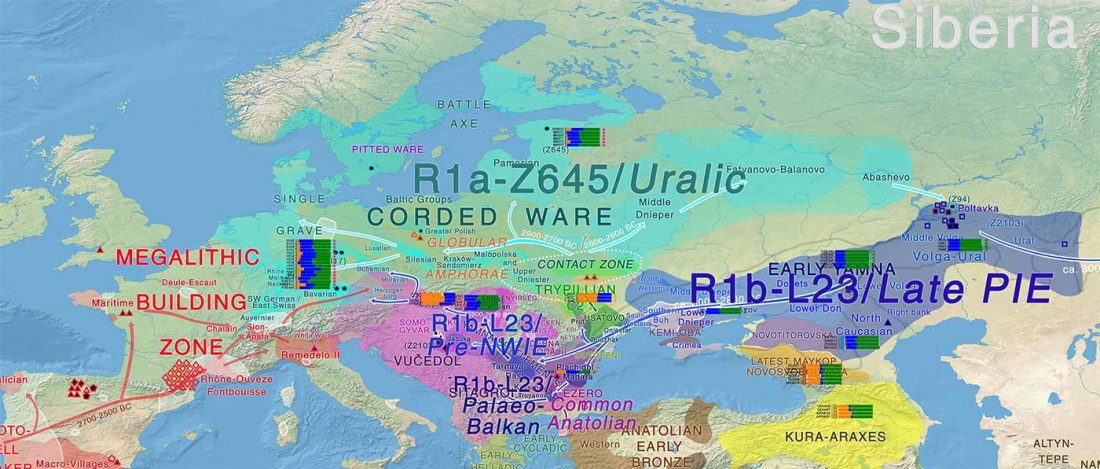
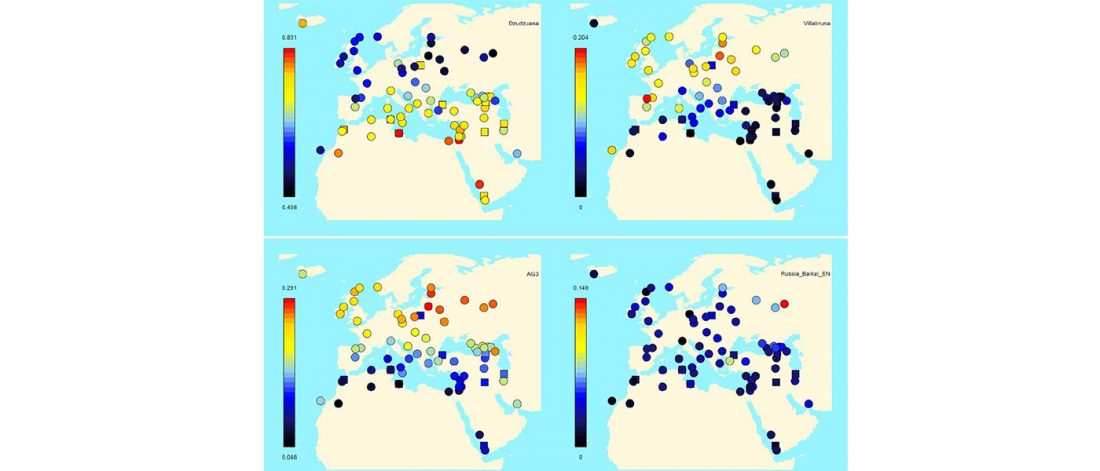
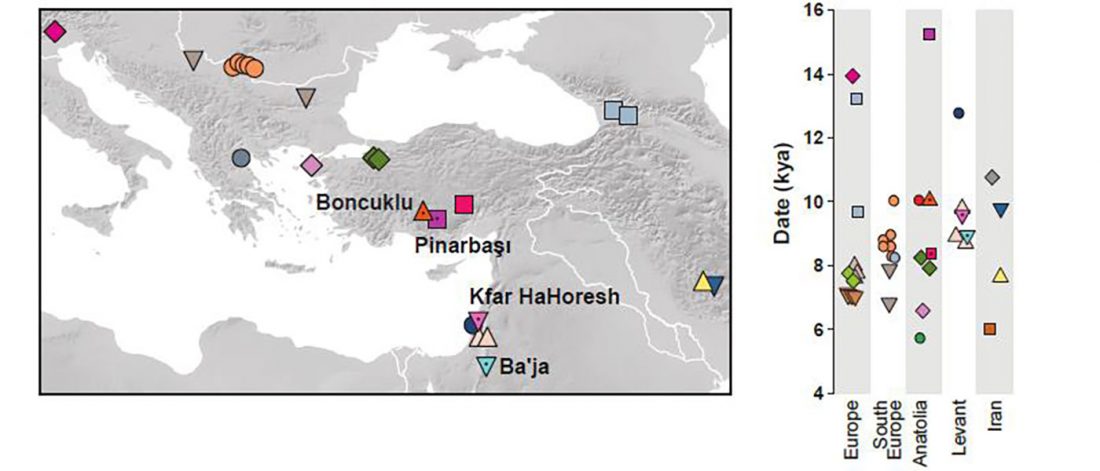
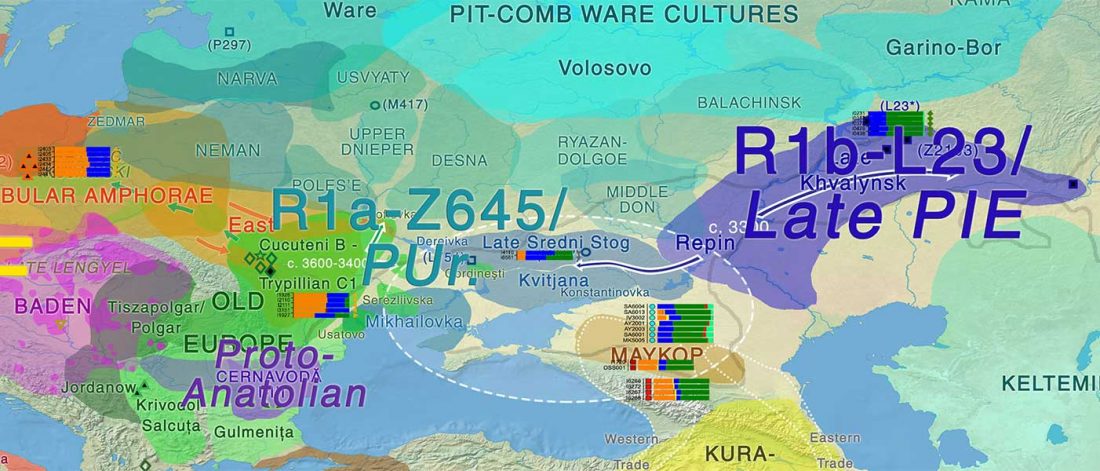
New interesting preprint Ancient DNA from chewing gums connects material culture and genetics of Mesolithic hunter-gatherers in Scandinavia, by Kashuba et al. (2018).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Mitochondrial genomes from all three individuals belong to the U5a2d haplogroup. (…) The mitochondrial