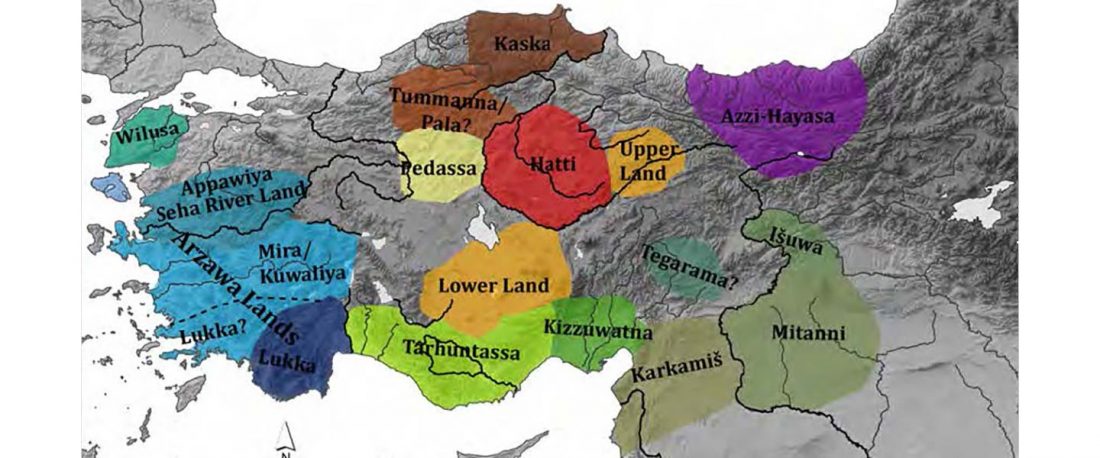
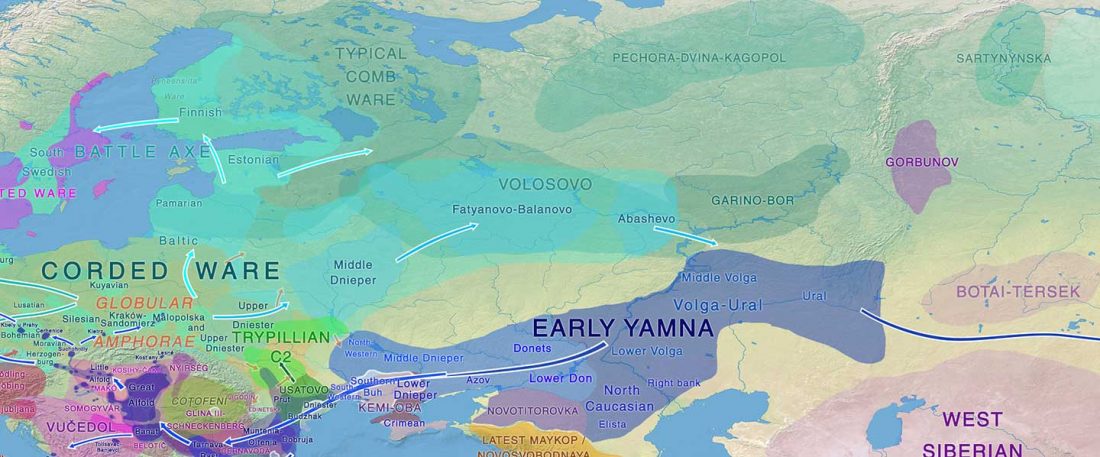
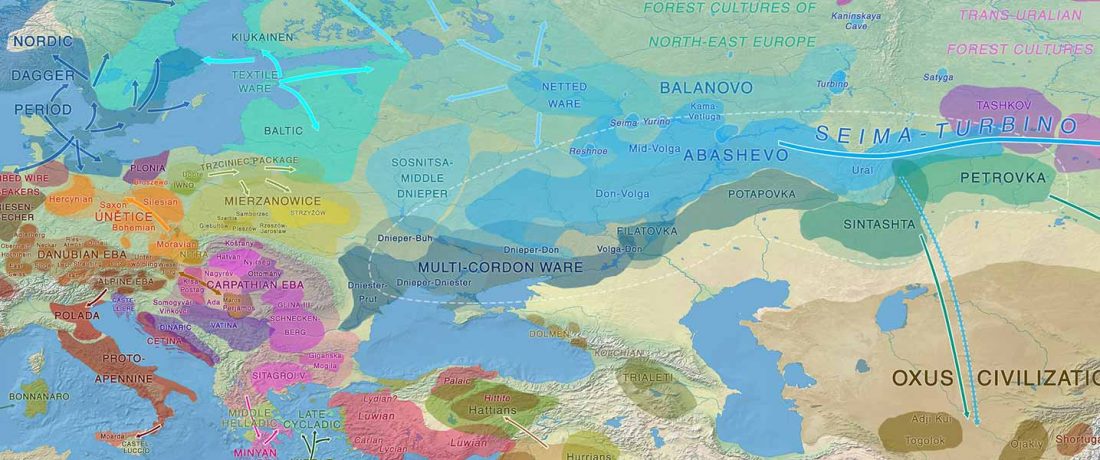
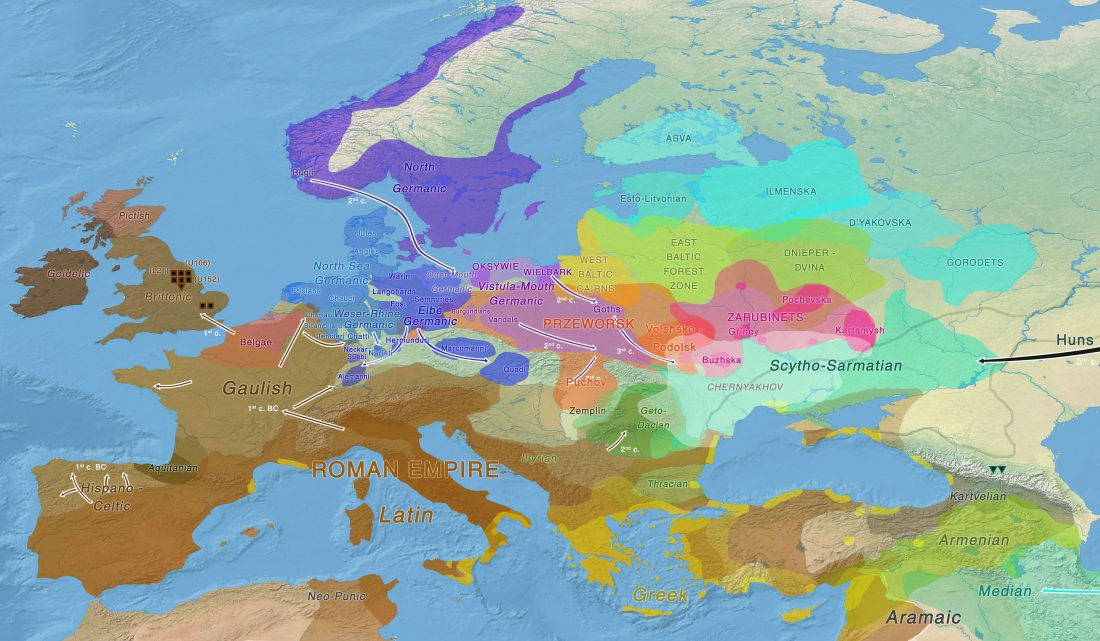
The standard textbook for studying language contact, as far as I know, was Language Contact, Creolization, and Genetic Linguistics, by Sarah