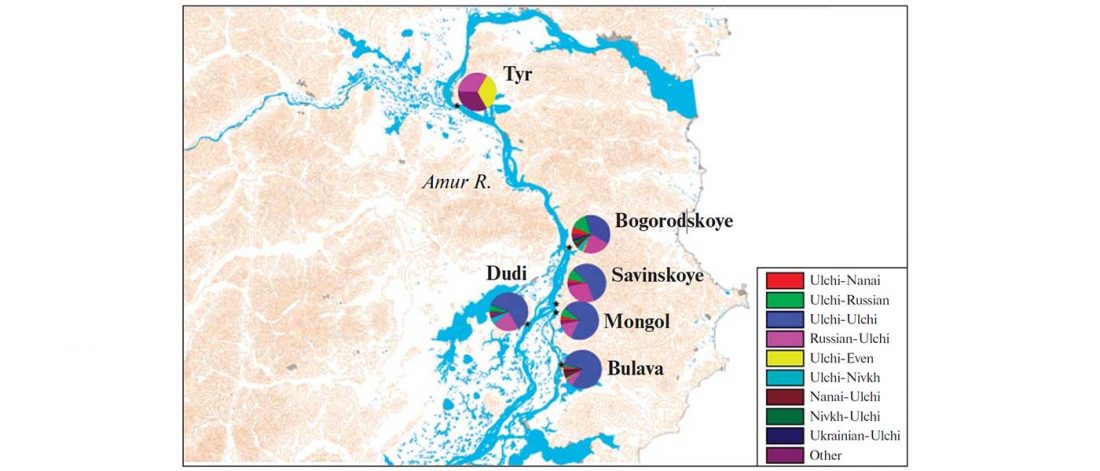
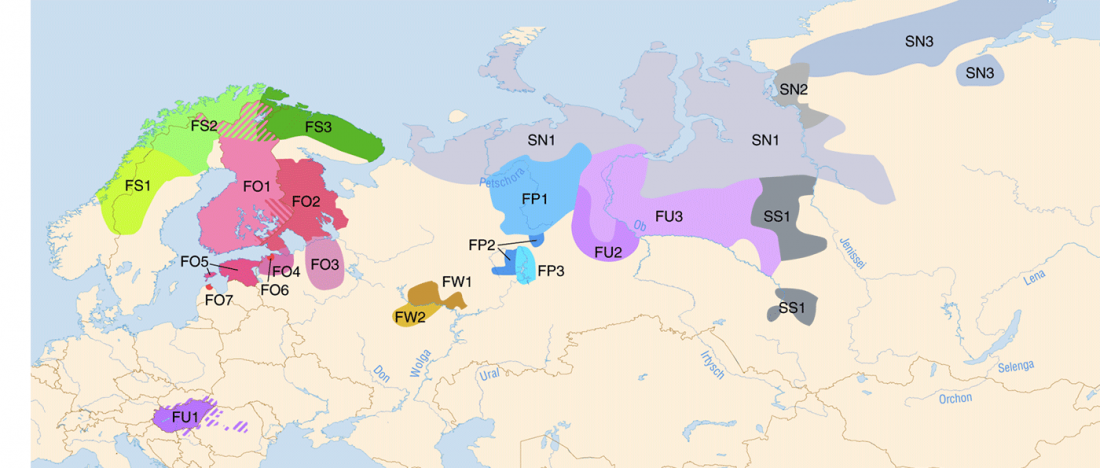
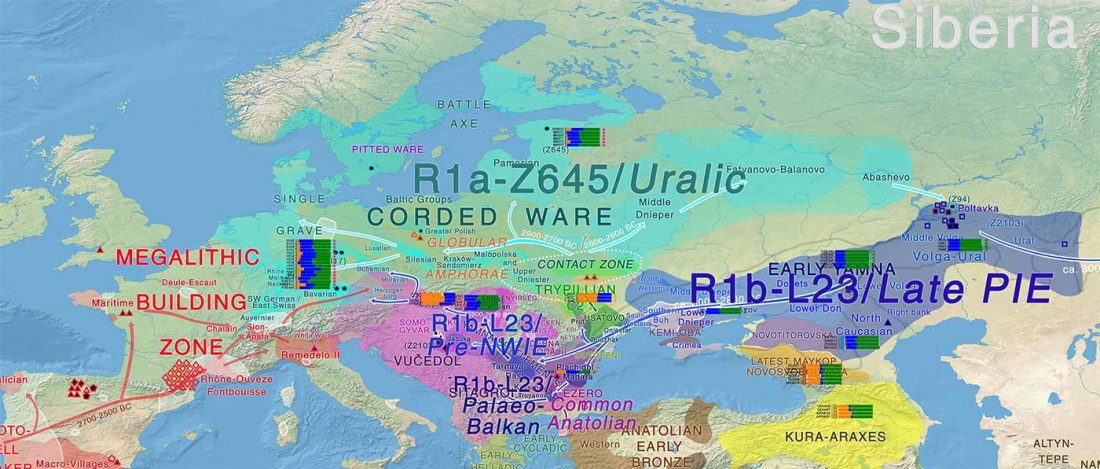
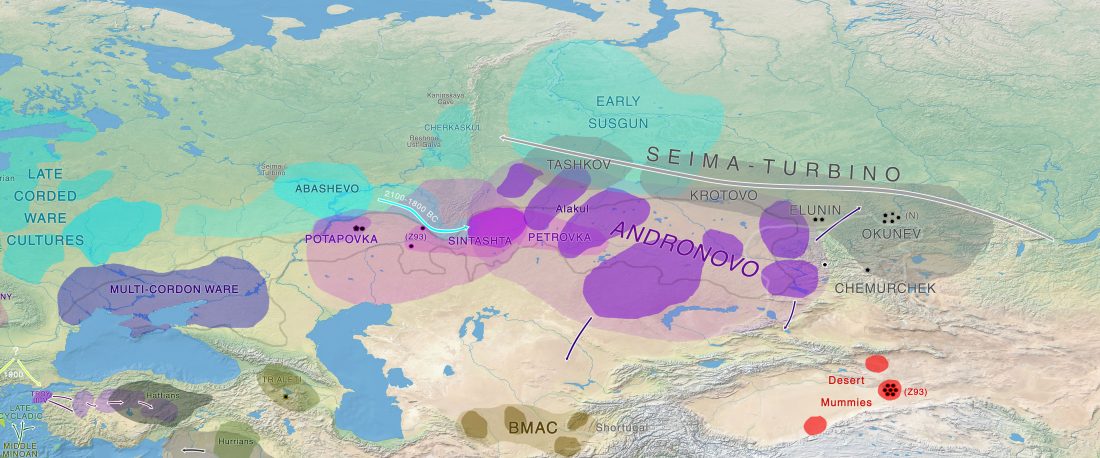
Open access Siberian genetic diversity reveals complex origins of the Samoyedic-speaking populations, by Karafet et al. Am J Hum Biol (2018) e23194.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Siberian groups
