New open access paper Human population dynamics and Yersinia pestis in ancient northeast Asia, by Kılınç et al. Science Advances (2021).
Content under CC-BY-NC license. Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
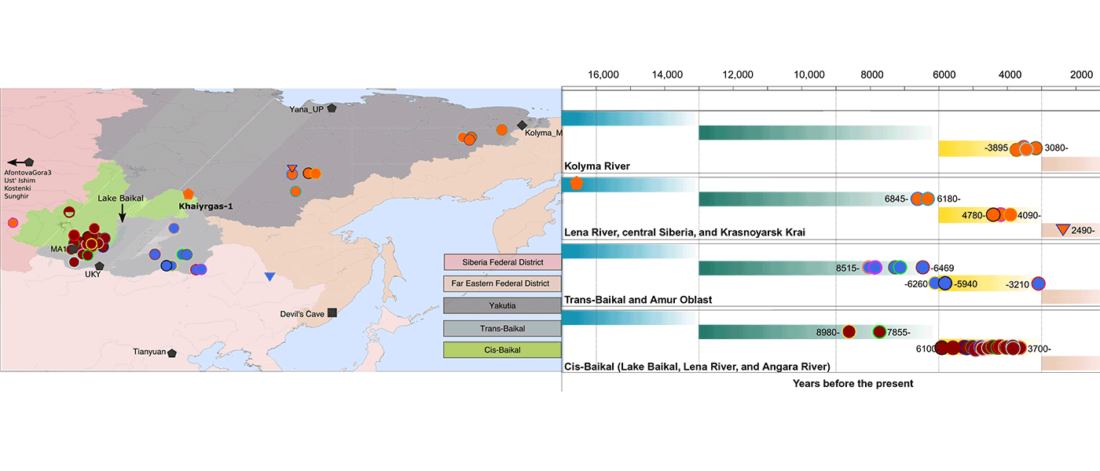
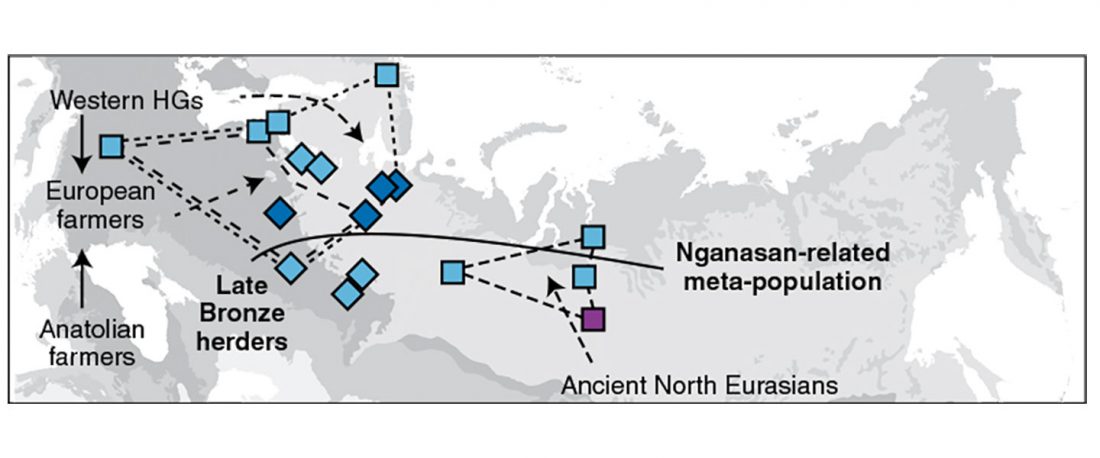
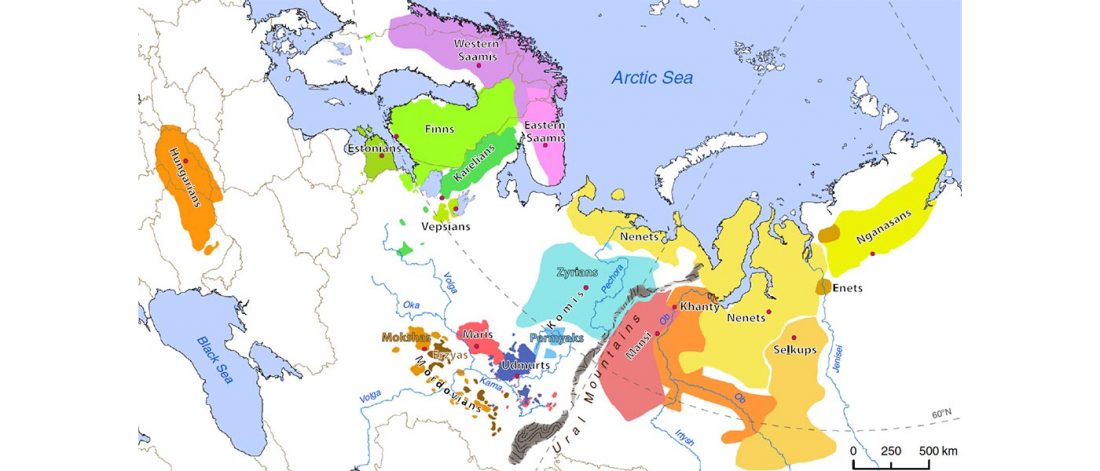
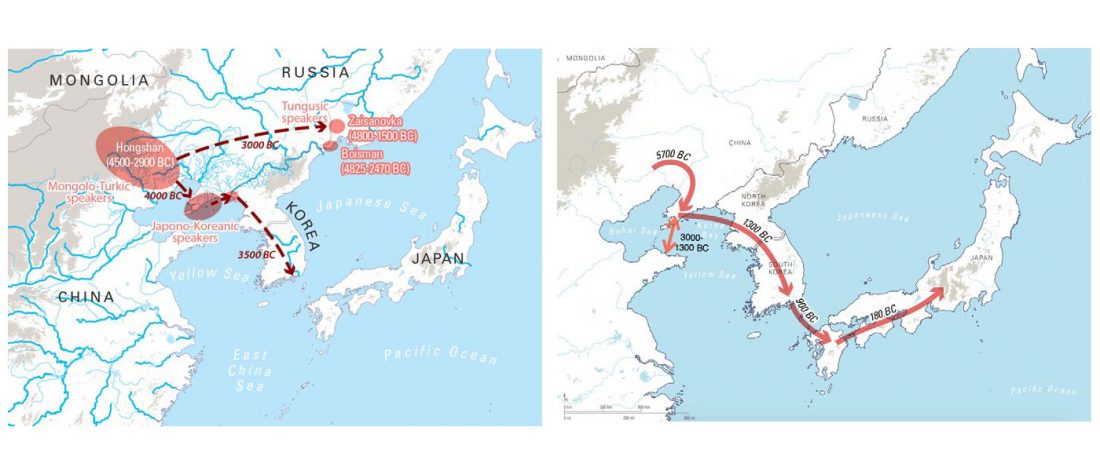
We produced whole-genome sequence data from 40 ancient individuals spanning from the Late Upper Paleolithic to the Medieval era and representing five distinct administrative regions in the Russian Federation encompassing Yakutia, Trans-Baikal, Cis-Baikal, Krasnoyarsk Krai, and Amur Oblast (…) All individuals were accredited to either Y macro-haplogroup Q or N and non-African mitochondrial macrohaplogroups of M, N, and R.
Population dynamics during and after the LGM in northeast Asia
… Read the rest “Haplogroup N-L708 & Q-L53 hotspot, around Lake Baikal”We