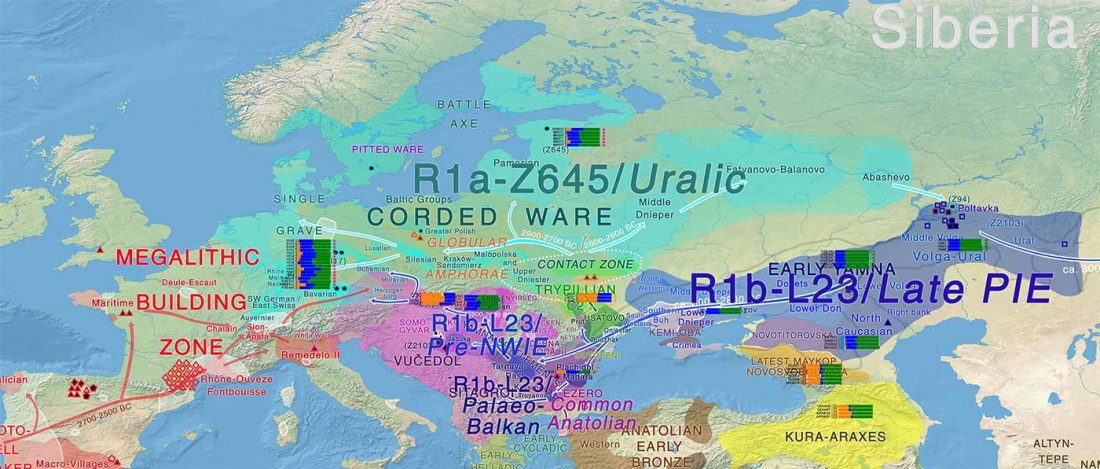
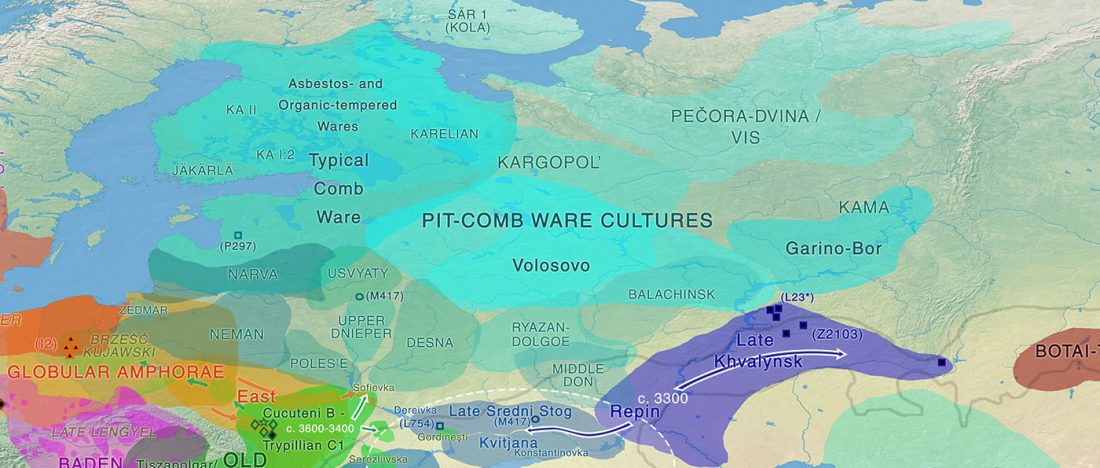
This is the first of four posts on the Corded Ware—Uralic identification:
- Corded Ware—Uralic (I): Differences and similarities with Yamna
- Corded Ware—Uralic (II): Finno-Permic and the expansion of N-L392/Siberian ancestry
- Corded Ware—Uralic (III): “Siberian ancestry” and Ugric-Samoyedic expansions
- Corded Ware—Uralic (IV): Haplogroups R1a and N in Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic
I was reading The Bronze Age Landscape in the Russian Steppes: The Samara Valley Project (2016), and I was really surprised to find the following excerpt by David W. Anthony:
… Read the rest “Corded Ware—Uralic (I): Differences and similarities with Yamna”The Samara Valley links the central steppes with the western steppes and is a north-south ecotone between the pastoral