U5a2d haplogroup is consistent with earlier published results for ancient individuals from Scandinavia, U5a being the most common within SHG. Of the 16 Mesolithic individuals from Scandinavia published prior to our study, seven belong to the U5a haplogroup, nine share the U2 and U4 haplogroups
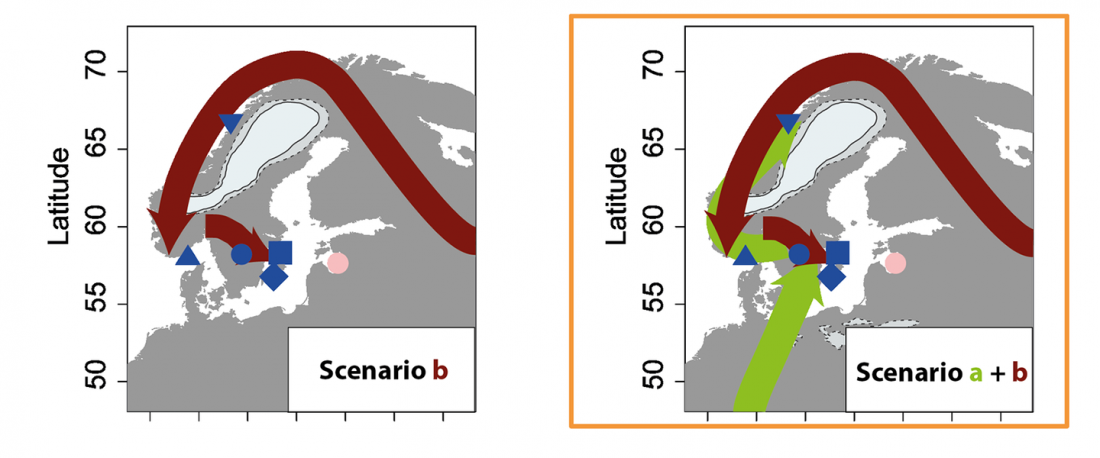
… Read the rest “Eastern pressure blade technology in west Scandinavia associated with WHG”We divided the SHG group into two groups: SHGa and SHGb (ancient