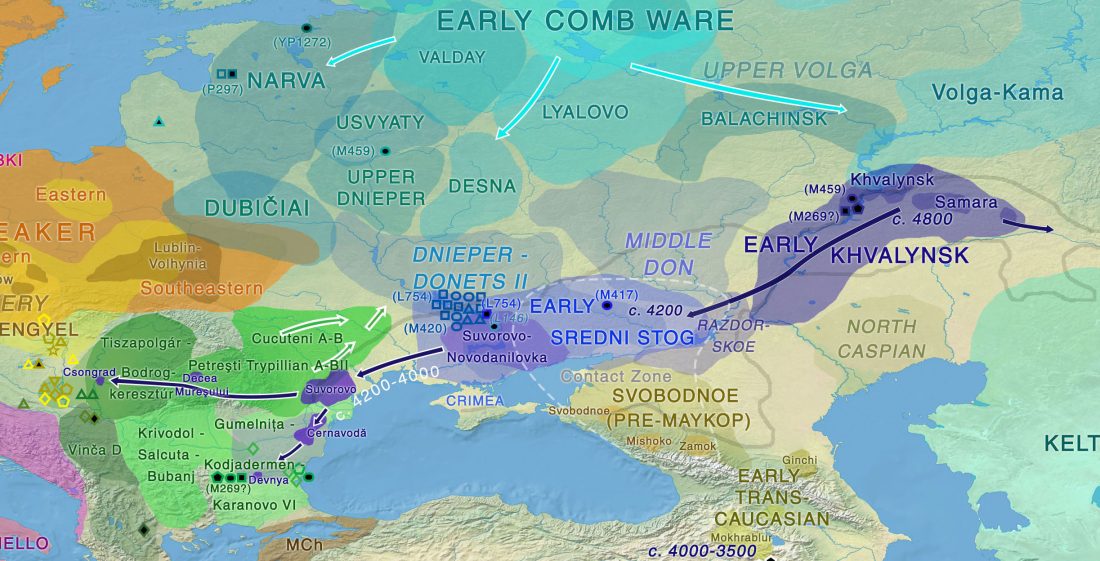
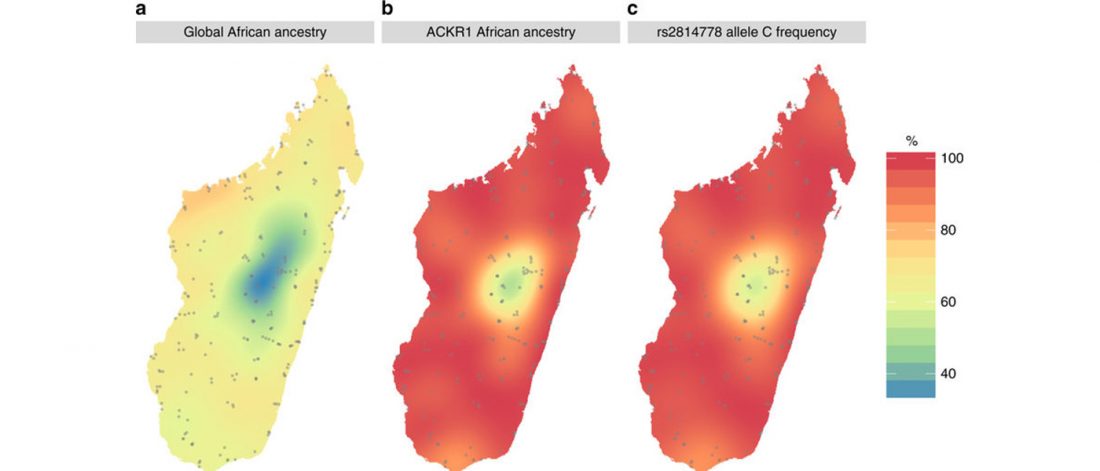
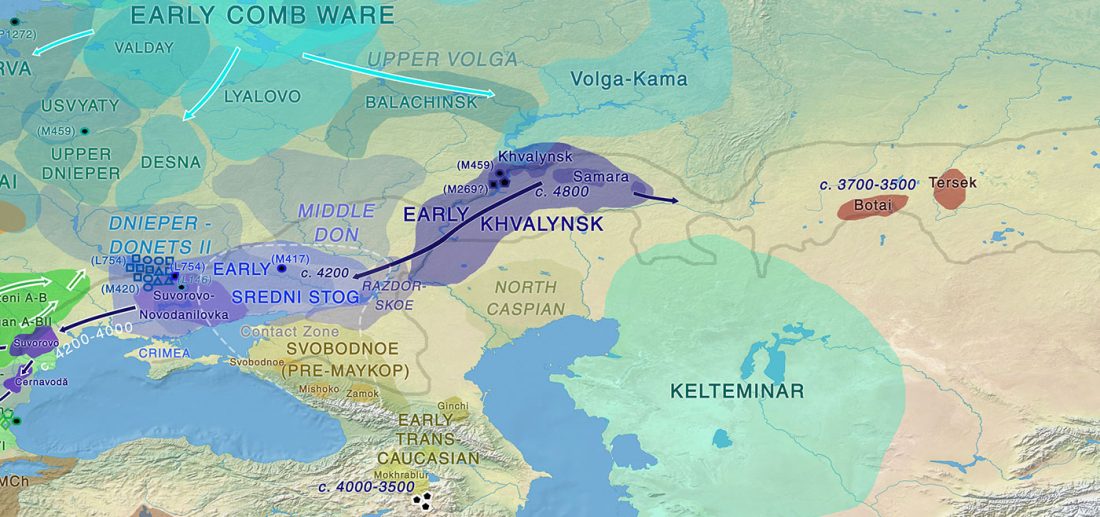
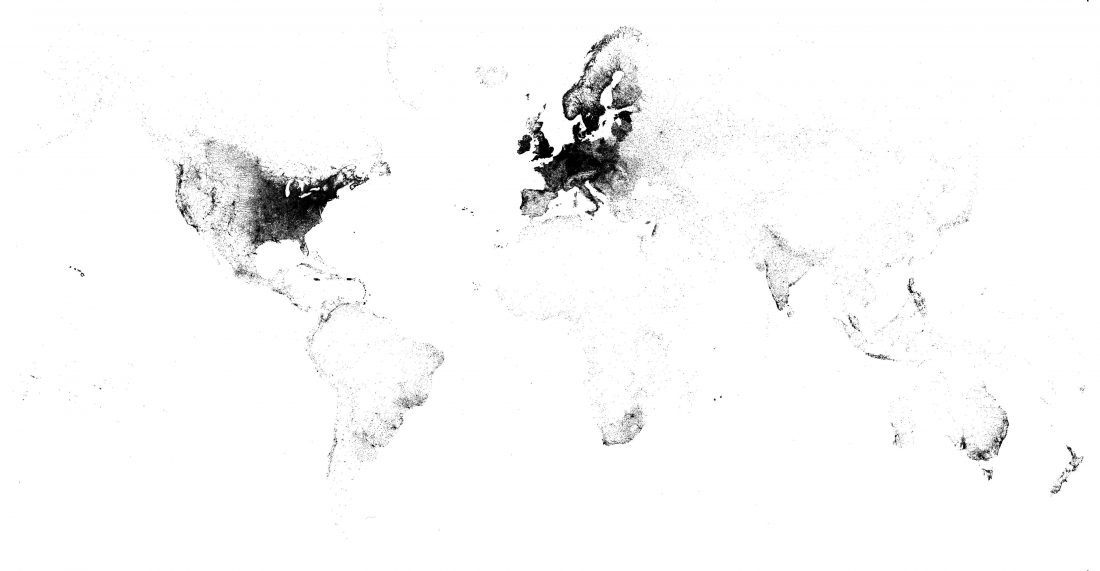
Open access preprint (which I announced already) at bioRxiv Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula, by Bycroft et al. (2018).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Patterns of genetic differentiation and the footprints of historical migrations in the Iberian Peninsula”Genetic differences within or between human populations (population structure) has been studied using a variety of approaches over many years. Recently there has been an increasing focus on studying genetic differentiation at fine geographic scales, such as within countries. Identifying such structure allows the study of recent population history, and identifies the potential for confounding in association studies, particularly when testing rare, often recently arisen variants. The Iberian