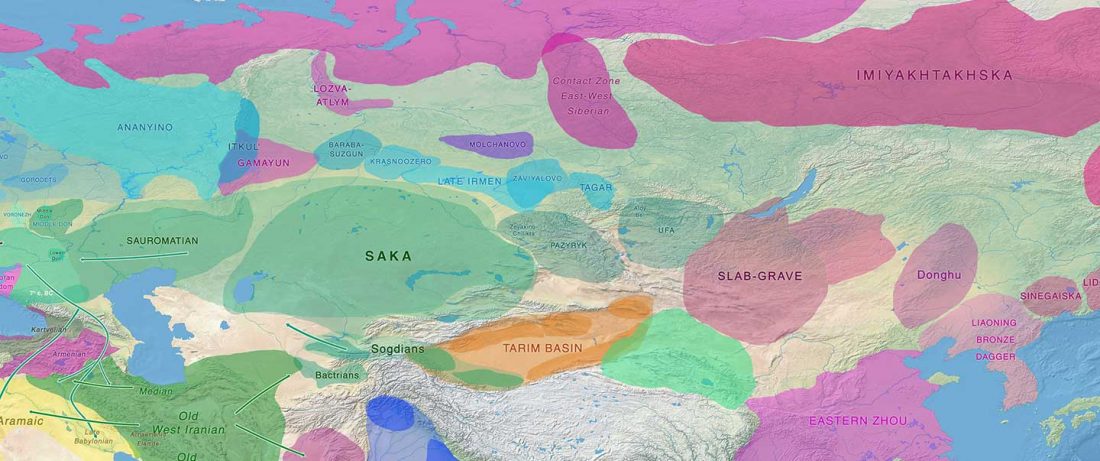
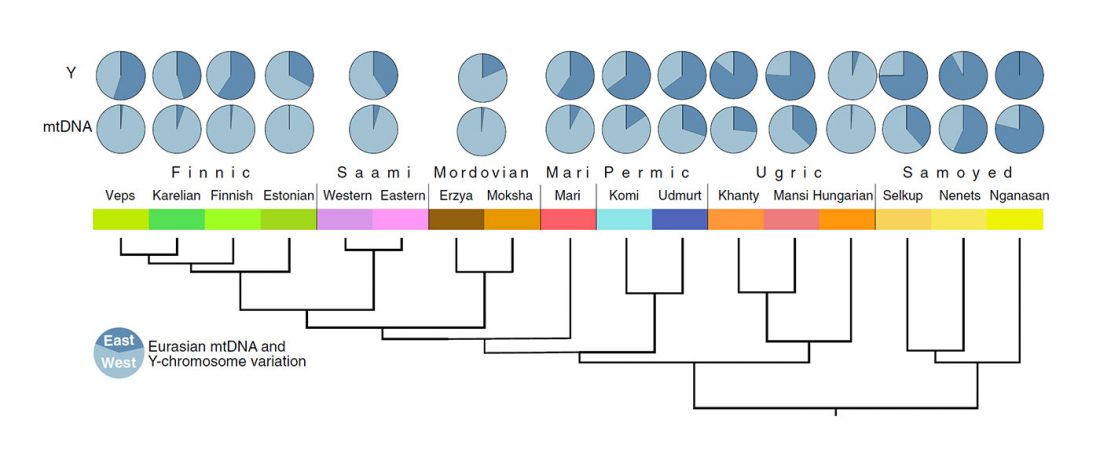
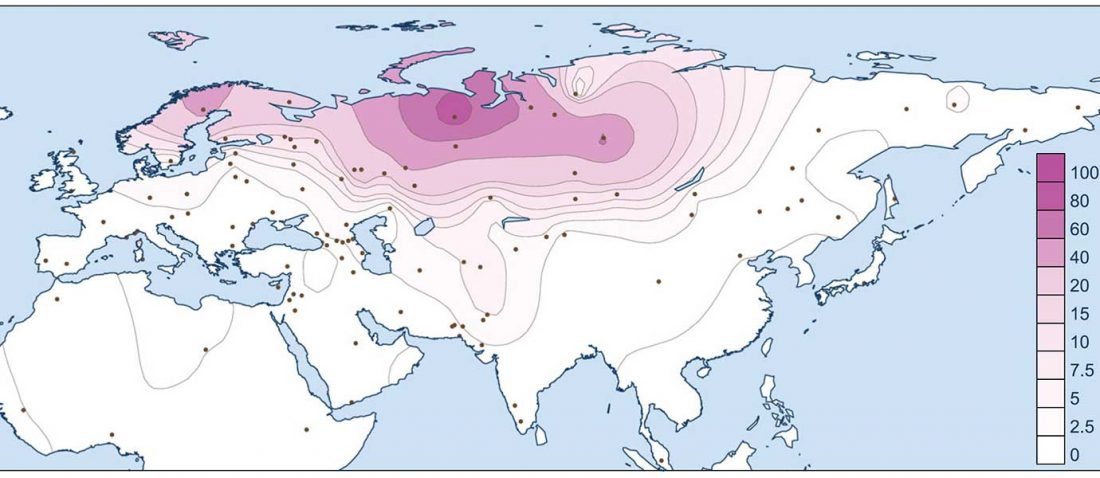
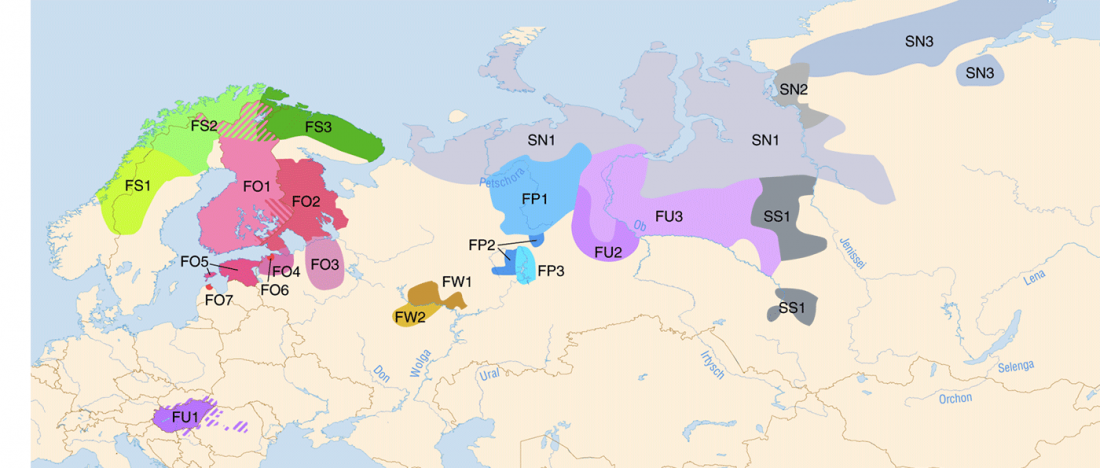
Matrilineal and patrilineal genetic continuity of two iron age individuals from a Pazyryk culture burial, by Tikhonov, Gurkan, Peler, & Dyakonov, Int J Hum Genet (2019).
