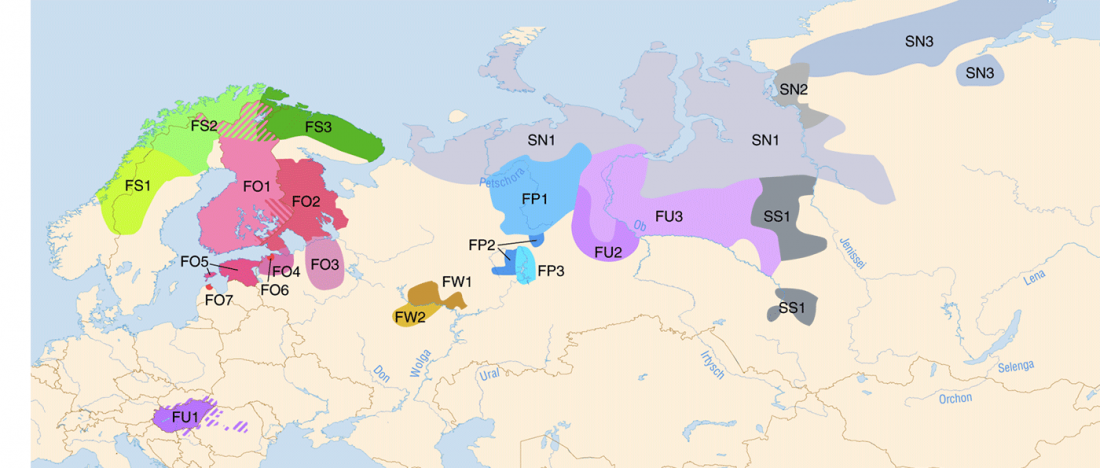
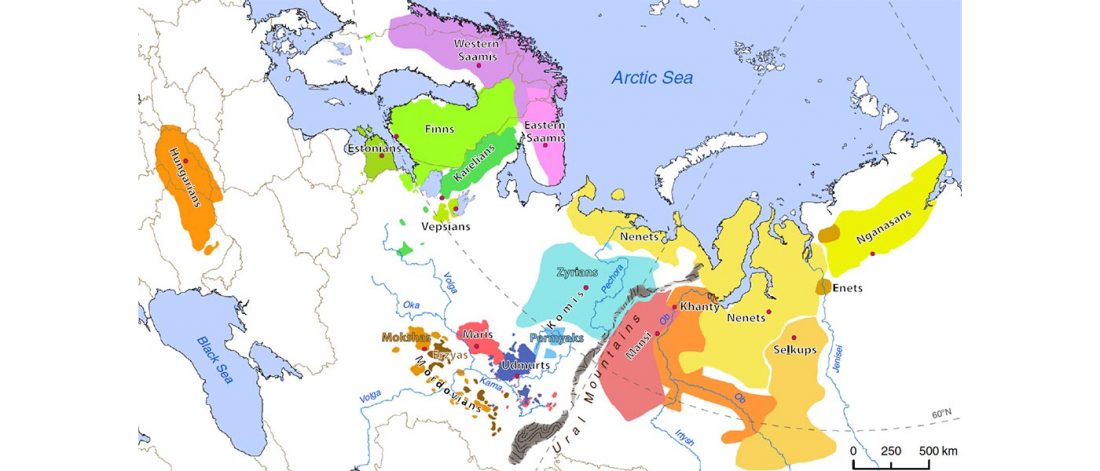
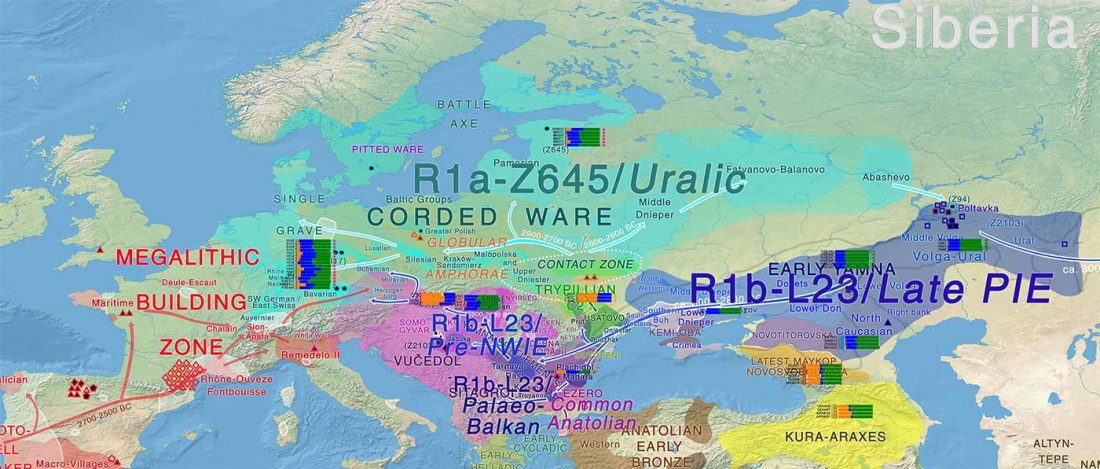
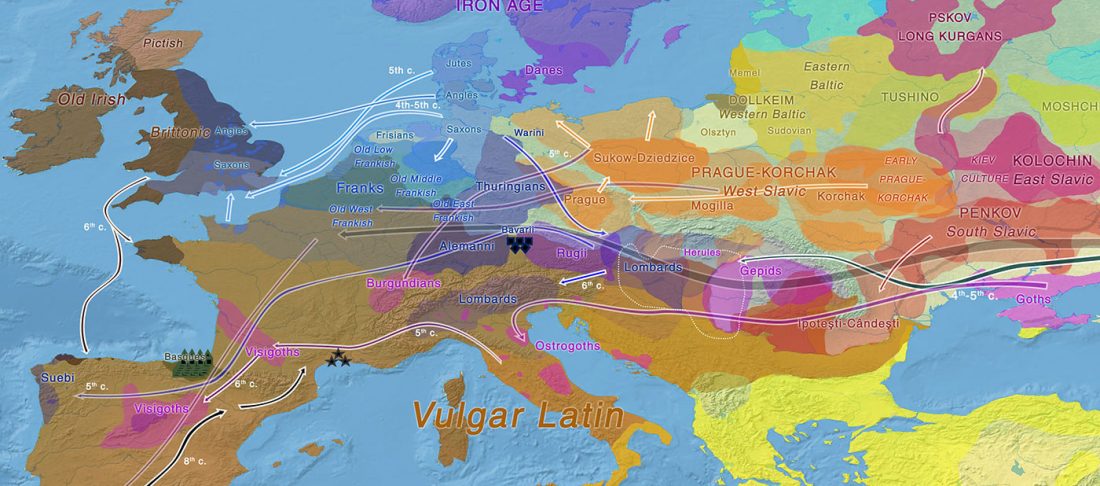
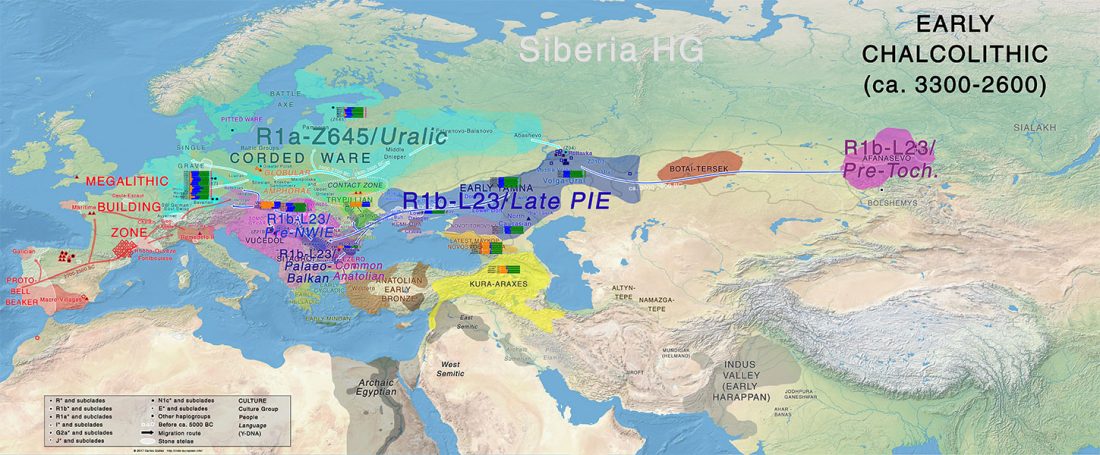
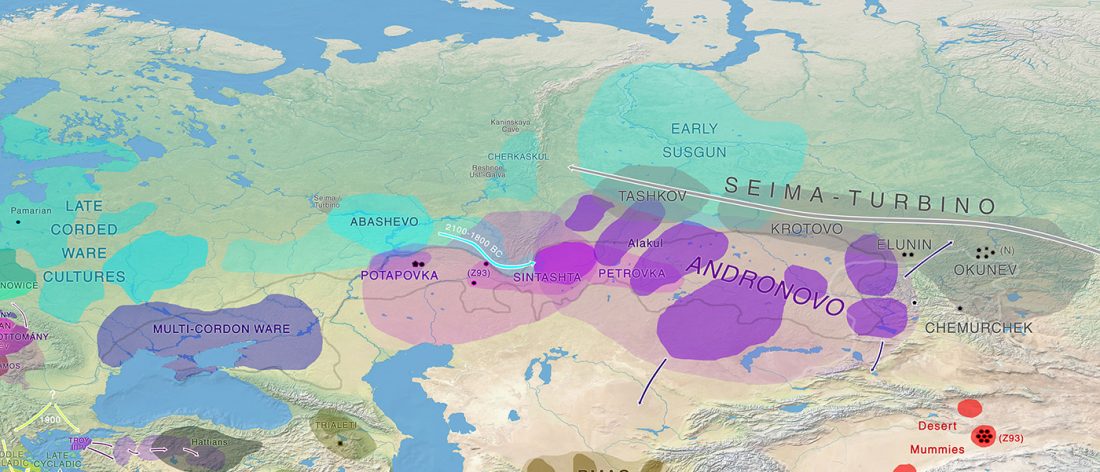
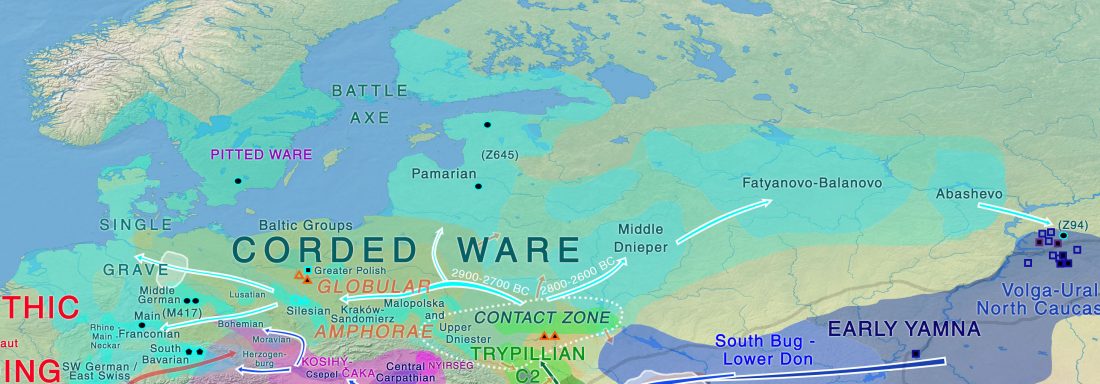
Iron Age bottleneck of the Proto-Fennic population in Estonia
