Short report on advances in Genomics, and on the Reich Lab:
Some interesting details:
- The Lab is impressive. I would never dream of having something like this at our university. I am really jealous of that working environment.
- They are currently working on population transformations in Italy; I hope we can have at last Italic and Etruscan samples.
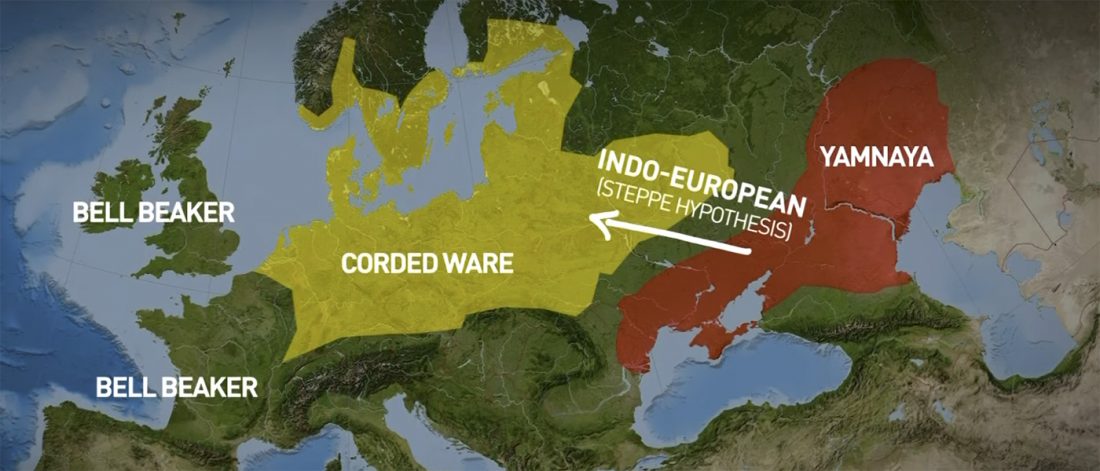
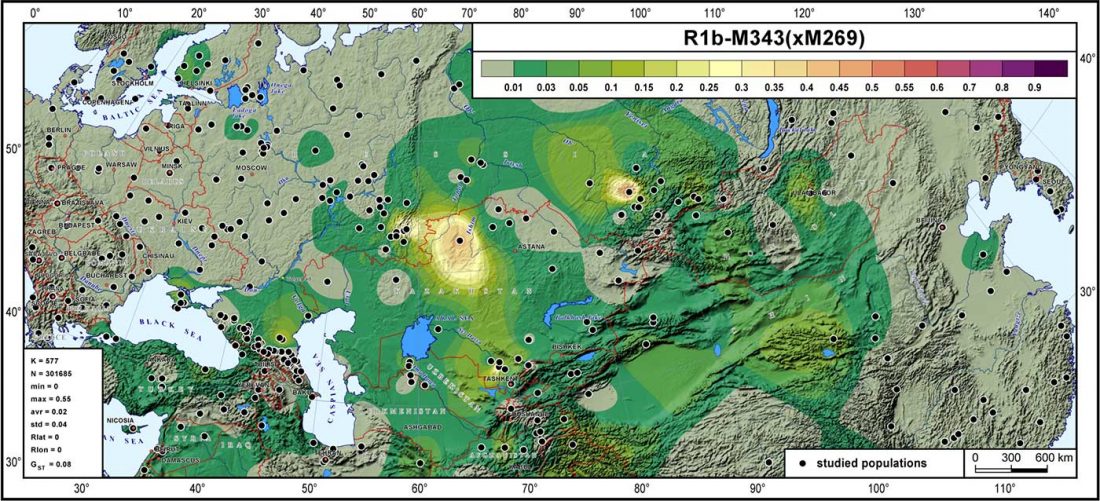
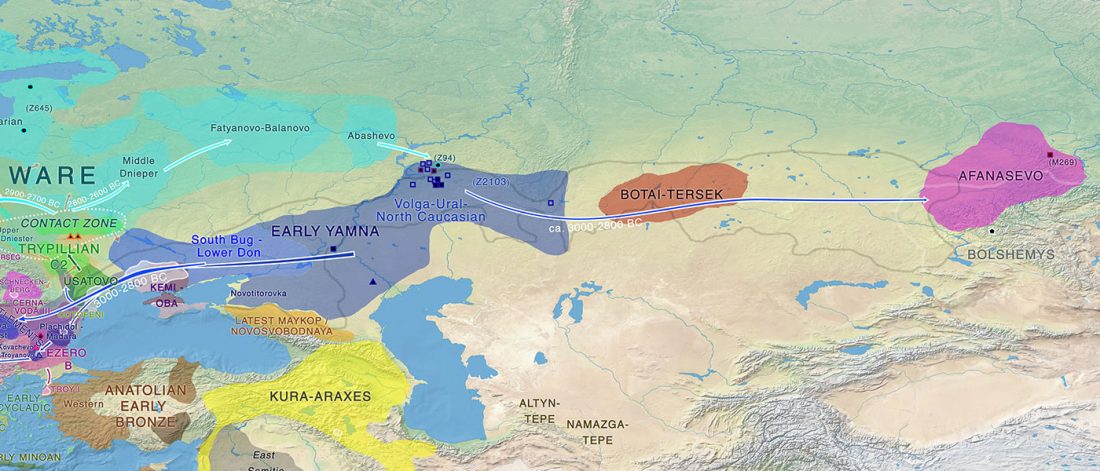
- It is always worth it to repeat that we are all the source of multiple admixture events, many of them quite recent; and I liked the Star Wars simile.
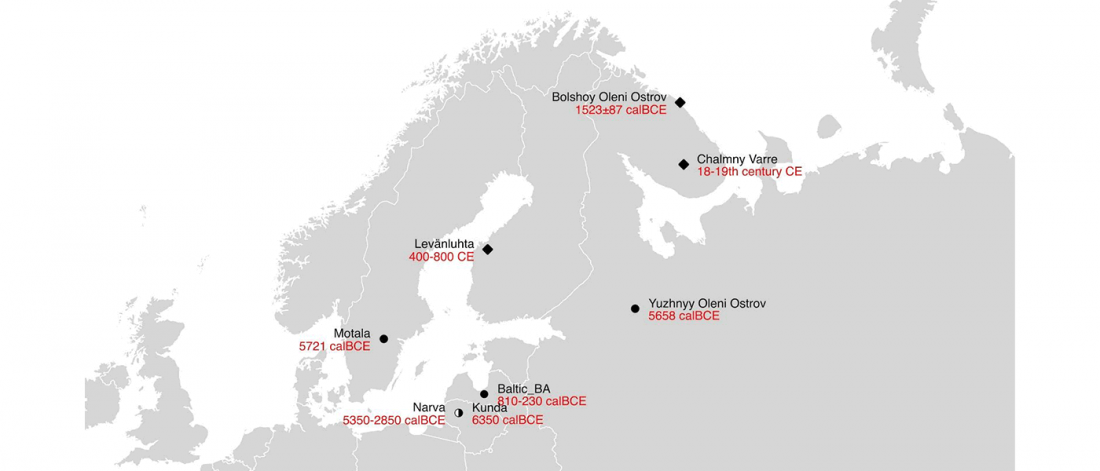
- Also, some names hinting at potential new samples?? Zajo-I, Chanchan, Gurulde?, Володарка