Relevant excerpts (emphasis mine):
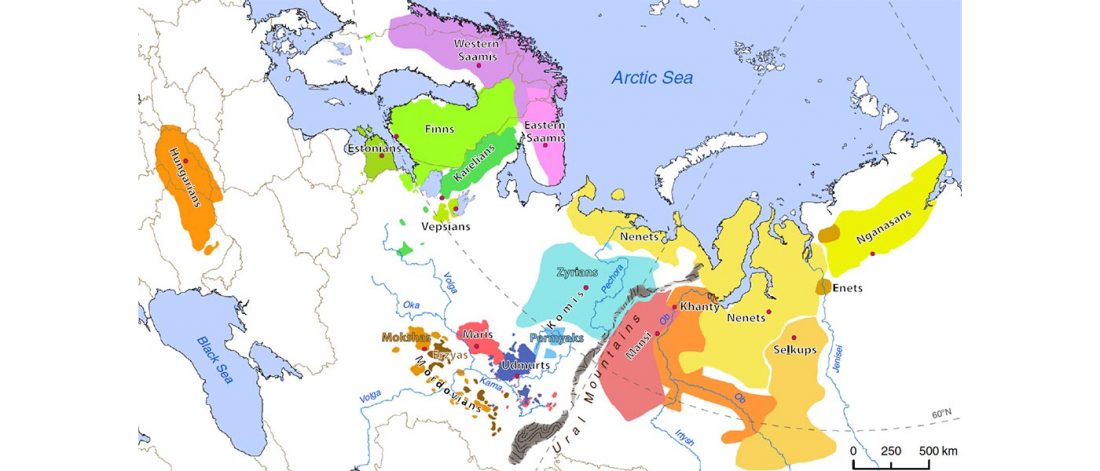
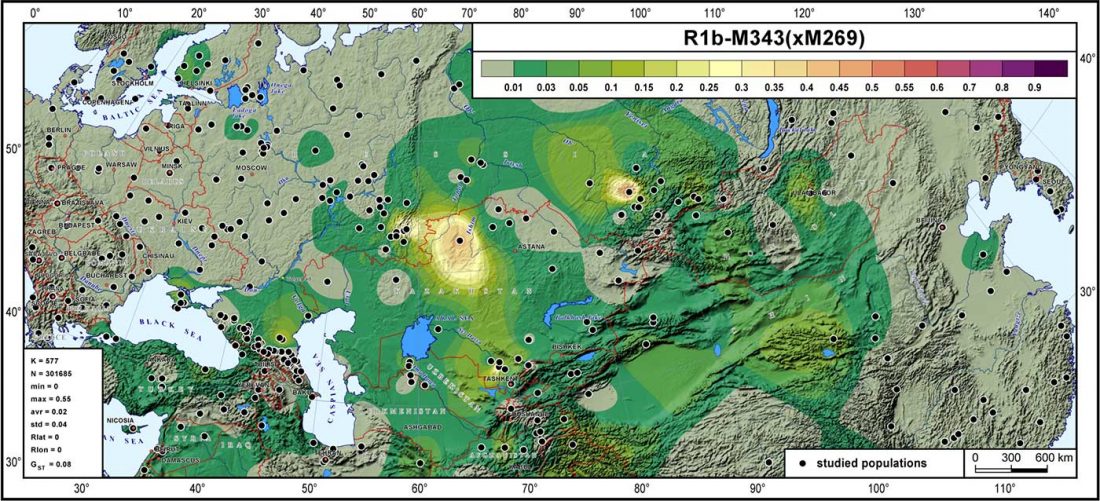
… Read the rest “The Pazyryk culture spoke a “Uralic-Altaic” language… because haplogroup N”Of particular interest to the current study are the archaeogenetic investigations associated with the exemplary mound 1 from the Ak-Alakha-1 site on the Ukok Plateau in the Altai Republic (Polosmak 1994a; Pilipenko et al. 2015). This typical Pazyryk “frozen grave” was dated around 2268±39 years before present (Bln-4977) (Gersdorff and Parzinger 2000). Initial anthropological findings suggested an undisturbed dual inhumation comprising “a middle-aged European- type man” and “a young