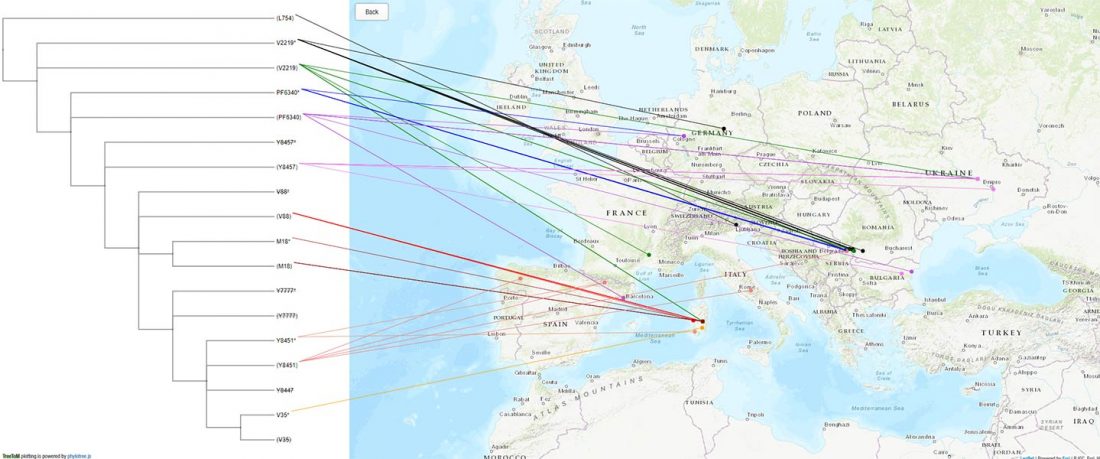
Yesterday the Eaton Lab at Columbia University announced on Twitter a nifty little tool by Carlos Alonso Maya-Lastra called TreeToM, which accepts Newick trees and CSV latitude/longitude data to explore phylogeny and geography interactively, with no coding required.
I thought it could complement nicely my All Ancient DNA Dataset, particularly for those newly described SNPs (FTDNA private variants, etc.) that have not been incorporated yet into SNP Tracker.
Here are two examples with snippets to copy&paste to the appropriate boxes in TreeToM. Feel free to add others in the comments:… Read the rest “Visualizing phylogenetic trees of ancient DNA in a map”