Demographic data and figures derived from Estonian Iron Age graves, by Raili Allmäe, Papers on Anthropology (2018) 27(2).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Introduction
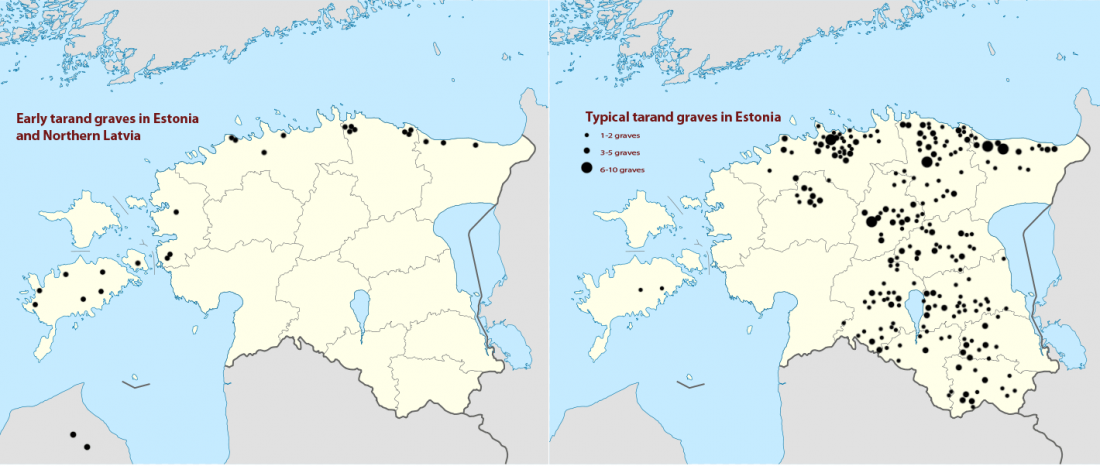
… Read the rest “Iron Age bottleneck of the Proto-Fennic population in Estonia”Inhumation and cremation burials were both common in Iron Age Estonia; however, the pattern which burials were prevalent has regional as well temporal peculiarities. In Estonia, cremation burials appear in the Late Bronze Age (1100–500 BC), for example, in stone-cist graves and ship graves, although inhumation is still characteristic of the period [28, 18]. Cremation burials have occasionally been found beneath the Late Bronze Age cists and the Early Iron Age (500 BC–450 AD) tarand graves