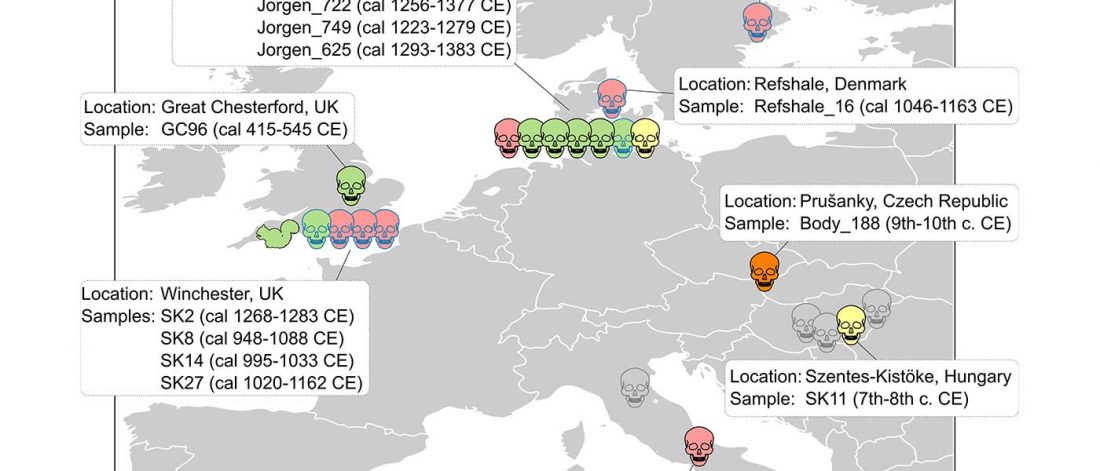
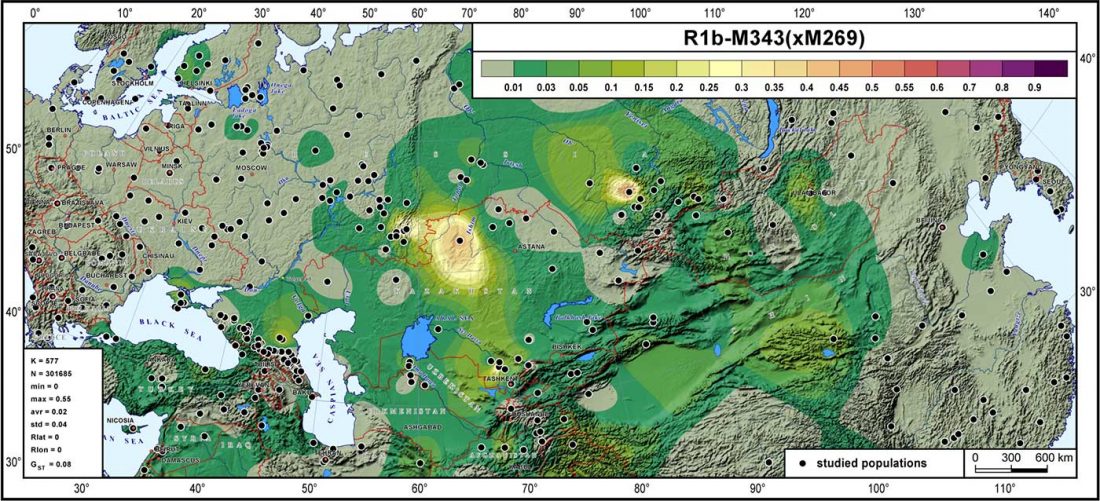
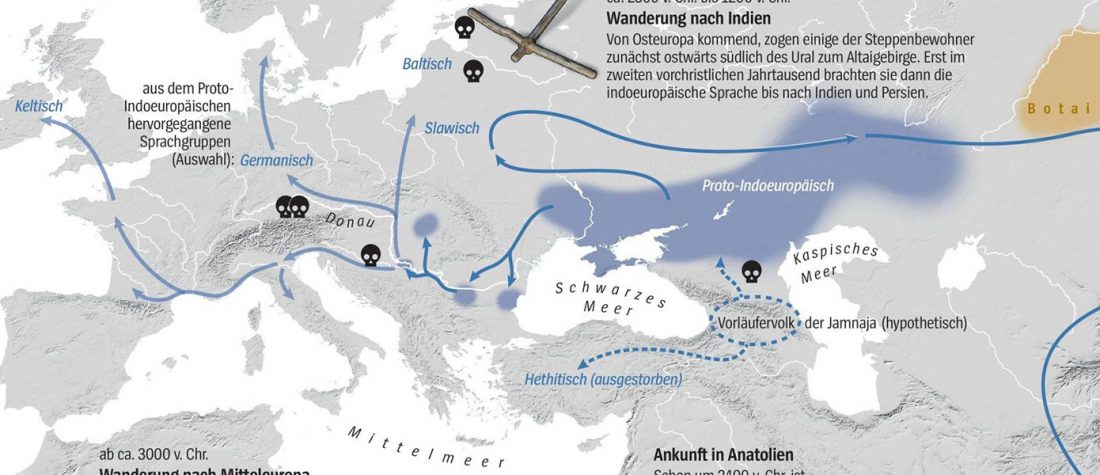
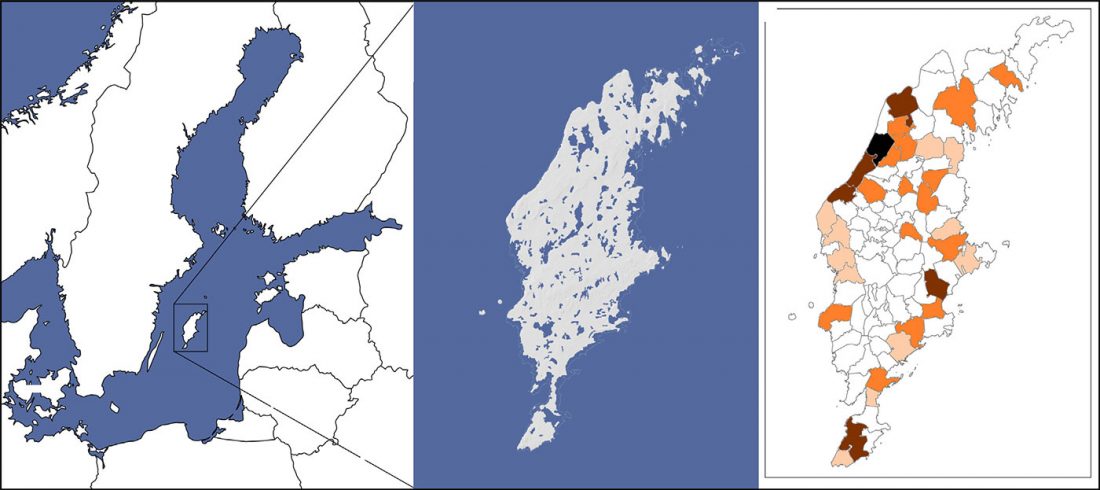
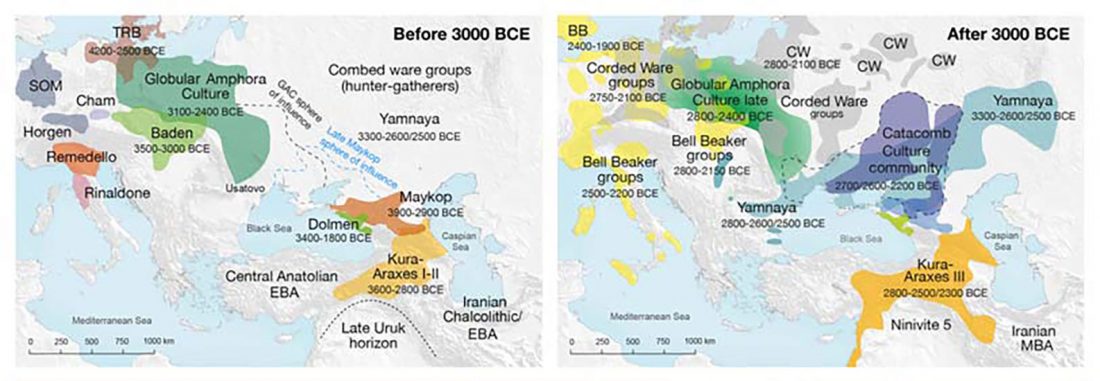
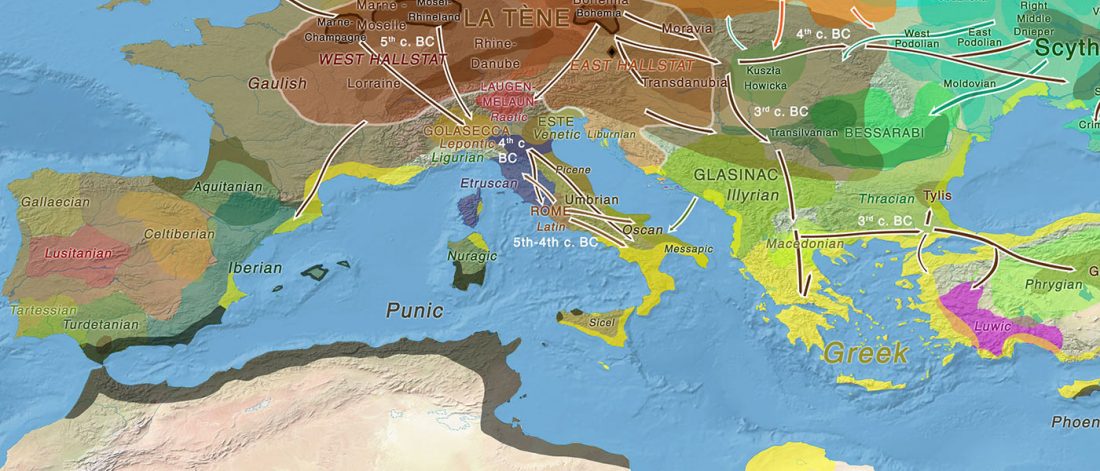
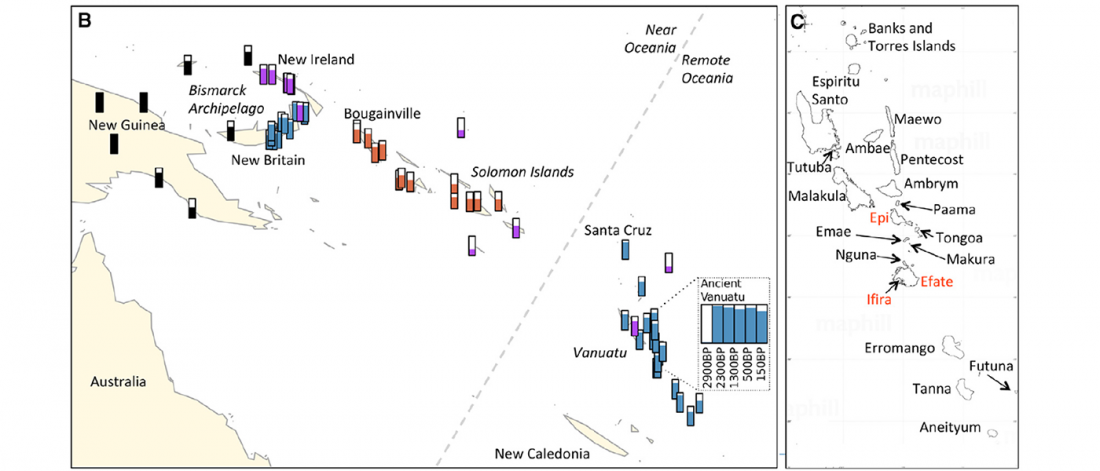
