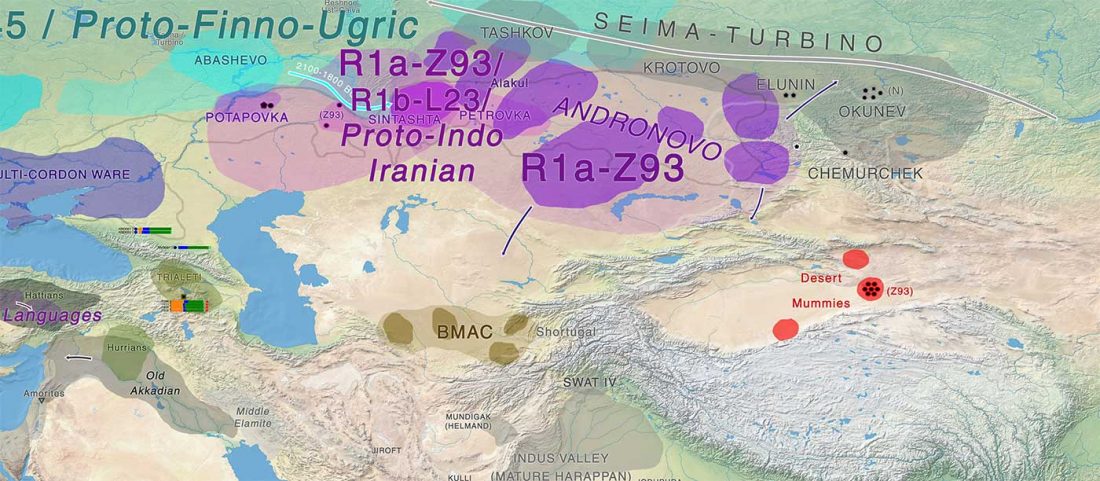
Modern Sardinians show elevated Neolithic farmer ancestry shared with Basques
New paper (behind paywall), Genomic history of the Sardinian population, by Chiang et al. Nature Genetics (2018), previously published as a preprint at bioRxiv (2016).
#EDIT (18 Sep 2018): Link to read paper for free shared by the main author.
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Modern Sardinians show elevated Neolithic farmer ancestry shared with Basques”Our analysis of divergence times suggests the population lineage ancestral to modern-day Sardinia was effectively isolated from the mainland European populations ~140–250 generations ago, corresponding to ~4,300–7,000 years ago assuming a generation time of 30 years and a mutation rate of 1.25 × 10−8 per basepair per generation. (…) in terms of relative values,