Grey Thomason & Terrence Kaufman, UCP (1991, c1988). The reader will surely recognize many of this text’s proposals of language contacts in my books.
Posts of the Language Contact series (reverse chronology):
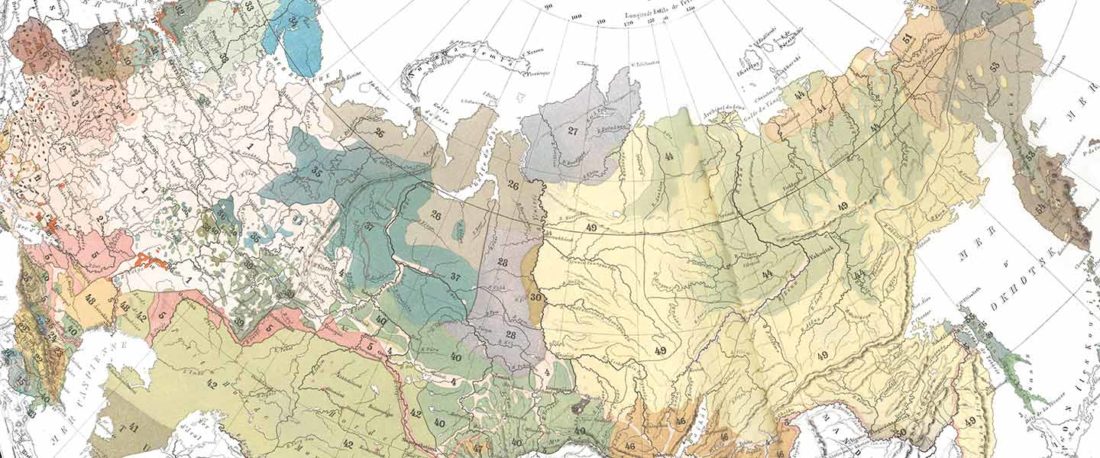
- Proto-Hungarian Homeland: East and West of the Urals?
