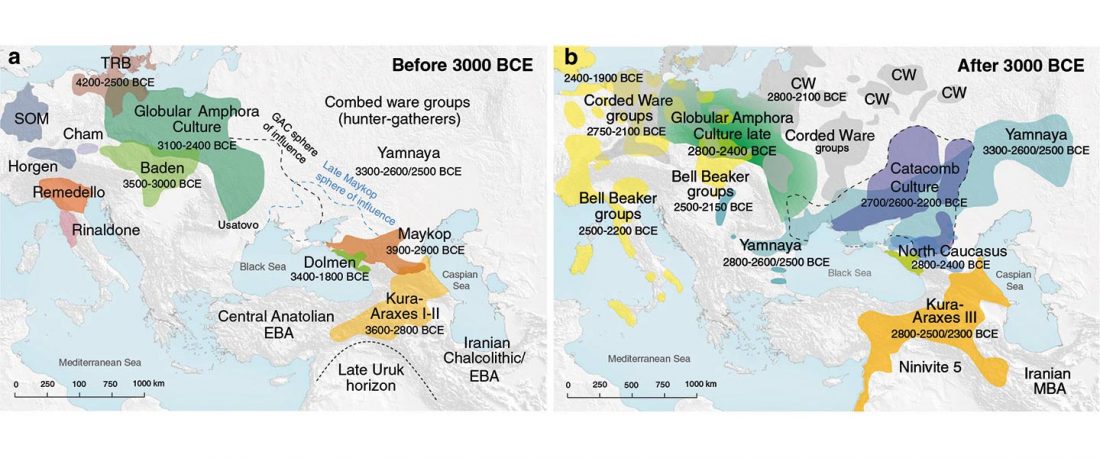
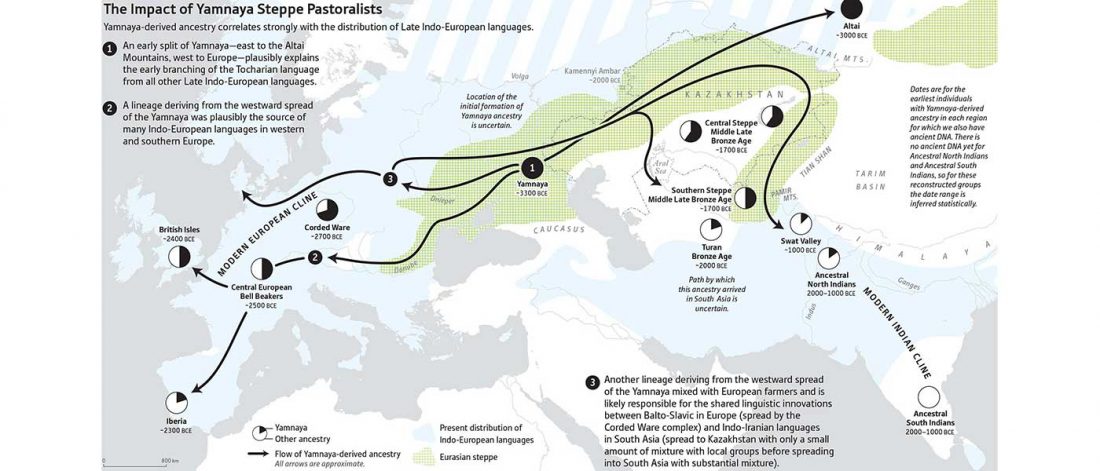
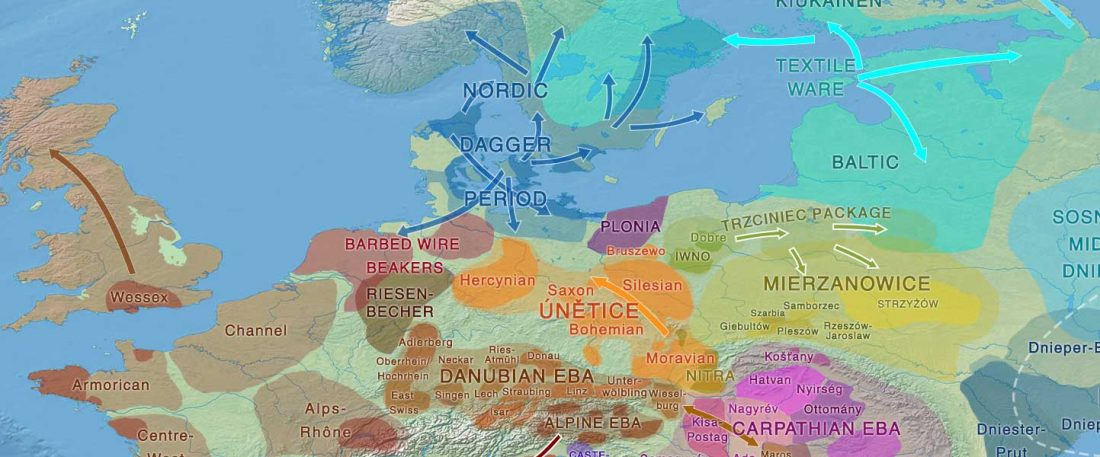
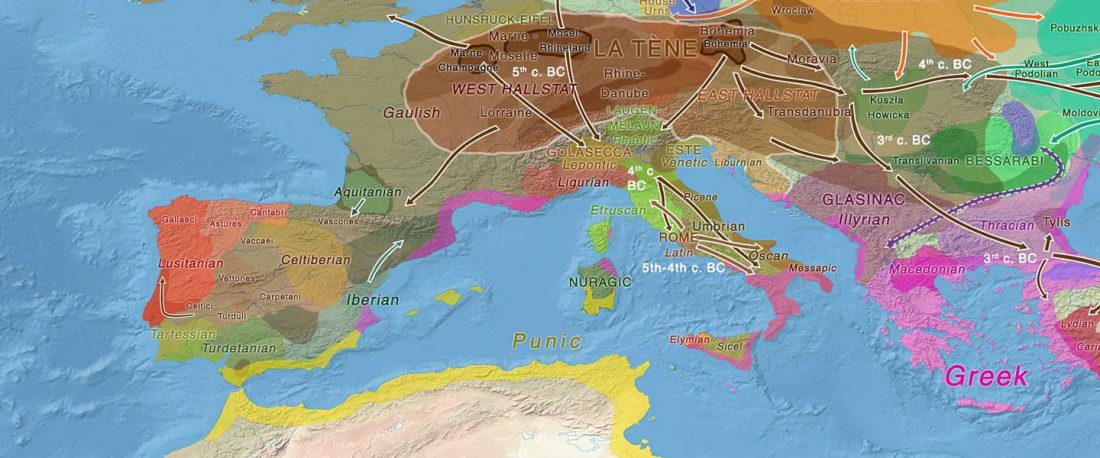
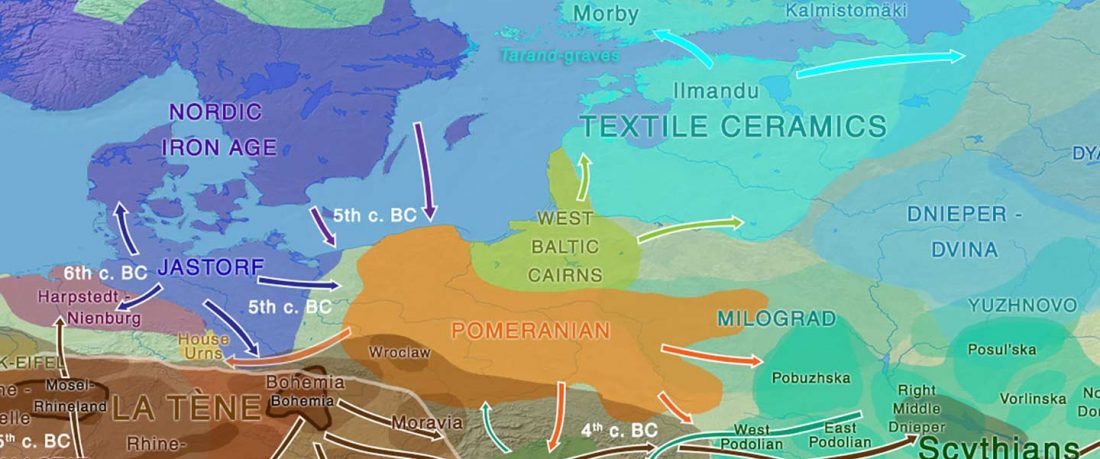
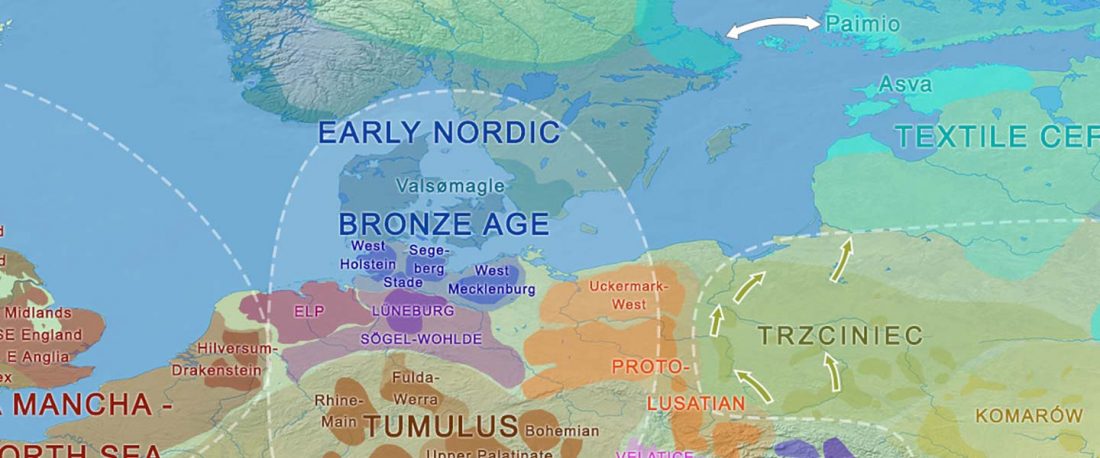
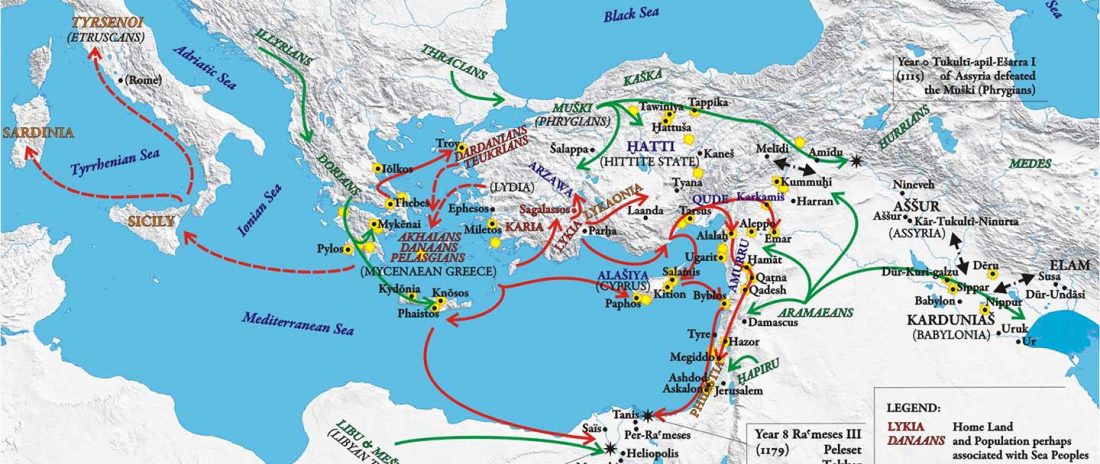
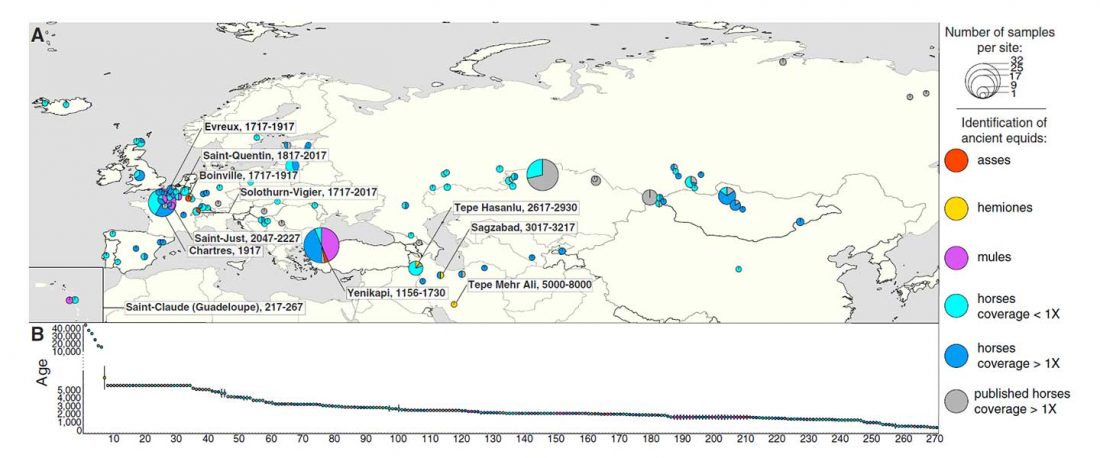
The recent update on the Indo-Anatolian homeland in the Middle Volga region and its evolution as the Indo-Tocharian homeland in the Don–Volga area as described in Anthony (2019) has, at last, a strong scientific foundation, as it relies on previous linguistic and archaeological theories, now coupled with ancient phylogeography and genomic ancestry.
There are still some inconsistencies in the interpretation of the so-called “Steppe ancestry”, though, despite the one and a half years that have passed since we first had access to the closest Pontic–Caspian steppe source populations. Even my post “Steppe ancestry” step by step from a year ago … Read the rest ““Steppe ancestry” step by step (2019): Mesolithic to Early Bronze Age Eurasia”