Given my reduced free time in these months, I have decided to keep updating the text on Indo-European and Uralic migrations and/or this blog, simultaneously or alternatively, to make the most out of the time I can dedicate to this. I will add the different ‘A Song of Sheep and Horses (ASoSaH) reread’ posts to the original post announcing the books. I would be especially interested in comments and corrections to the book chapters rather than the posts, but any comments are welcome (including in the forum, where comments are more likely to stick).
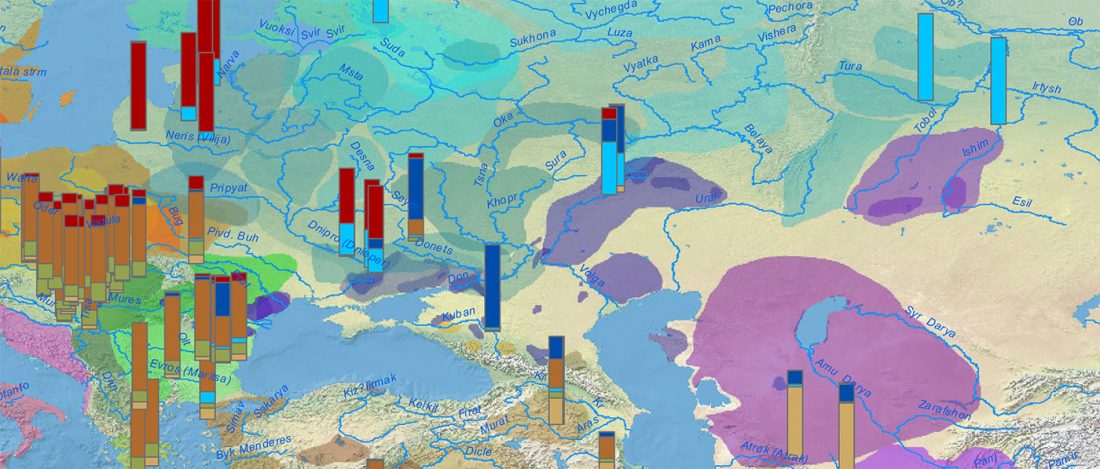
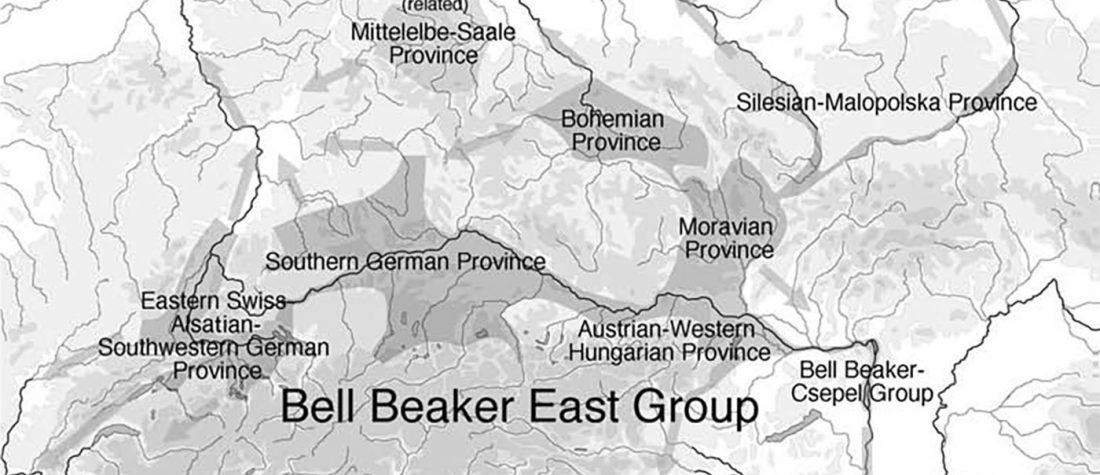
