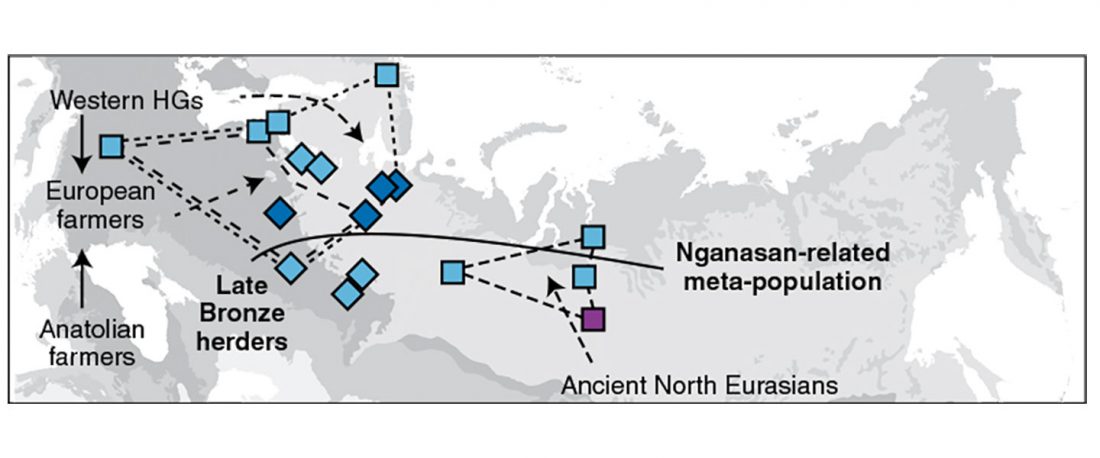
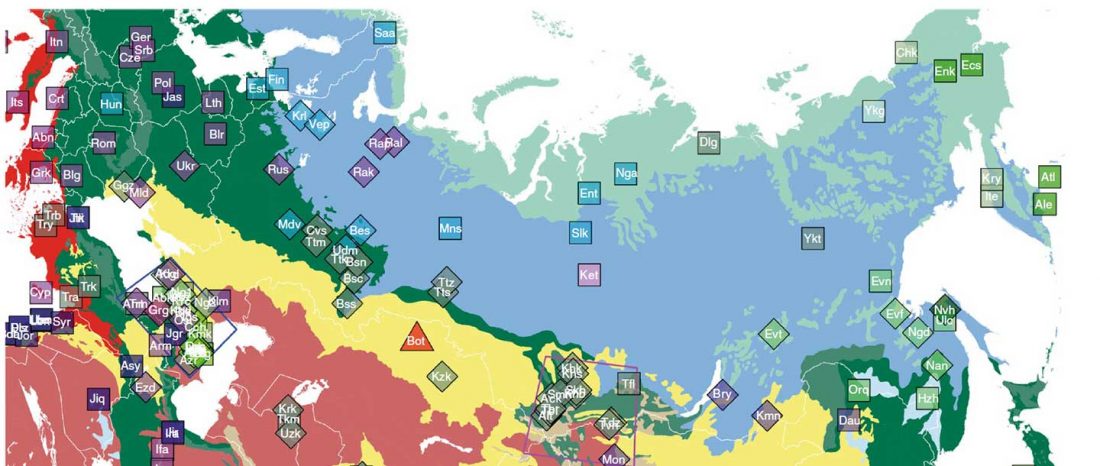
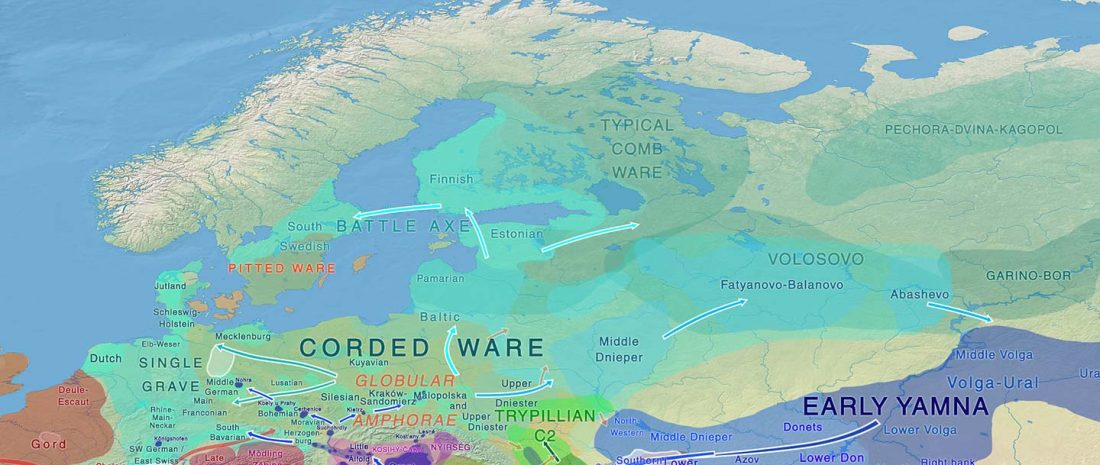
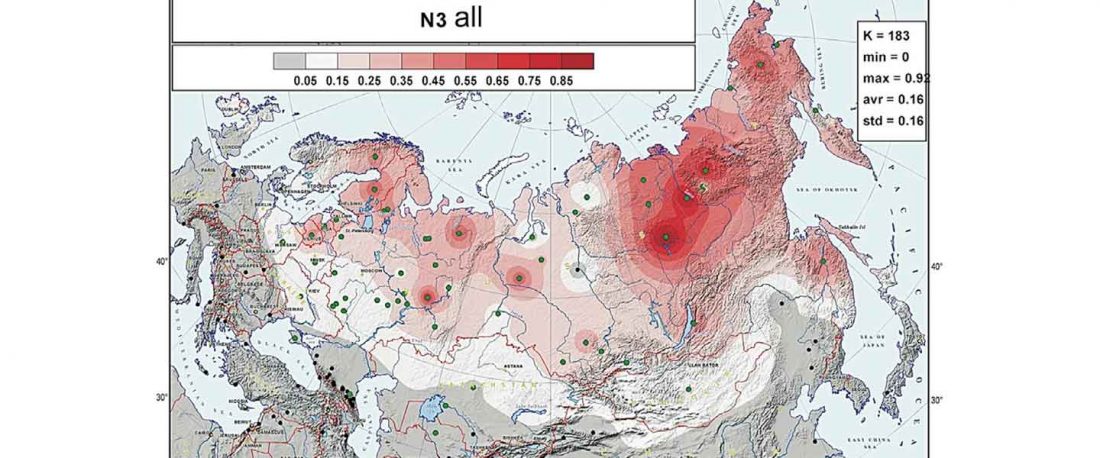
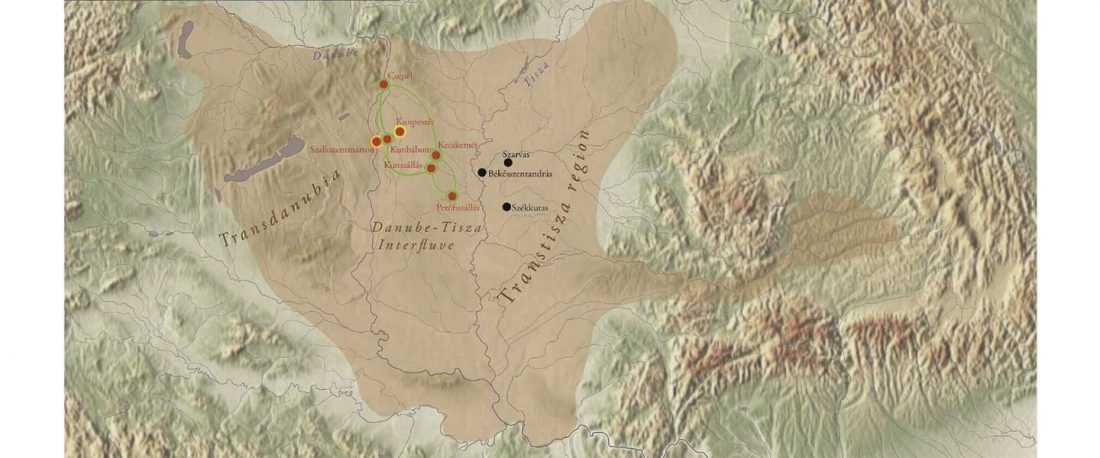
Now that it has become evident that Late Repin (i.e. Yamnaya/Afanasevo) ancestry was associated with the migration of R1b-L23-rich Late Proto-Indo-Europeans from the steppe in the second half of the the 4th millennium BC, there’s still the question of how R1a-rich