This post is part of a draft on South Siberian language homelands and Sprachbünde.
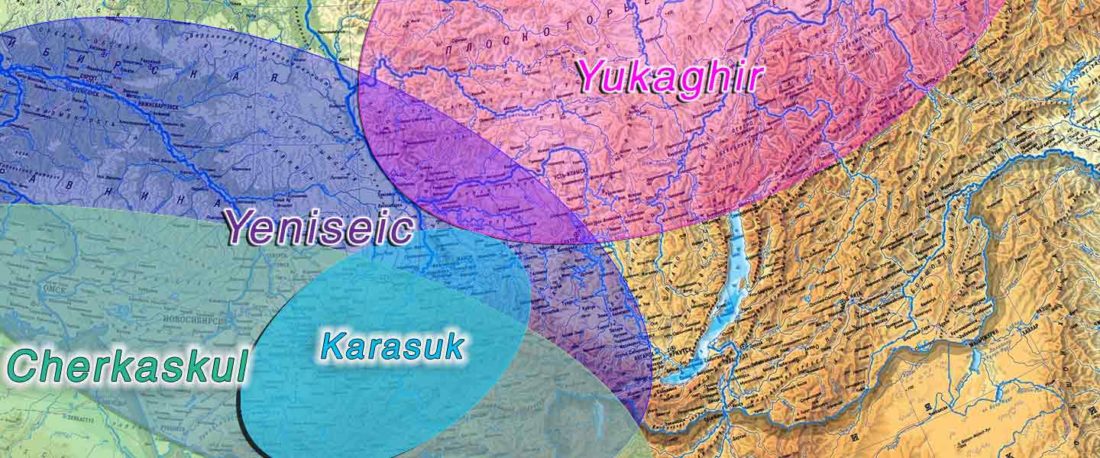
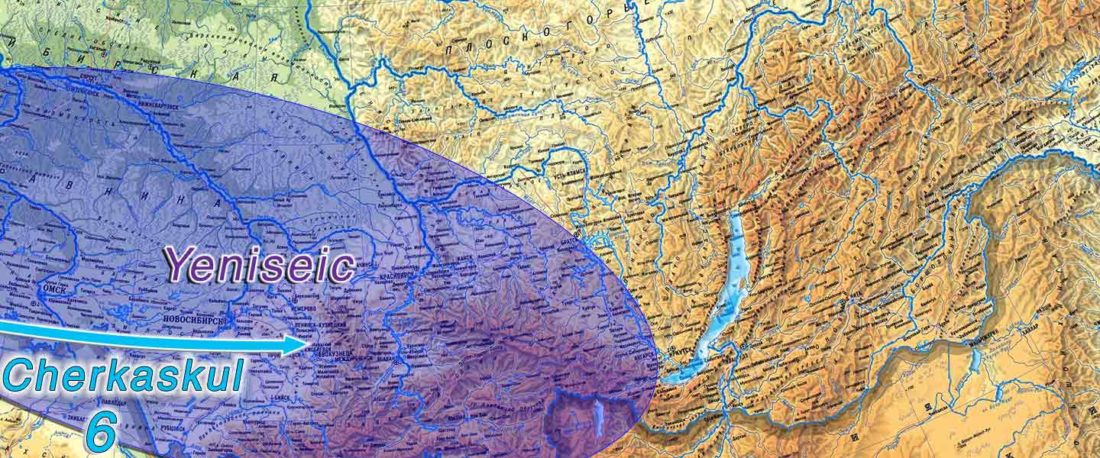
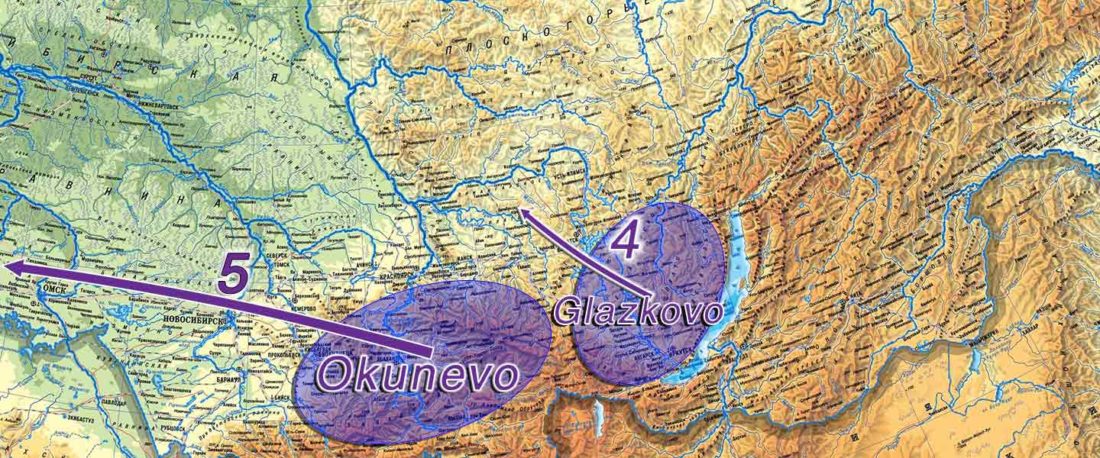
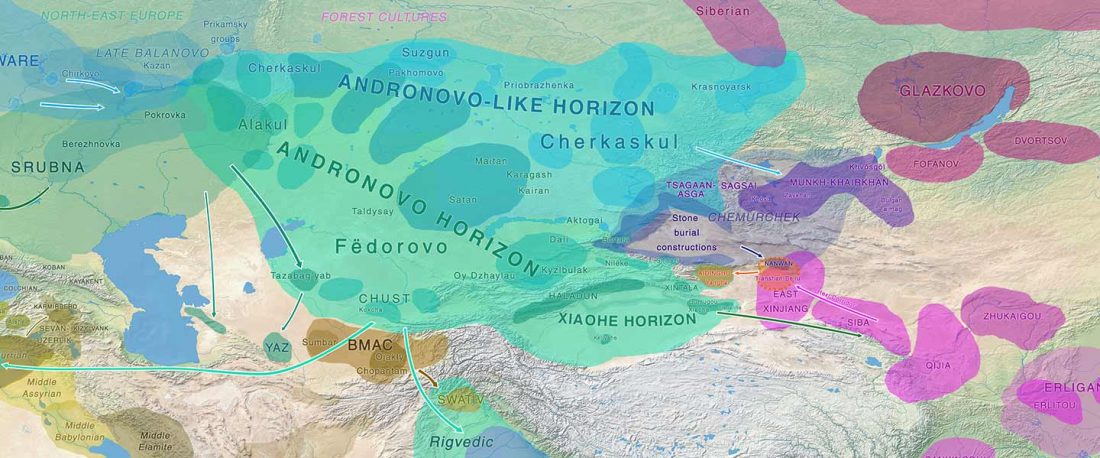
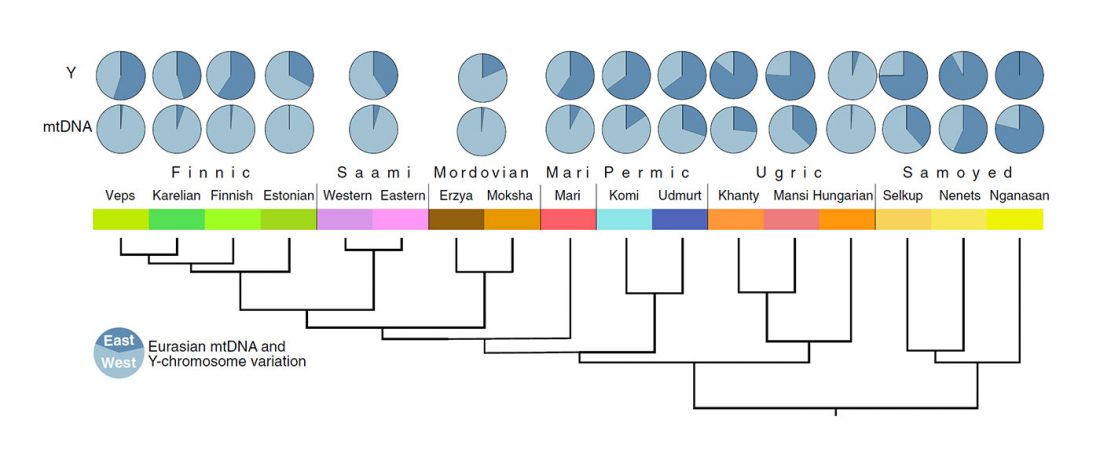
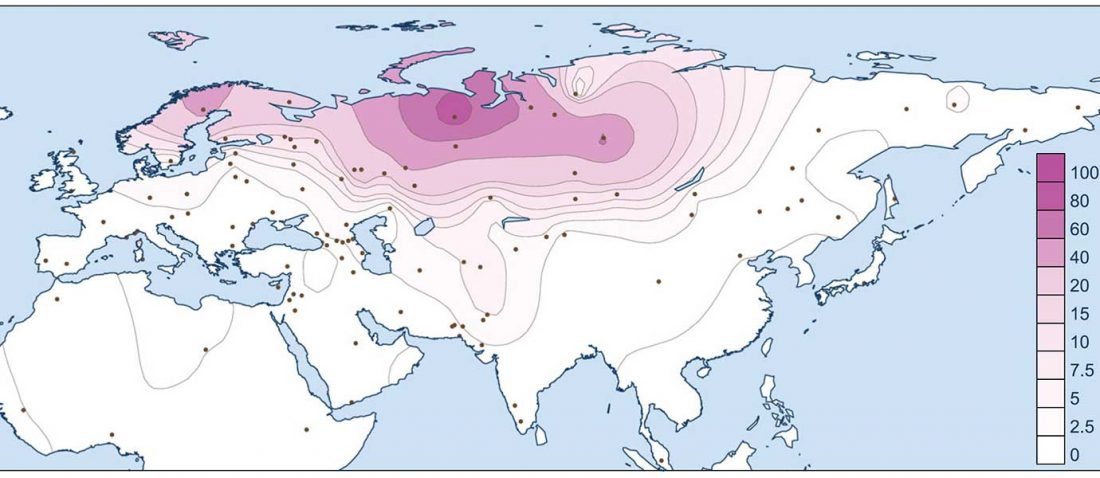