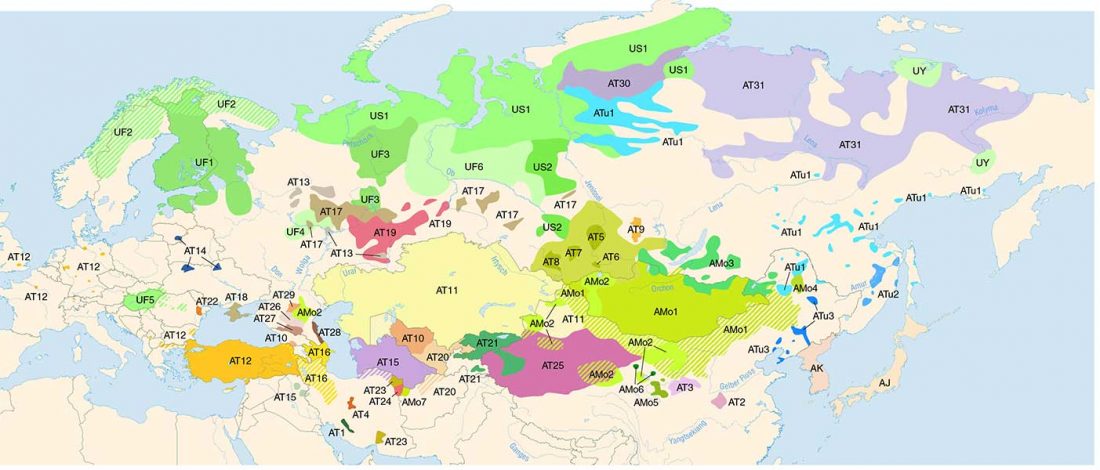
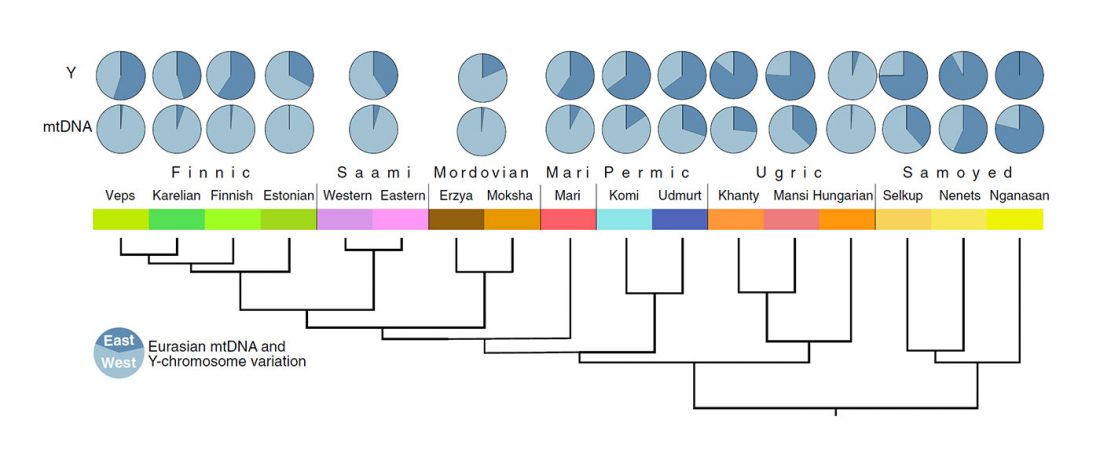
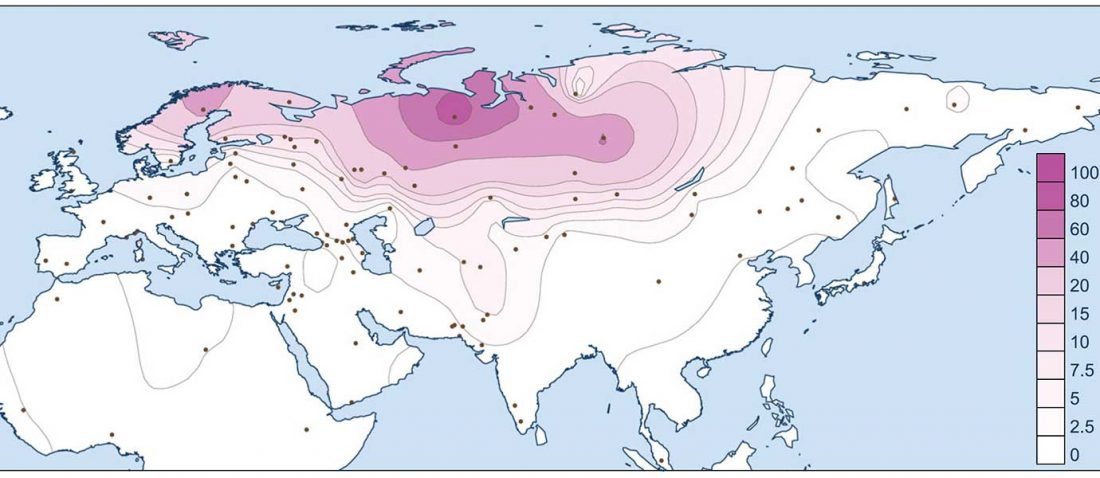
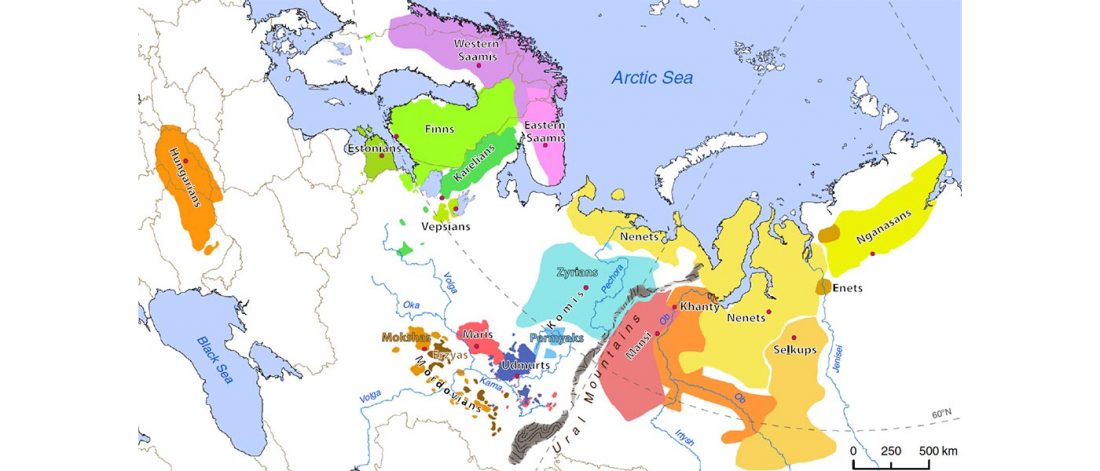
… Read the rest “The complex origin of Samoyedic-speaking populations”Consistent with their origin, Mongolic-speaking Buryats demonstrate genetic similarity with Mongols, and Turkic-speaking Altai-Kizhi and Teleuts are drawn close to CAS groups. The Tungusic-speaking Evenks collected in central and eastern Siberia cluster together and overlap with Yukagirs. Dolgans are widely scattered in the plot, justifying their recent origin from one Evenk clan, Yakuts, and Russian peasants in the 18th century (Popov, 1964). Uralic-speaking populations comprise a very wide cluster with Komi