This post is part of a draft on South Siberian language homelands and Sprachbünde.
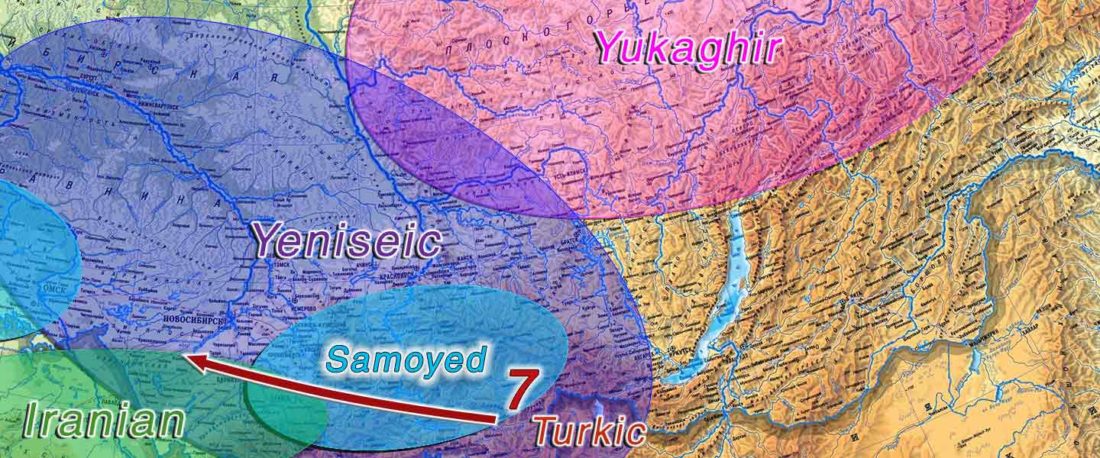
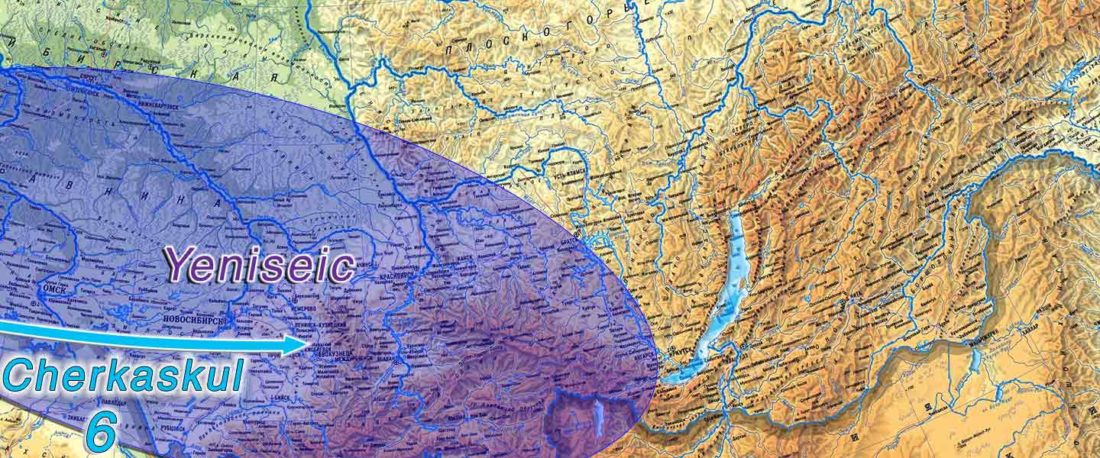
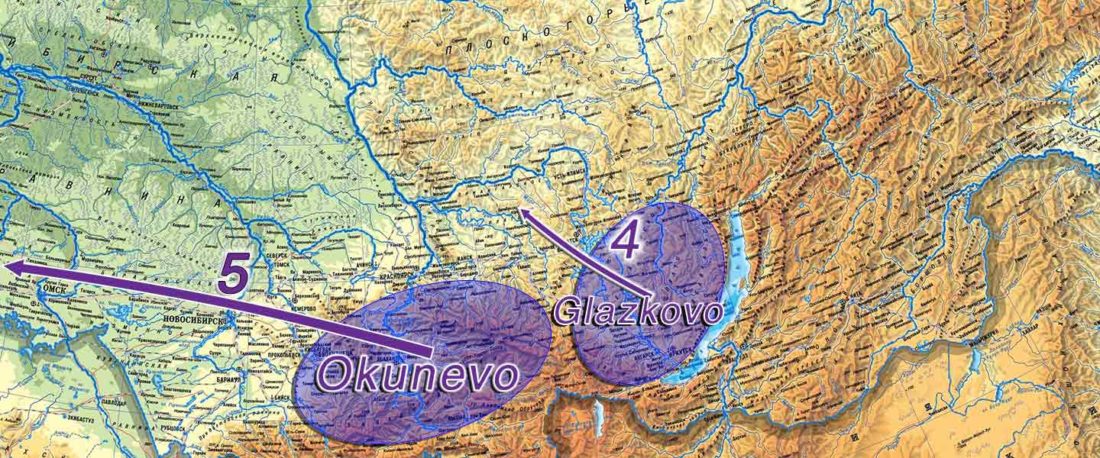
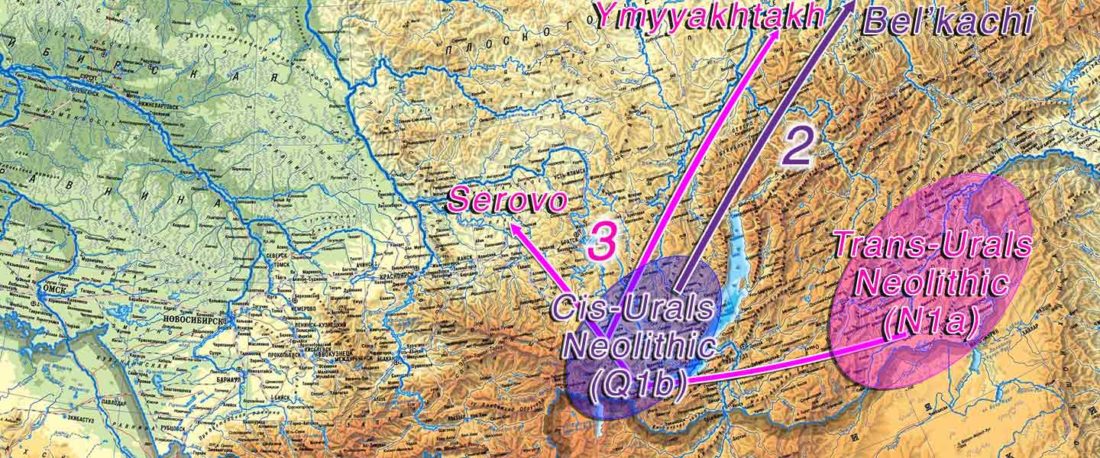
The following text contains a description of Proto-Turkic and its main dialectal split. Contacts with Samoyed, Ob-Ugric, Iranian, Yeniseian, Tocharian, Chinese and Mongolic, as well as palaeolinguistics, hydronymy, and ethnonymy are taken into account to pinpoint the succeeding homelands and expansion territories. The archaeological-archaeogenetic discussion is focused on the Middle and Late Bronze Age Altai Mönkhkhairkhan and Deer Stone-Khirigsuur Complex and related groups, as well as on Ulaanzukh; Early Iron Age “Scytho-Siberian” Pazyryk & Uyuk and Slab Grave cultures; and on the Late … Read the rest “Proto-Turkic homeland”