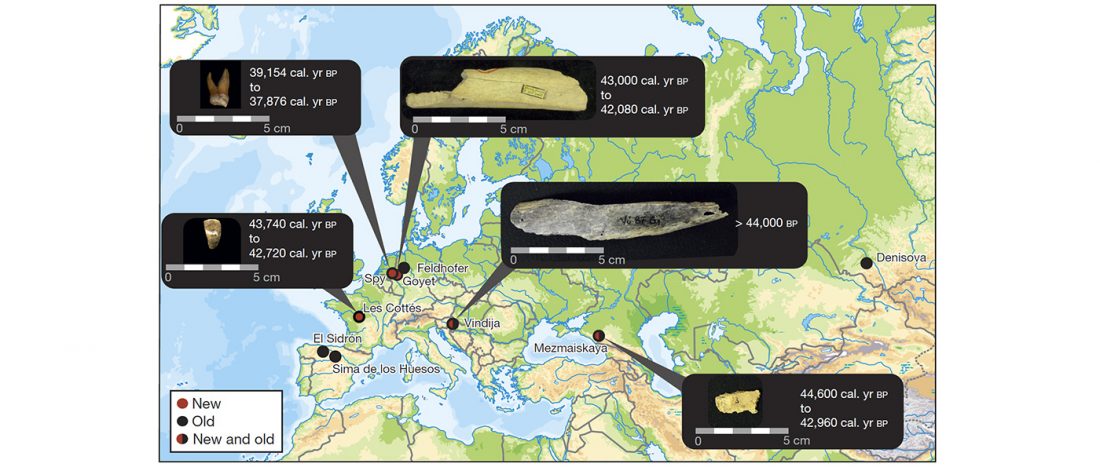
Reconstructing the genetic history of late Neanderthals
New paper (behind paywall) Reconstructing the genetic history of late Neanderthals, by Mateja Hajdinjak, Qiaomei Fu, Alexander Hübner, et al. Nature (2018).
Abstract (edited):
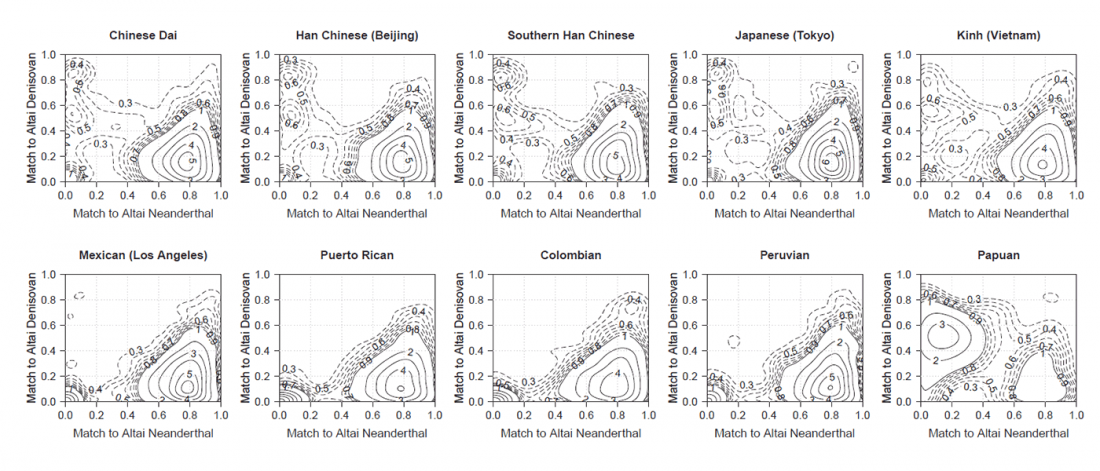
… Read the rest “Reconstructing the genetic history of late Neanderthals”Although it has previously been shown that Neanderthals contributed DNA to modern humans, not much is known about the genetic diversity of Neanderthals or the relationship between late Neanderthal populations at the time at which their last interactions with early modern humans occurred and before they eventually disappeared. Our ability to retrieve DNA from a larger number of Neanderthal individuals has been limited by poor preservation of endogenous DNA and contamination of Neanderthal skeletal remains