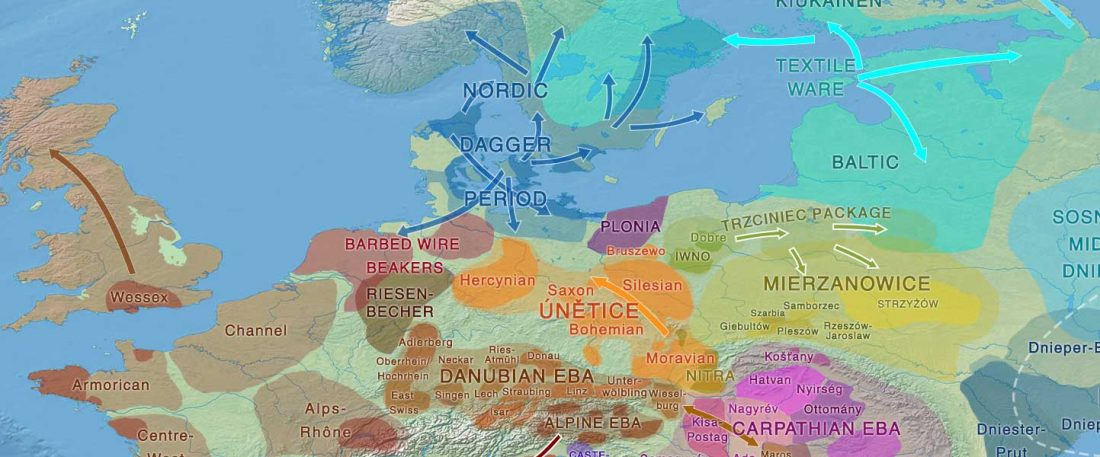
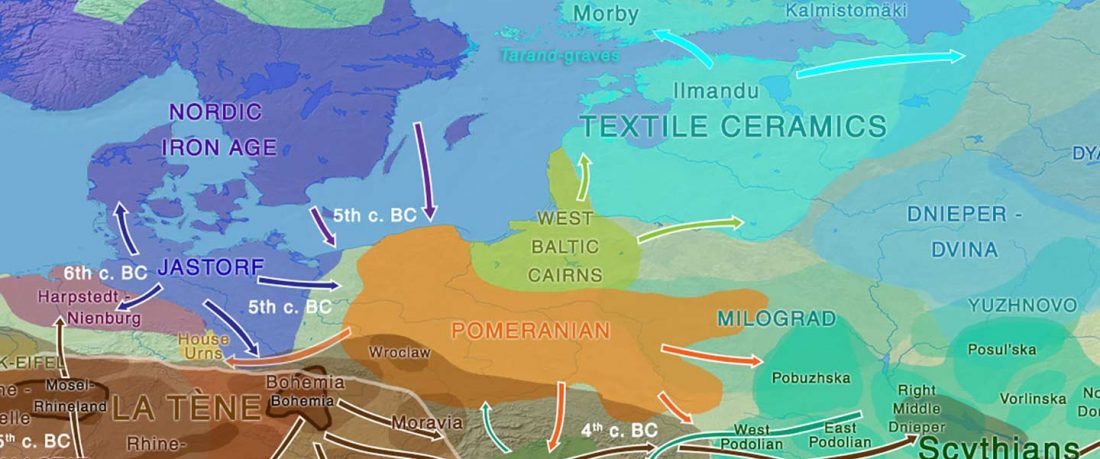
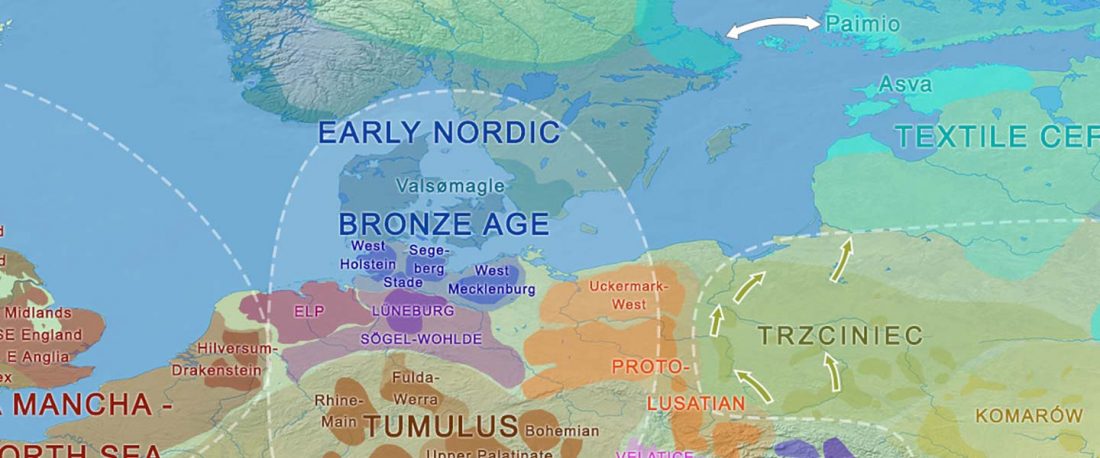
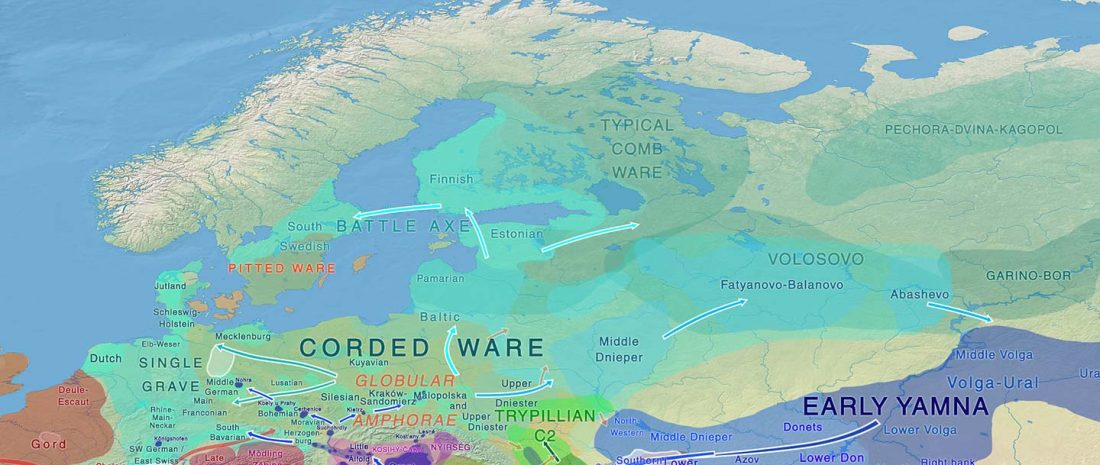
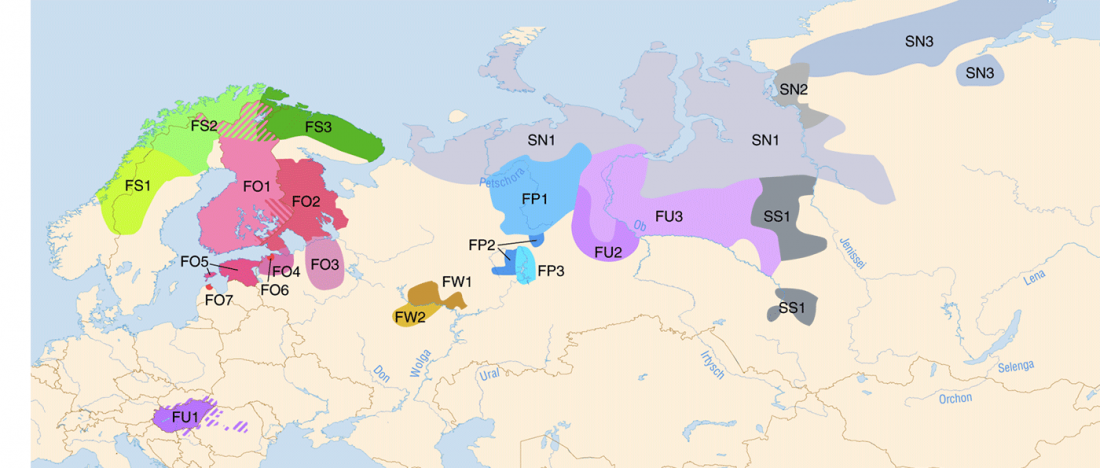
The BAM files from Egfjord et al. (2021) are out, and Y-SNPs of two-year-old Nordic MN_LN/LN migrant Gjerrild 5 (ca. 2284-2035 calBC) were accurately reported, which means that the sample will need to be labelled R1b>L754>L389>(pre-?)V1636, since one derived read Y125110+ (A->G) in this and one ancestral in a Progress2 sample, PG2001, cannot be used to infer anything certain.
NOTE. It has one derived read (A-T) for FT3897 at the R1b>L754>L389>V1636>Y83069 level, but the other 8 SNPs ancestral, which is not really helpful to define a potential pre-Y83069 branch, given the doubts above. A possible relative could … Read the rest “The Last of the Single Gravers”