Scythians in Ukraine, Natufian and sub-Saharan ancestry in North Africa (ISBA 8, 21st Sep)
Interesting information from ISBA 8 sesions today, as seen on Twitter (see programme in PDF, and sessions from the 19th and the 20th september).
Official abstracts are listed first (emphasis mine), then reports and images and/or link to tweets. Here is the list for quick access:
- Scythian population genetics and settlement patterns
- North-Africans show ancestry from the ancient Near East and sub-Saharan Africa
- North-Africans show ancestry from the ancient Near East and sub-Saharan Africa
- Impact of colonization in north-eastern Siberia
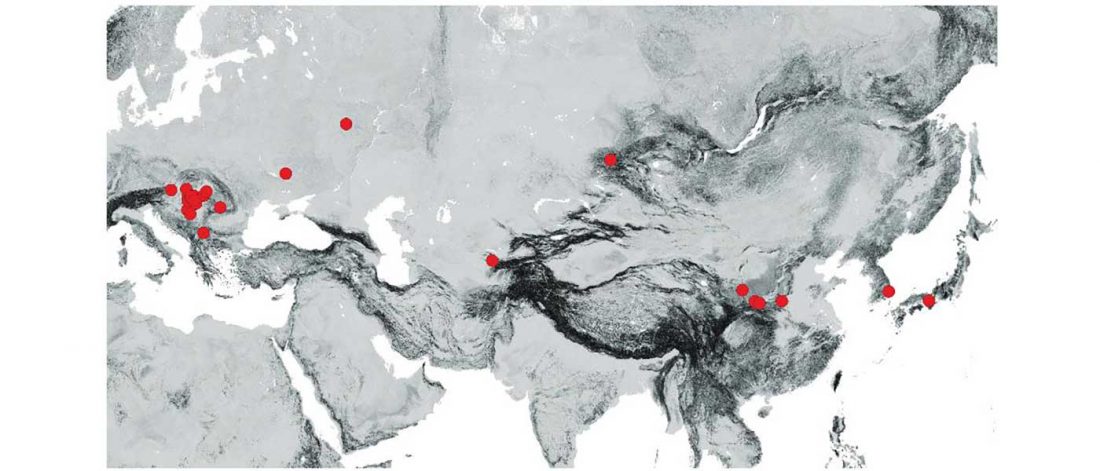
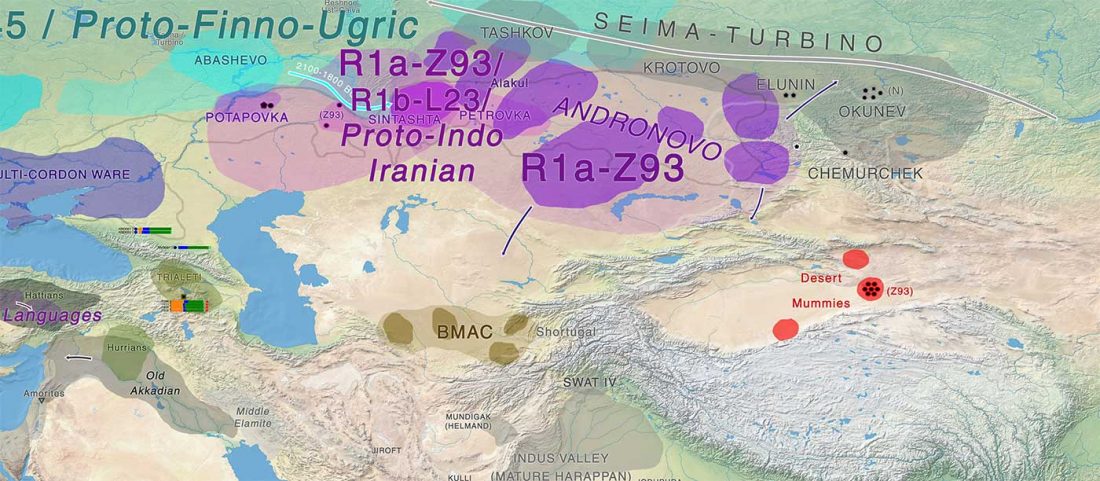
Scythian population genetics and settlement patterns
Genetic continuity in the western Eurasian Steppe broken not due to Scythian dominance, … Read the rest “Scythians in Ukraine, Natufian and sub-Saharan ancestry in North Africa (ISBA 8, 21st Sep)”