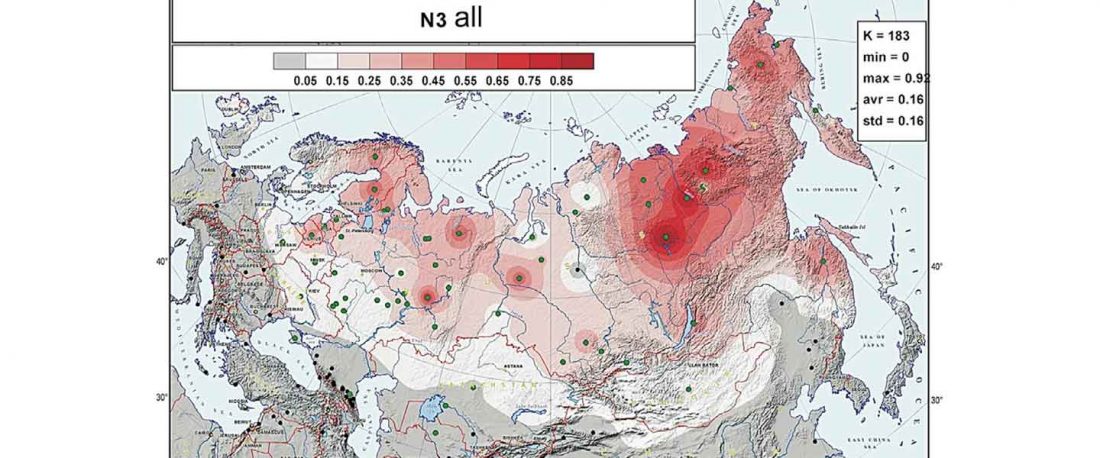
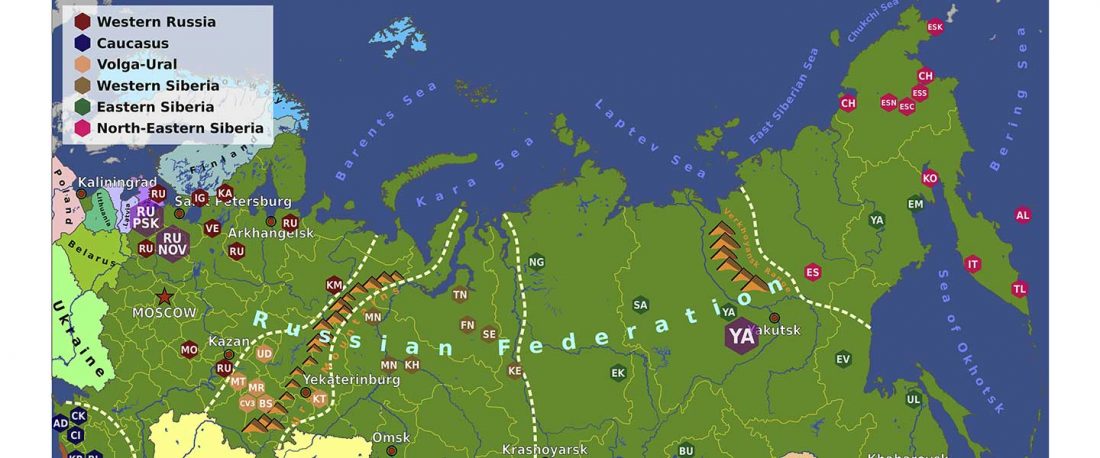
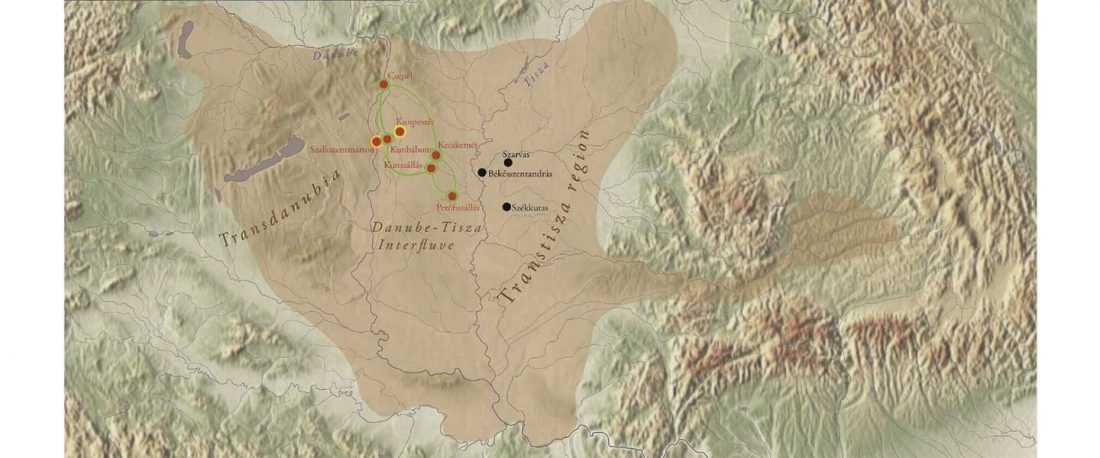
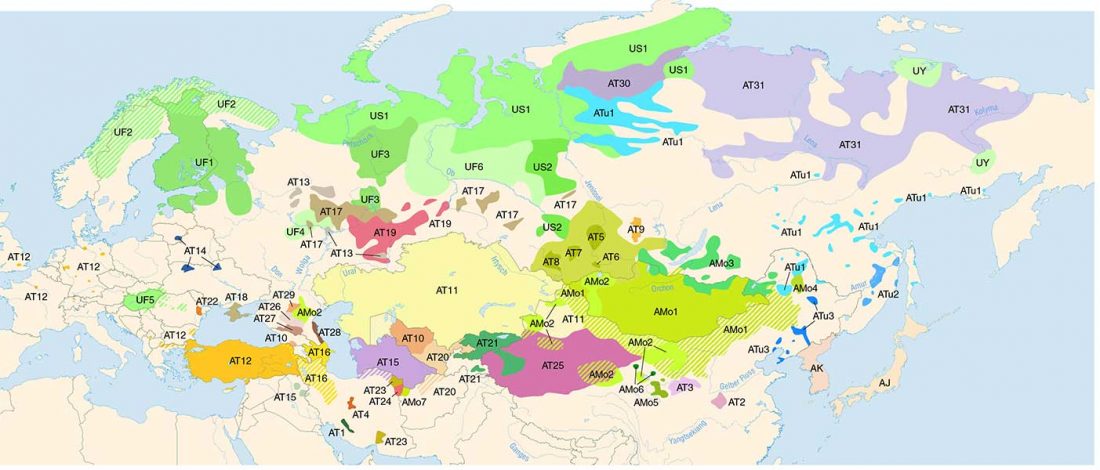
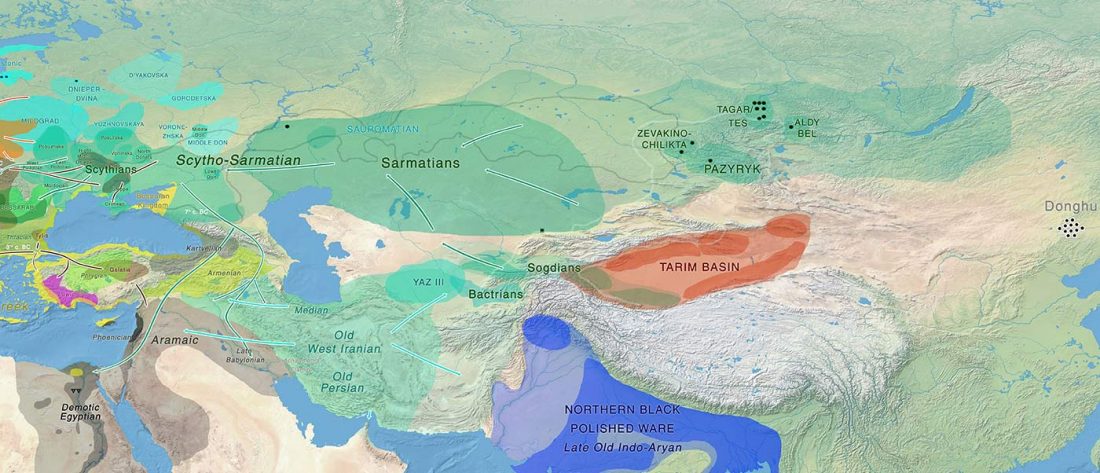
Second in popularity for the expansion of haplogroup N1a-L392 (ca. 4400 BC) is, apparently, the association with Turkic, and by extension with Micro-Altaic, after the Uralic link preferred in Europe; at least among certain eastern researchers.
New paper in a recently created journal, by the same main author of the group proposing that Scythians of hg. N1c were Turkic speakers: On the origins of the Sakhas’ paternal lineages: Reconciliation of population genetic / ancient DNA data, archaeological findings and historical narratives, by Tikhonov, Gurkan, Demirdov, and Beyoglu, Siberian Research (2019).
Interesting excerpts:
… Read the rest “N1c-L392 associated with expanding Turkic lineages in Siberia”According to the views of a