Minimal gene flow from western pastoralists in the Bronze Age eastern steppes
Open access paper Bronze Age population dynamics and the rise of dairy pastoralism on the eastern Eurasian steppe, by Jeong et al. PNAS (2018).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
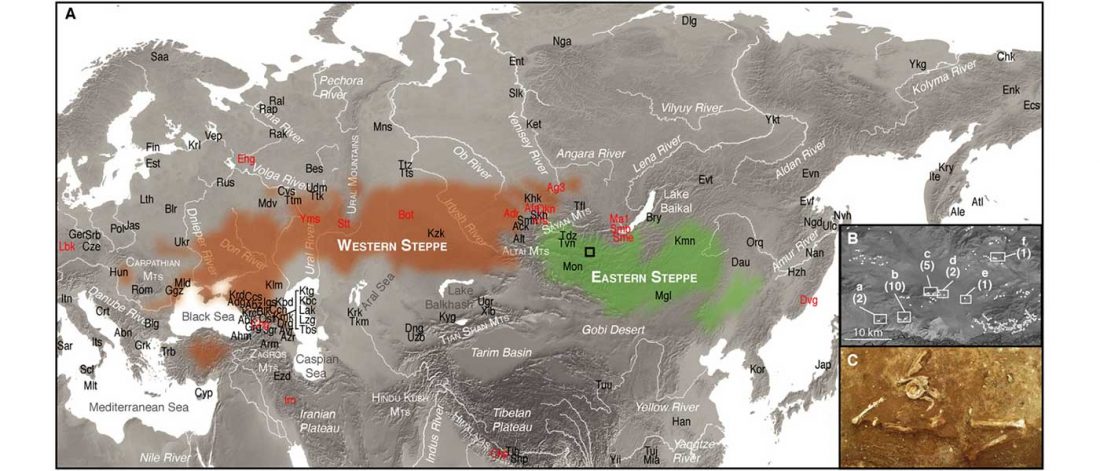
… Read the rest “Minimal gene flow from western pastoralists in the Bronze Age eastern steppes”To understand the population history and context of dairy pastoralism in the eastern Eurasian steppe, we applied genomic and proteomic analyses to individuals buried in Late Bronze Age (LBA) burial mounds associated with the Deer Stone-Khirigsuur Complex (DSKC) in northern Mongolia. To date, DSKC sites contain the clearest and most direct evidence for animal pastoralism in the Eastern steppe before ca. 1200 BCE.
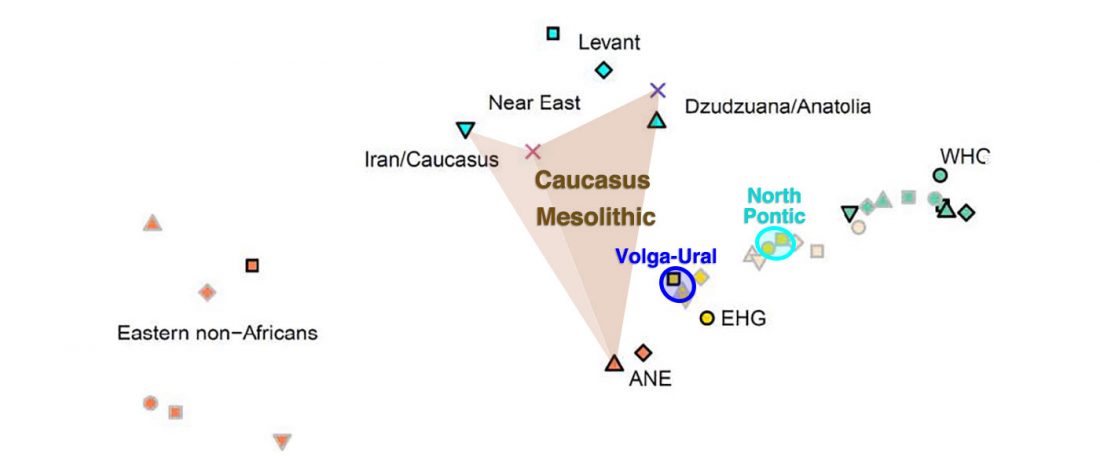
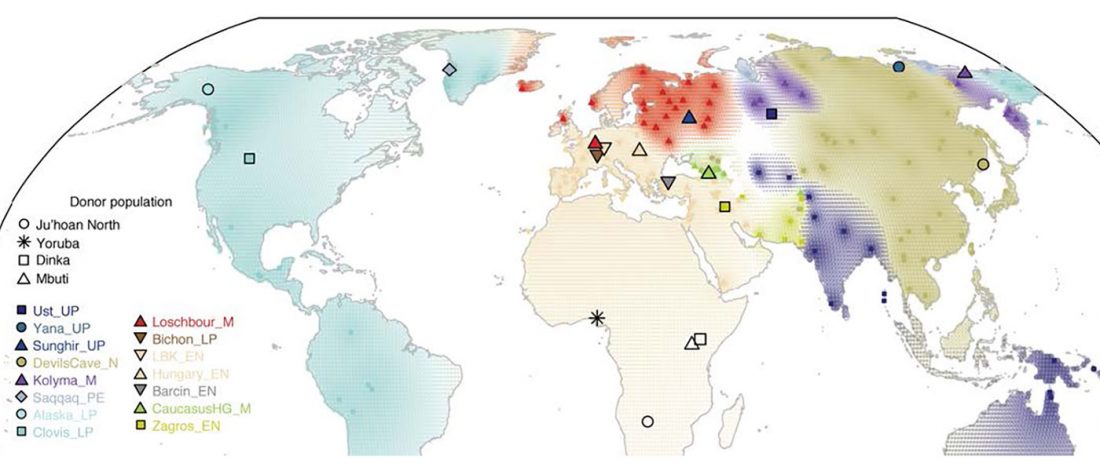
Most LBA Khövsgöls are projected on top