reason or another, is usually forgotten. In the words of David Reich, in Who We Are and How We Got … Read the rest “Corded Ware—Uralic (IV): Hg R1a and N in Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic expansions”