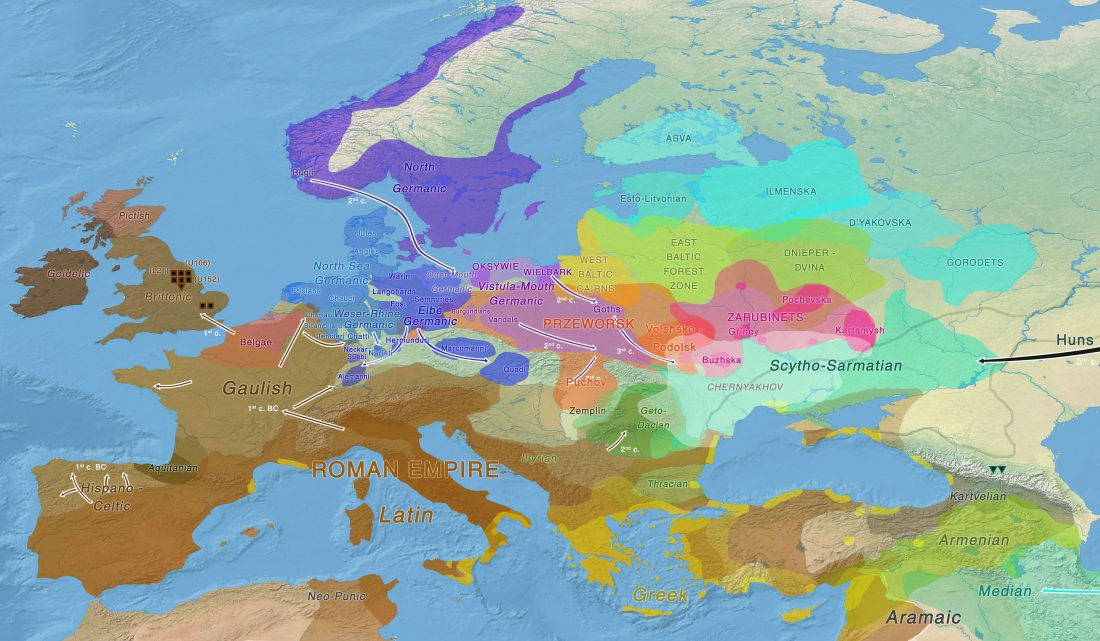
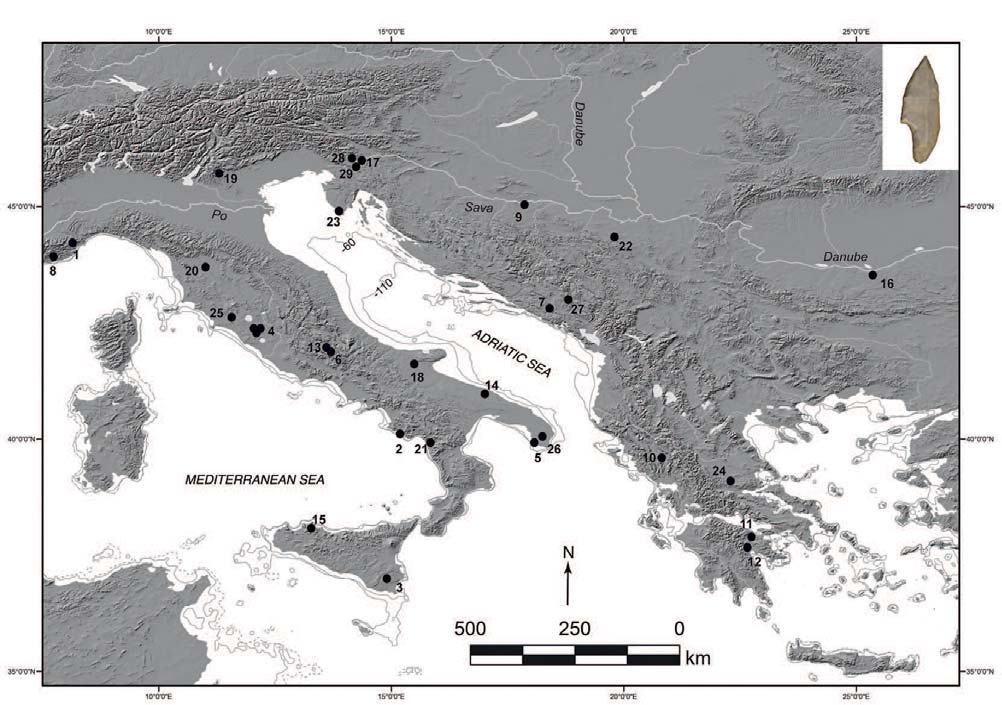
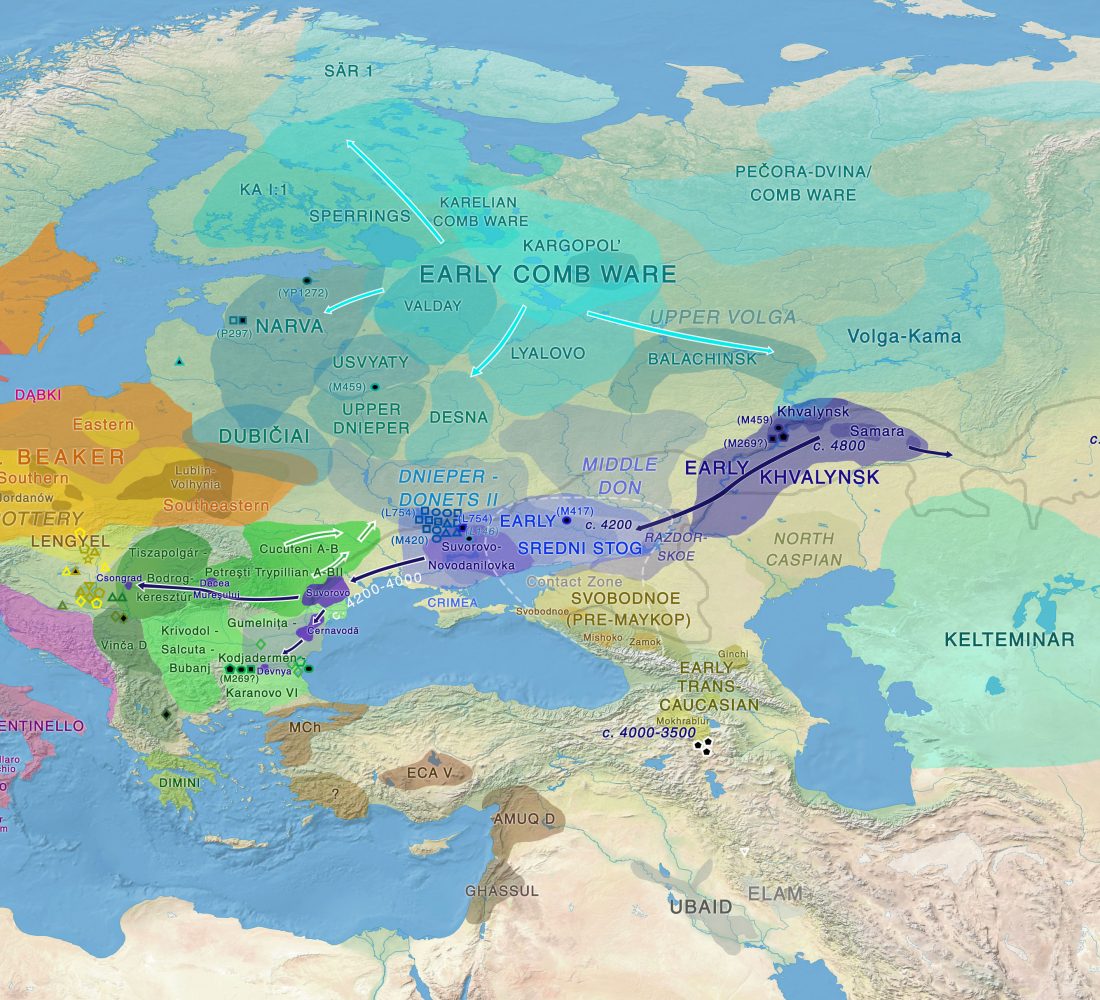
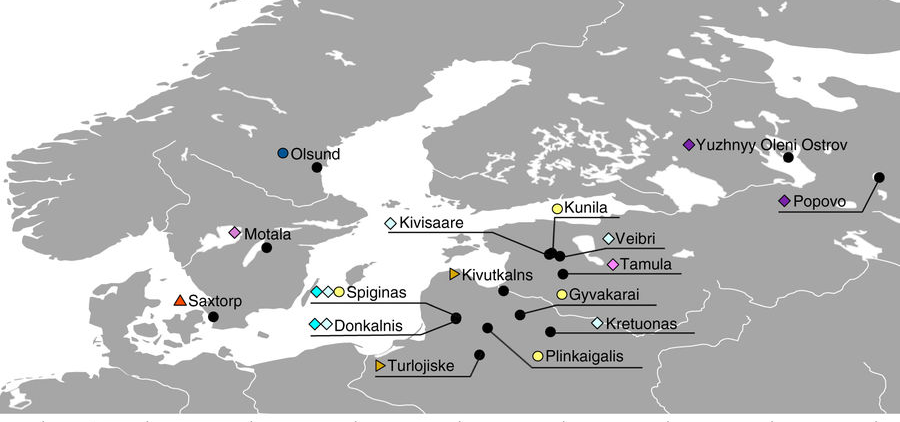
An interesting special issue of the journal Language Evolution has appeared, dedicated to Ancient DNA and language evolution.
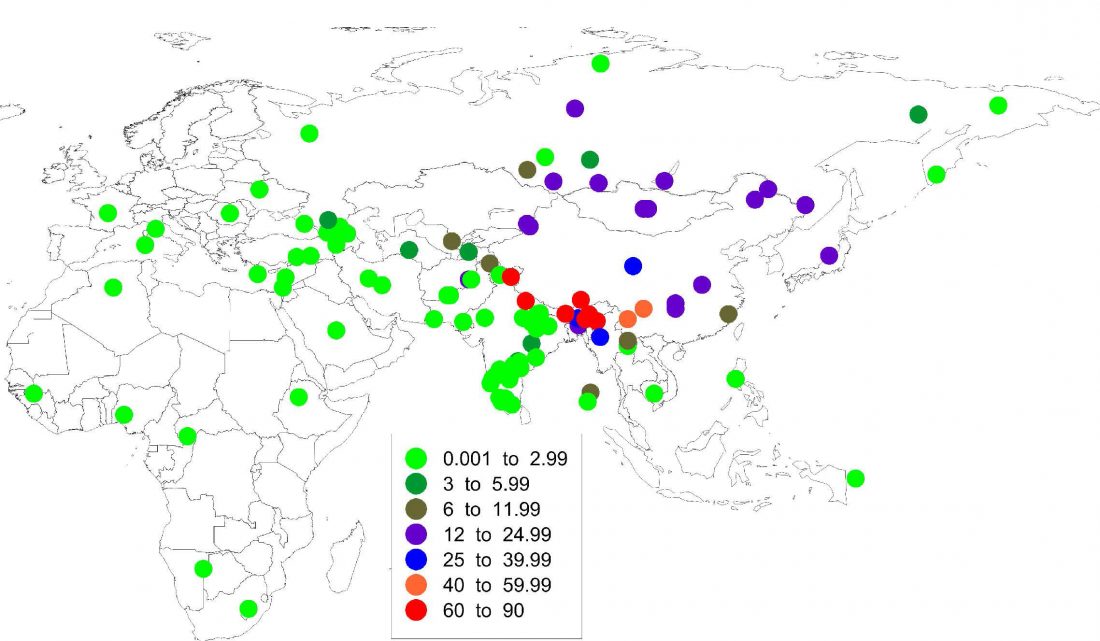
Also, check out the preprint at BioRxiv, Geospatial distributions reflect rates of evolution of features of language, by Kauhanen et al. (2018).
Abstract:
… Read the rest “Language evolution and language change related to ancient DNA”Different structural features of human language change at different rates and thus exhibit different temporal stabilities. Existing methods of linguistic stability estimation depend upon the prior genealogical classification of the world’s languages into language families; these methods result in unreliable stability estimates for features which are sensitive to horizontal transfer between families and whenever data are aggregated