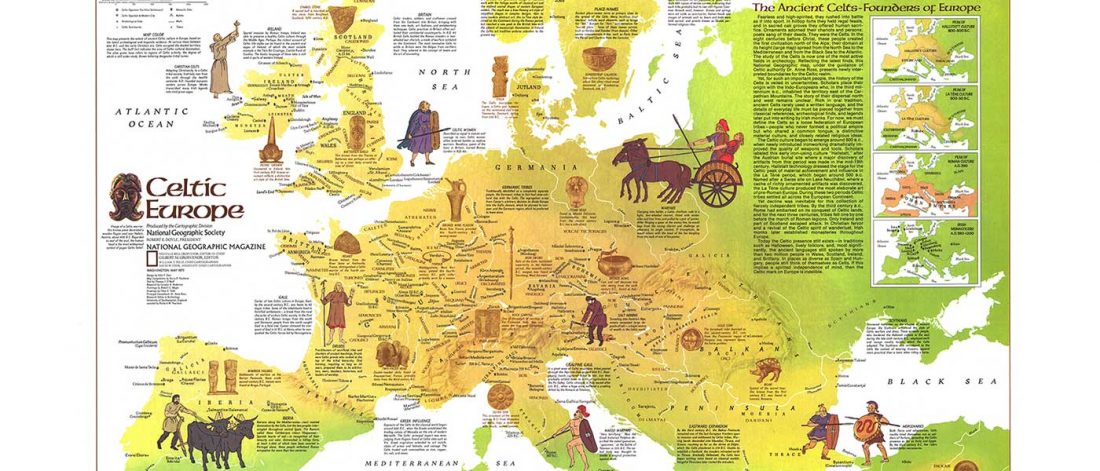
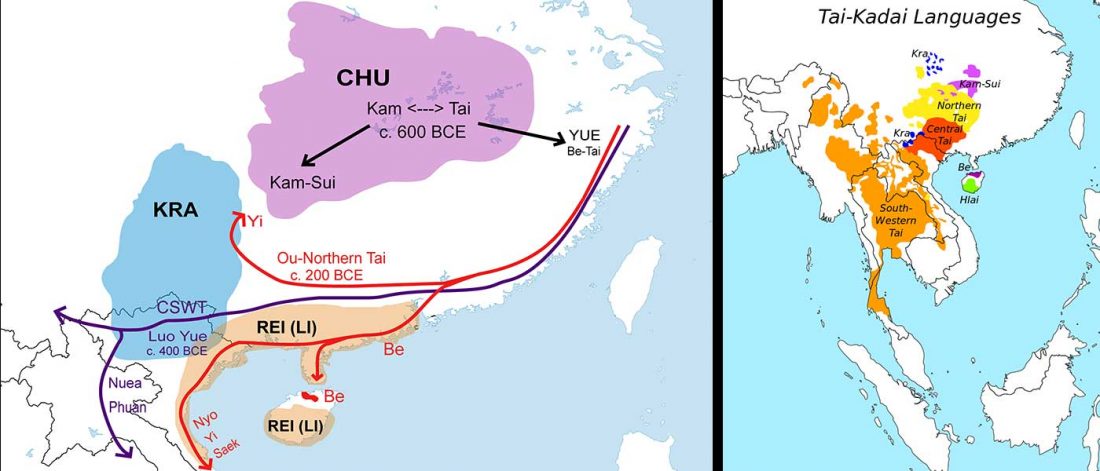
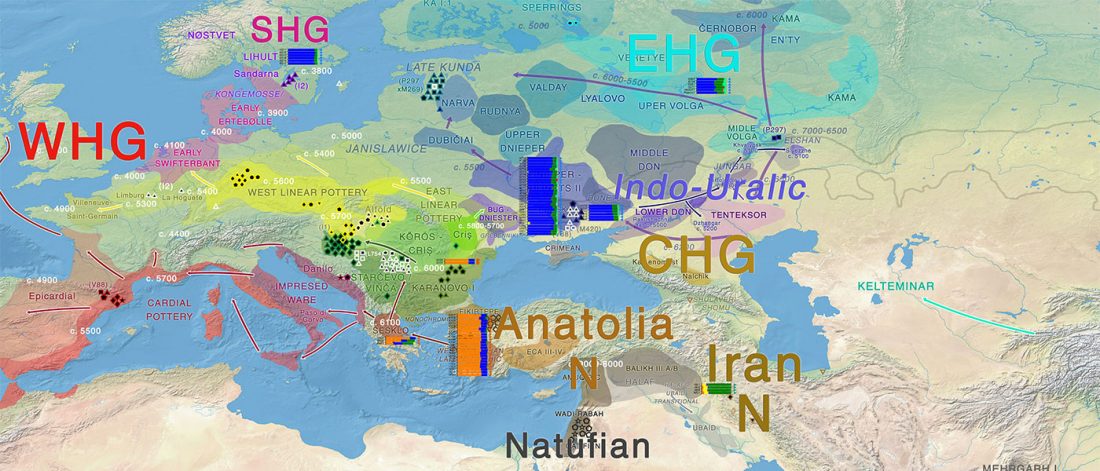
On Latin, Turkic, and Celtic – likely stories of mixed societies and little genetic impact
Recent article on The Conversation, The Roman dead: new techniques are revealing just how diverse Roman Britain was, about the paper (behind paywall) A Novel Investigation into Migrant and Local Health-Statuses in the Past: A Case Study from Roman Britain, by Redfern et al. Bioarchaeology International (2018), among others.
Interesting excerpts about Roman London:
… Read the rest “On Latin, Turkic, and Celtic – likely stories of mixed societies and little genetic impact”We have discovered, for example, that one middle-aged woman from the southern Mediterranean has black African ancestry. She was buried in Southwark with pottery from Kent and a fourth century local coin – her burial expresses British connections, reflecting how people’s communities and lives