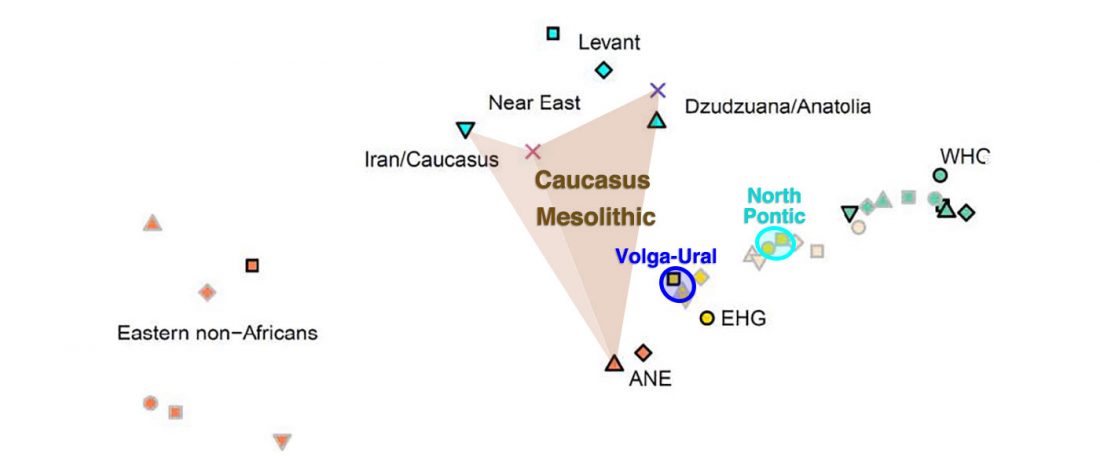
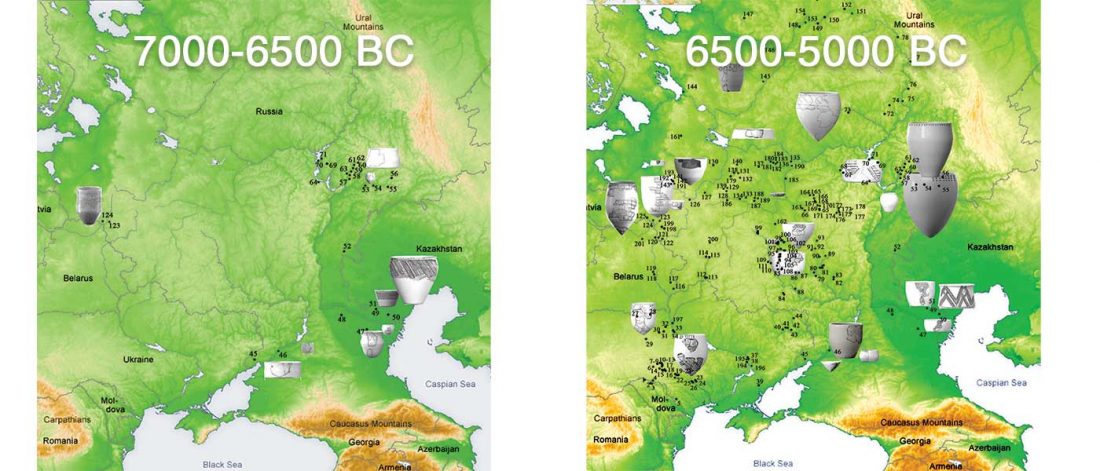
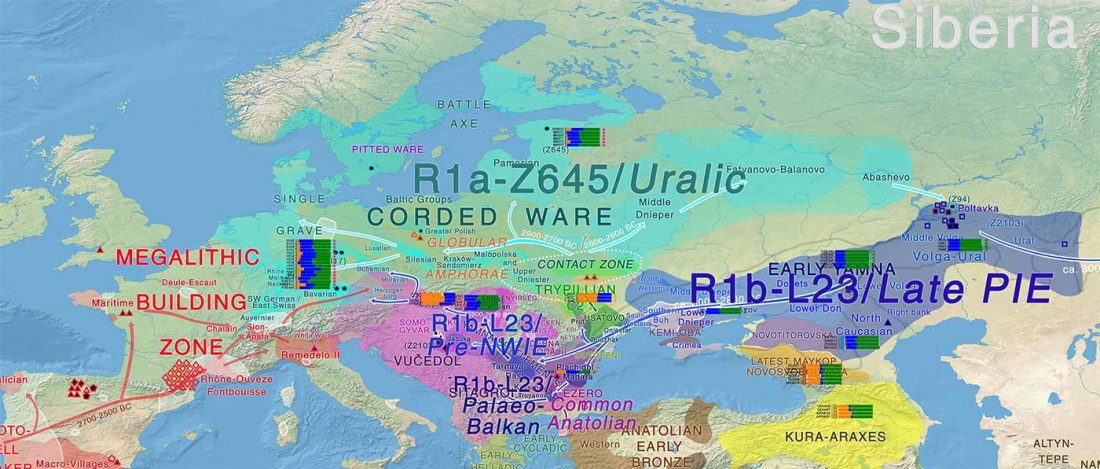
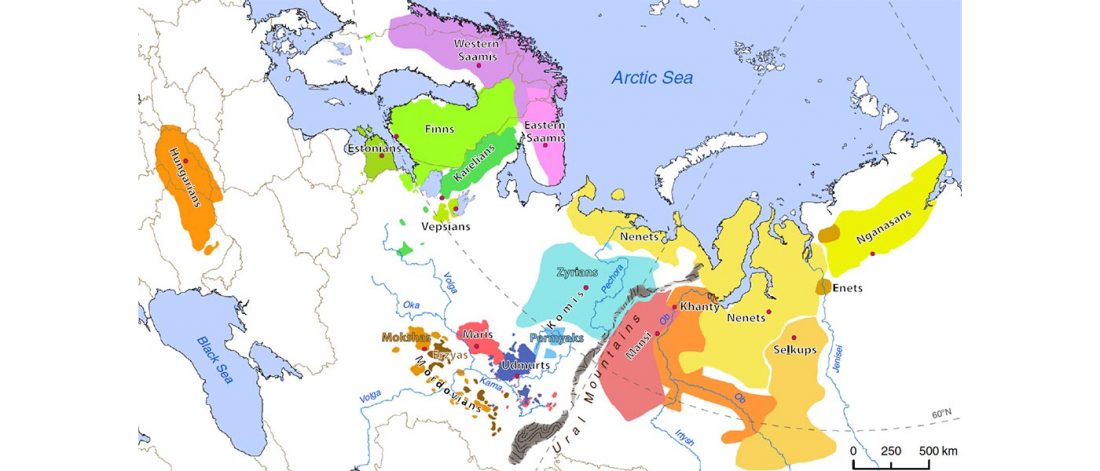
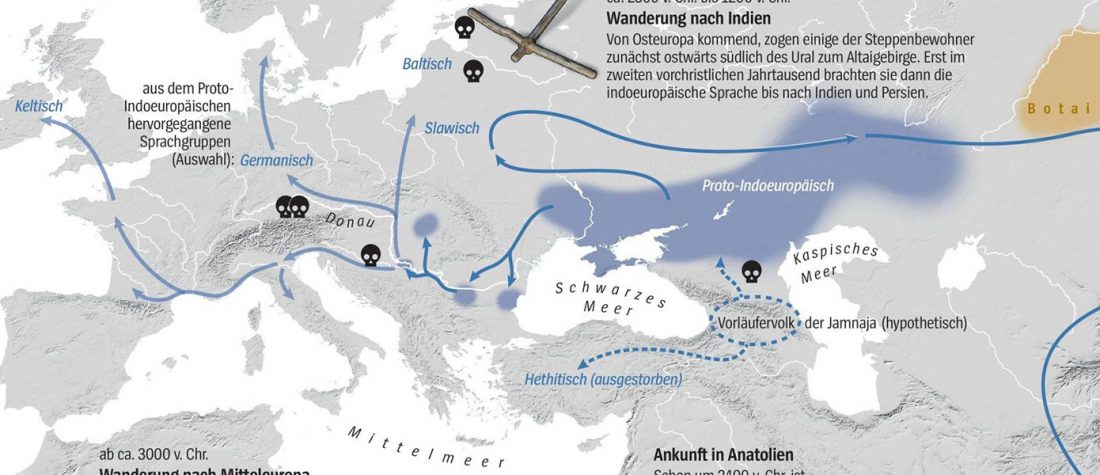
This is mainly a … Read the rest “ASoSaH Reread (I): Y-DNA haplogroups among Indo-Europeans (apart from R1b-L23)”