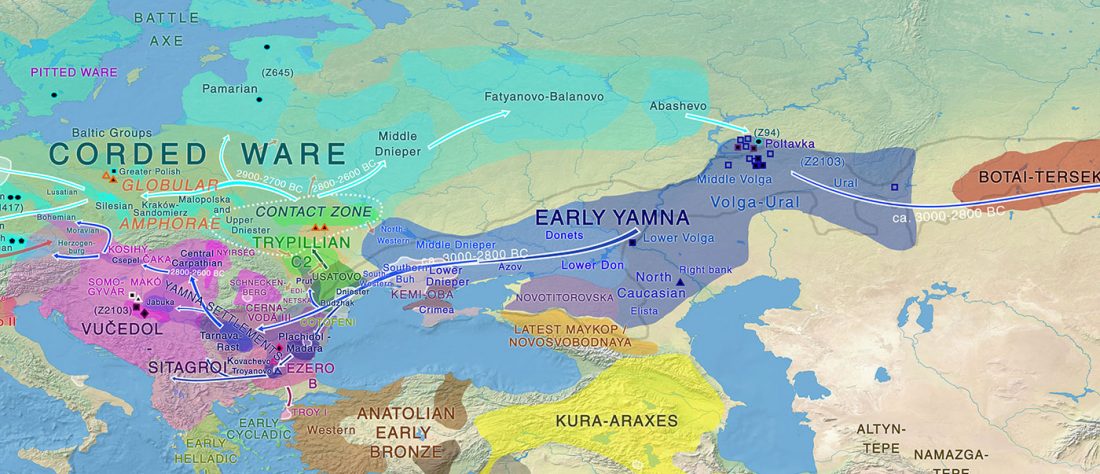
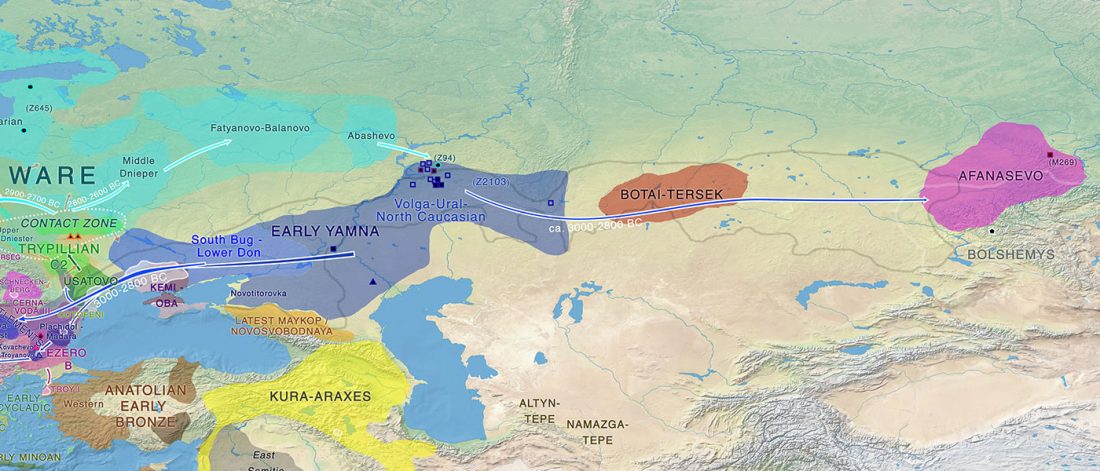
Phylogeny of leprosy, relevant for prehistoric Eurasian contacts
Some interesting studies were published at roughly the same time as Damgaard et al. (Nature 2018 and Science 2018), and that’s probably why they got little attention (at least by me).
Monica H. Green (also in Academia.edu), specialized in History of Medicine, summed up their relevance in Twitter quite well (her text is edited here for clarity):
… Read the rest “Phylogeny of leprosy, relevant for prehistoric Eurasian contacts”I’ve been disappointed that three recent exceptional studies of one of the world’s most historically important diseases, leprosy, have gotten so little notice from the science communication. It will take me a few hours to lay out their significance. But