Oral communication Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past by David Reich (March 3, 2021).
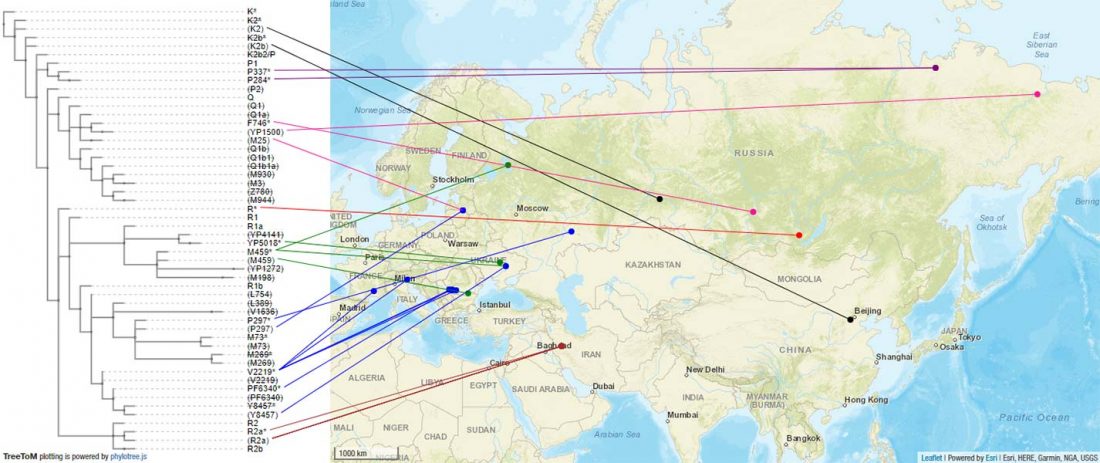
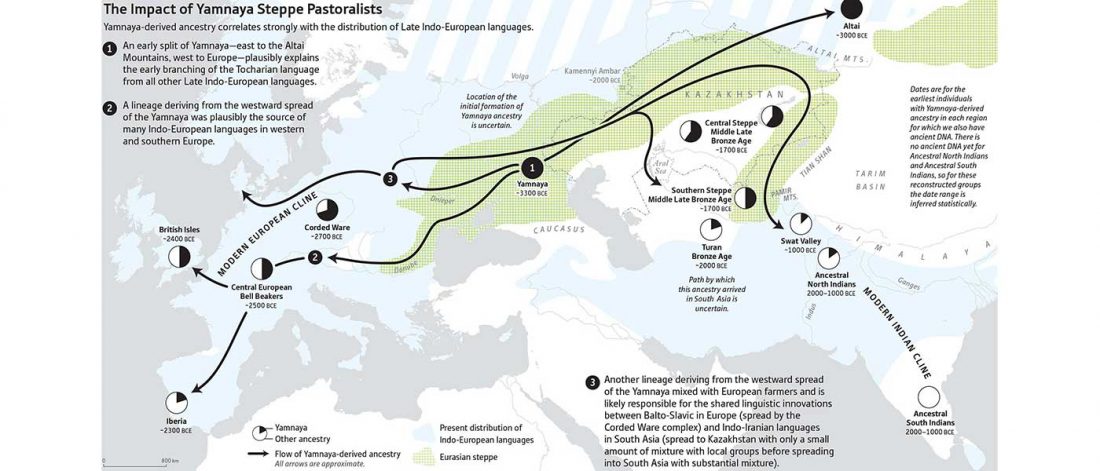
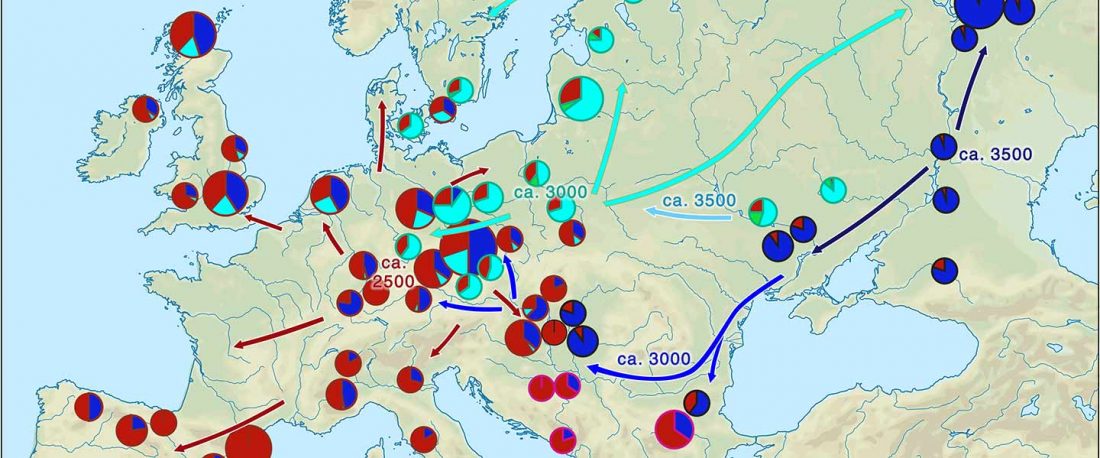
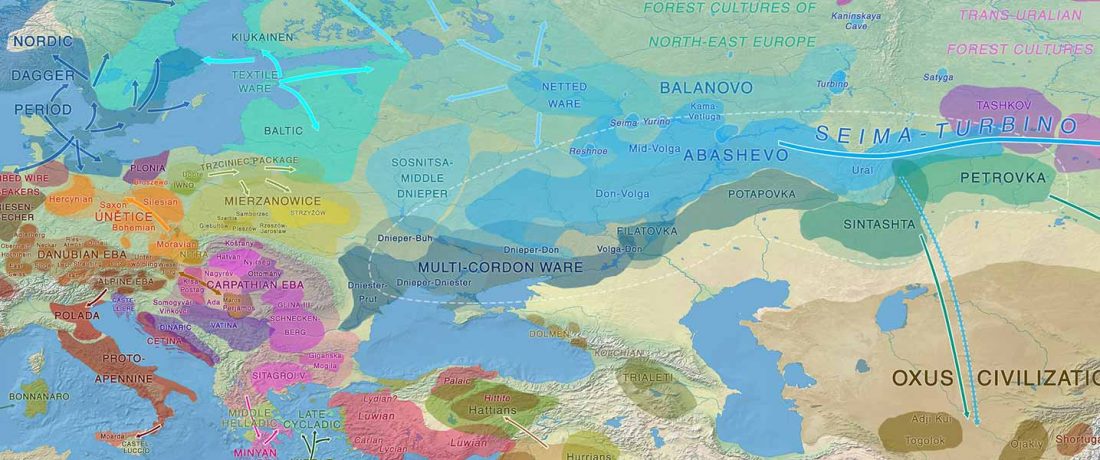
I noticed this interesting slide called “Caught red-handed”, at approximately 45m 17s, where David Reich asserts that sampled Corded Ware populations had many “close cousins” with Yamnaya-related populations “within