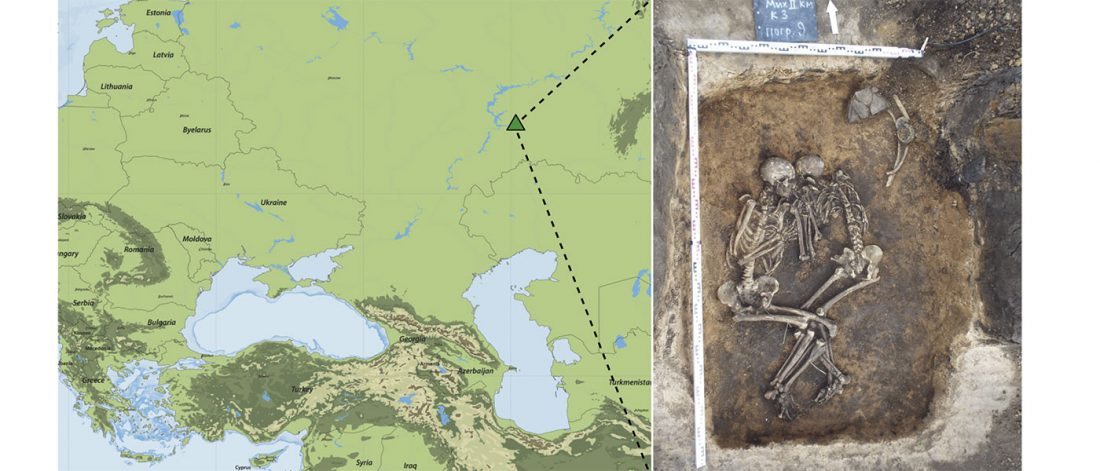
Canid Y-chromosome phylogeny reveals distinct haplogroups among Neolithic European dogs
Open access Analysis of the canid Y-chromosome phylogeny using short-read sequencing data reveals the presence of distinct haplogroups among Neolithic European dogs, by Oetjens et al., BMC Genomics (2018) 19:350.
Interesting excerpts (modified for clarity, emphasis mine):
Introduction
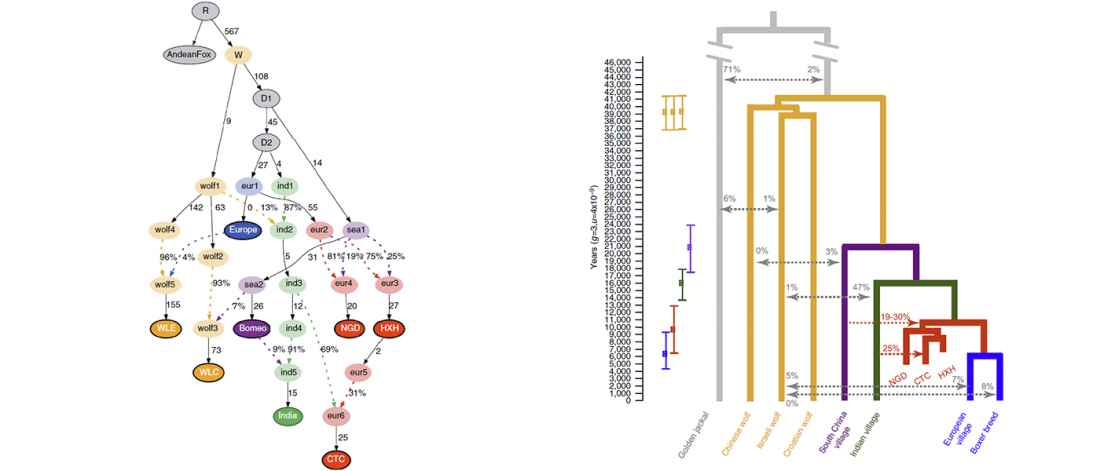
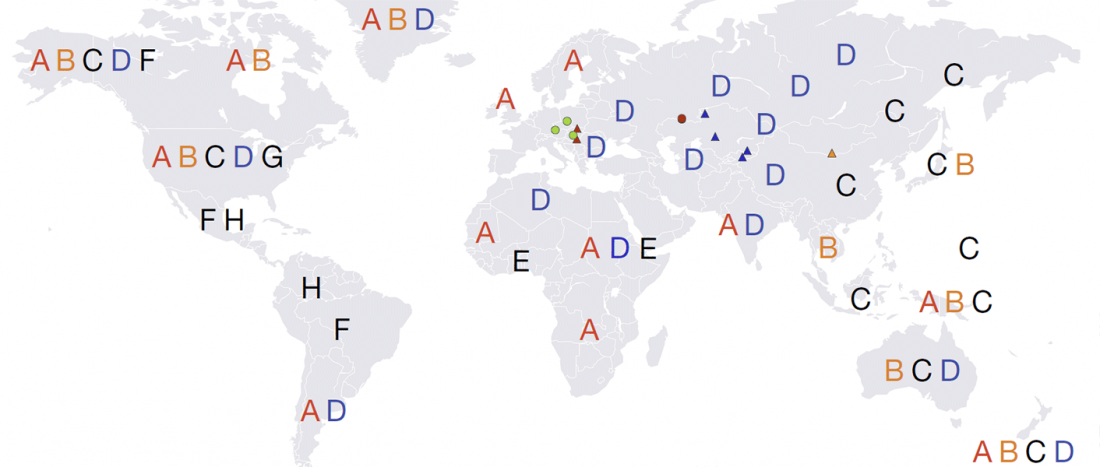
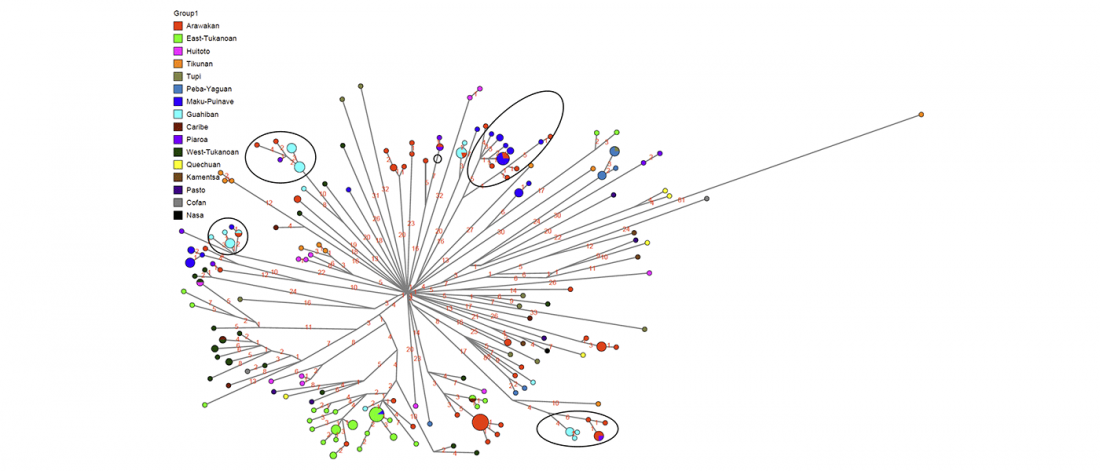
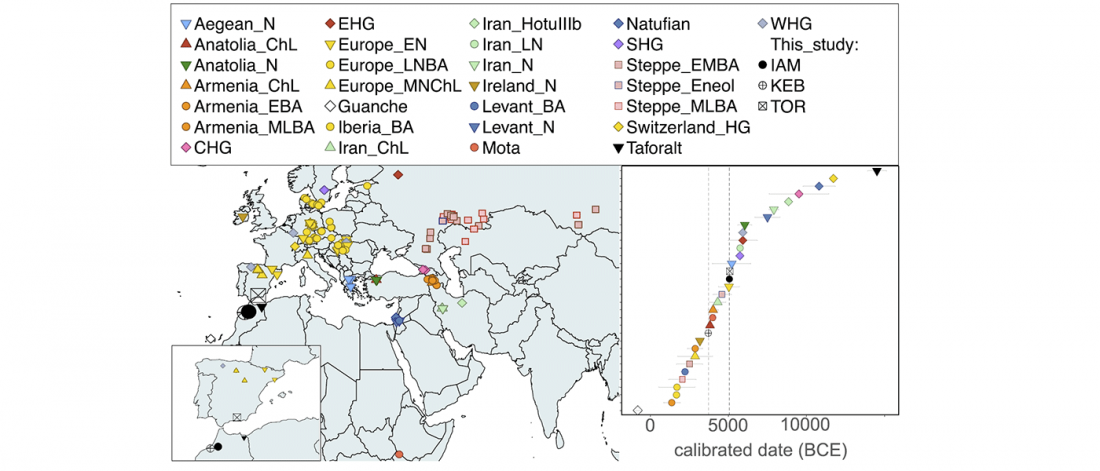
… Read the rest “Canid Y-chromosome phylogeny reveals distinct haplogroups among Neolithic European dogs”Canid mitochondrial phylogenies show that dogs and wolves are not reciprocally monophyletic. The mitochondrial tree contains four deeply rooted clades encompassing dogs and many grey wolf groups. These four clades form the basis of dog mitochondrial haplogroup assignment, known as haplogroups A-D. The time of the most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) of haplogroups A-D significantly predates estimates for domestication based on