- Tug of war between Balto-Slavic and West Uralic (II)
- Early Uralic – Indo-European contacts within Europe
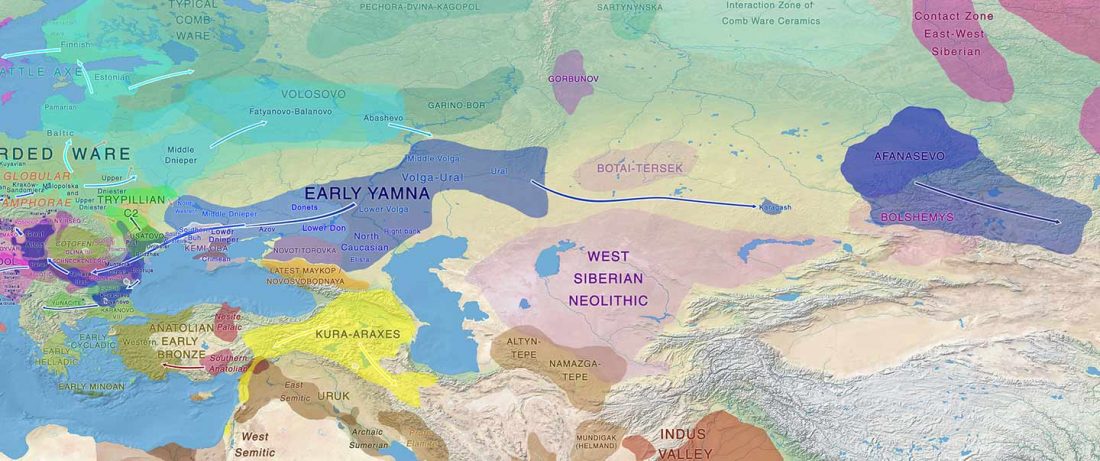
- Intense but irregular NWIE and Indo-Iranian contacts show Uralic disintegrated in the West
- Samoyedic shows Yeniseic substrate; both influenced Tocharian
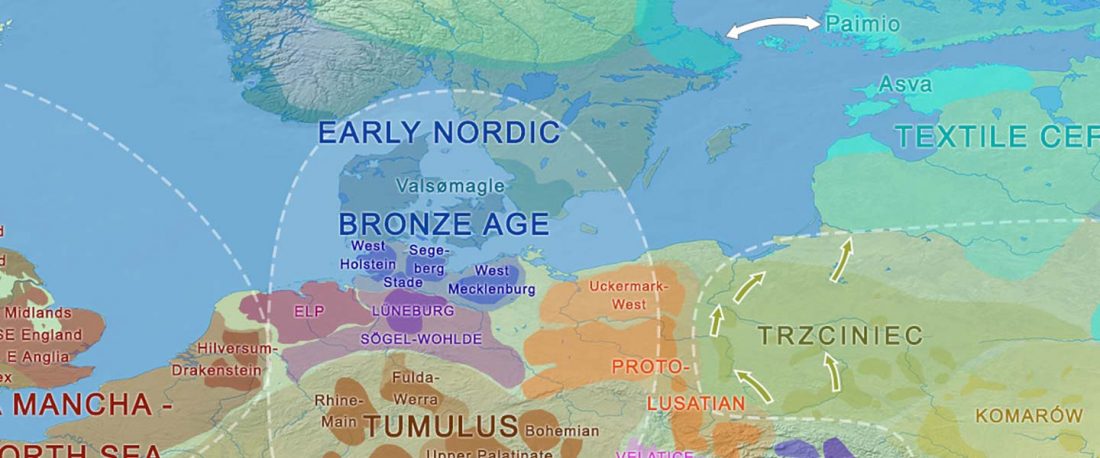
- Pre-Germanic