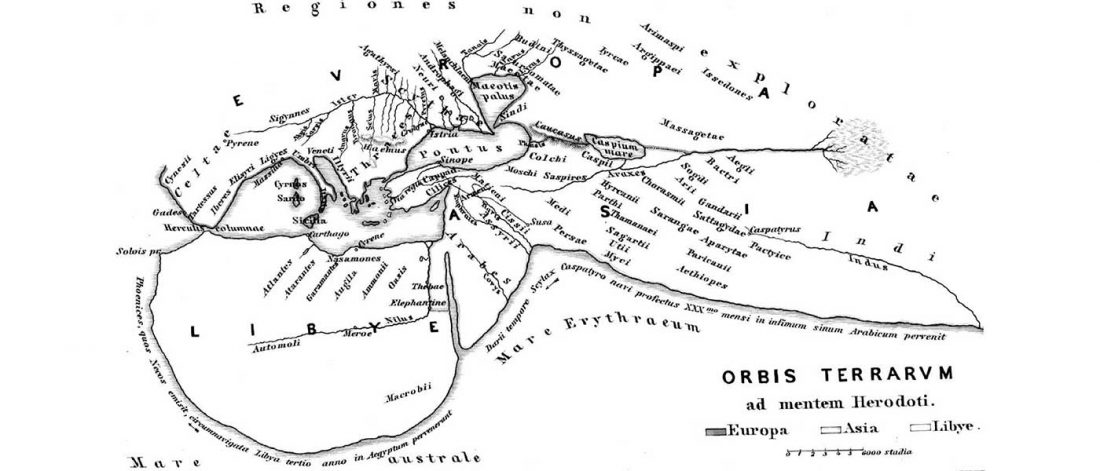
The following text contains a description of Pre- and Proto-Samoyedic stages and its dialectal diversification. Contacts with Indo-Iranian, Yeniseian, Tocharian, Yukaghir, and Turkic, as well as onomastics and palaeolinguistics are taken into account to pinpoint the succeeding homelands and expansion territories. The archaeological-archaeogenetic discussion is focused on the Middle Bronze Age Cherkaskul materials of the Andronovo period, on the Late Bronze Age Karasuk culture, and on the evolution and expansion of the Iron Age Tagar culture within the framework of “Scytho-Siberian” … Read the rest “Proto-Samoyed homeland”