Uralic speakers of Corded Ware ancestry expanded , and how they spread their languages throughout North Eurasia.
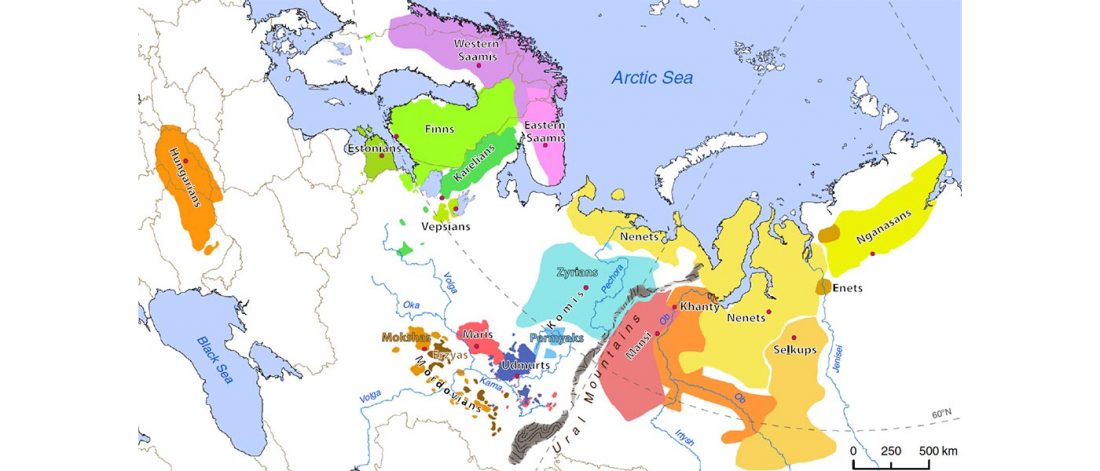
Modern North Eurasians
I have been collecting information from the supplementary data of the latest papers on modern and ancient North Eurasian peoples, including Jeong et al. (2019), Saag et al. (2019), Sikora et al. (2018), or … Read the rest “Corded Ware ancestry in North Eurasia and the Uralic expansion”