generations”. The method could also be used, always according to Reich, to identify “who the Yamnaya mixed with to form groups like Corded Ware”.
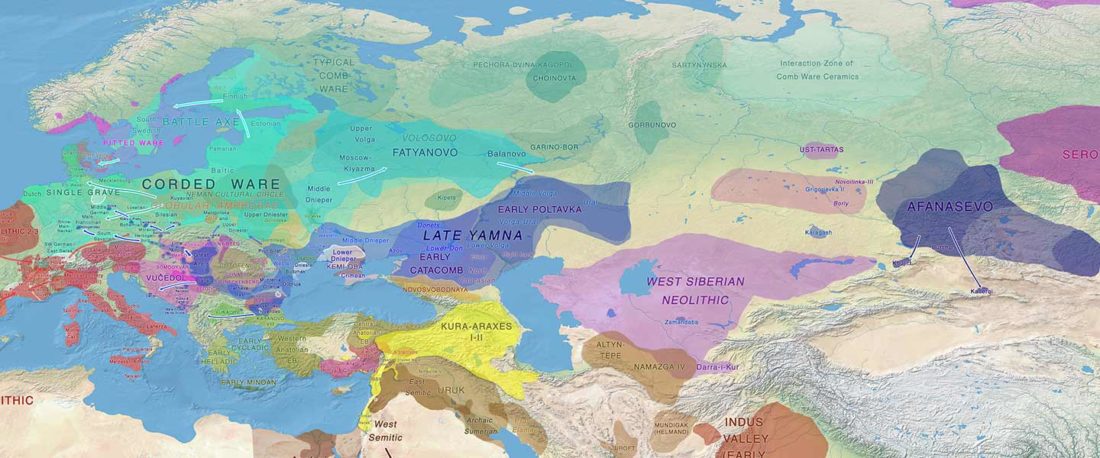
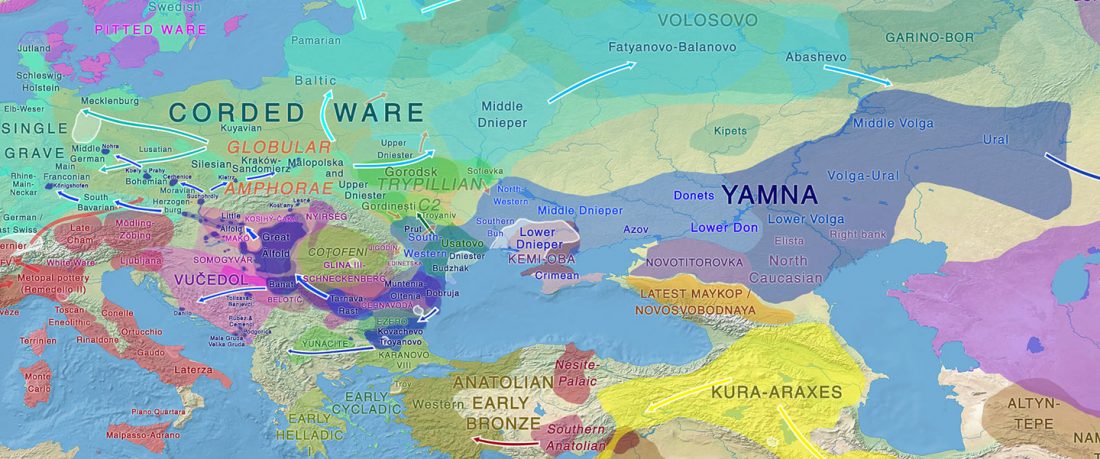
NOTE. Notice also the the number of new sampled individuals from Khvalynsk, Ekaterinovka, and new Yamnaya groups from Chelyabinsk, Urals, Volga, Don, Moldova, and Romania.
This represents the … Read the rest “IBD sharing between Corded Ware and Yamnaya-related populations”