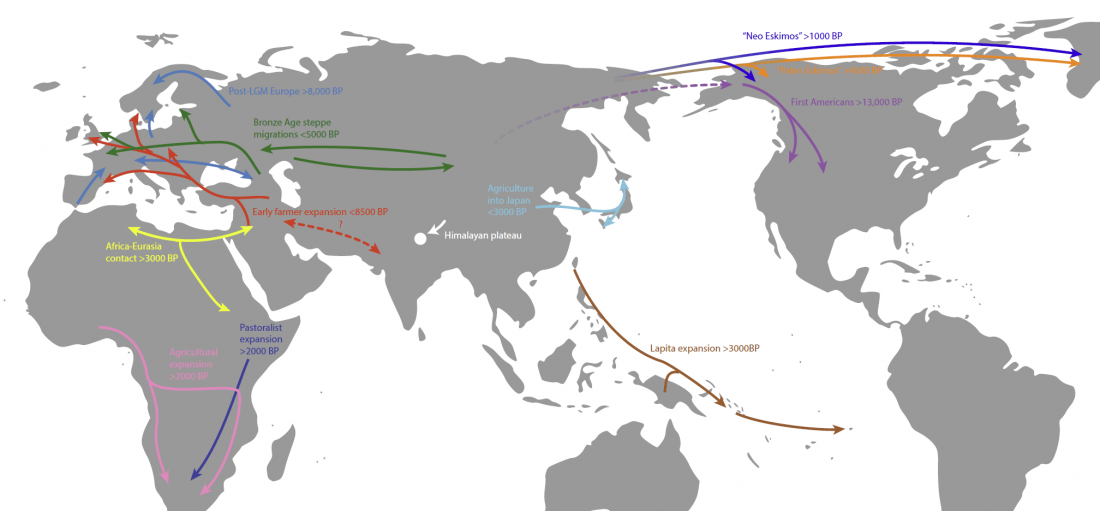
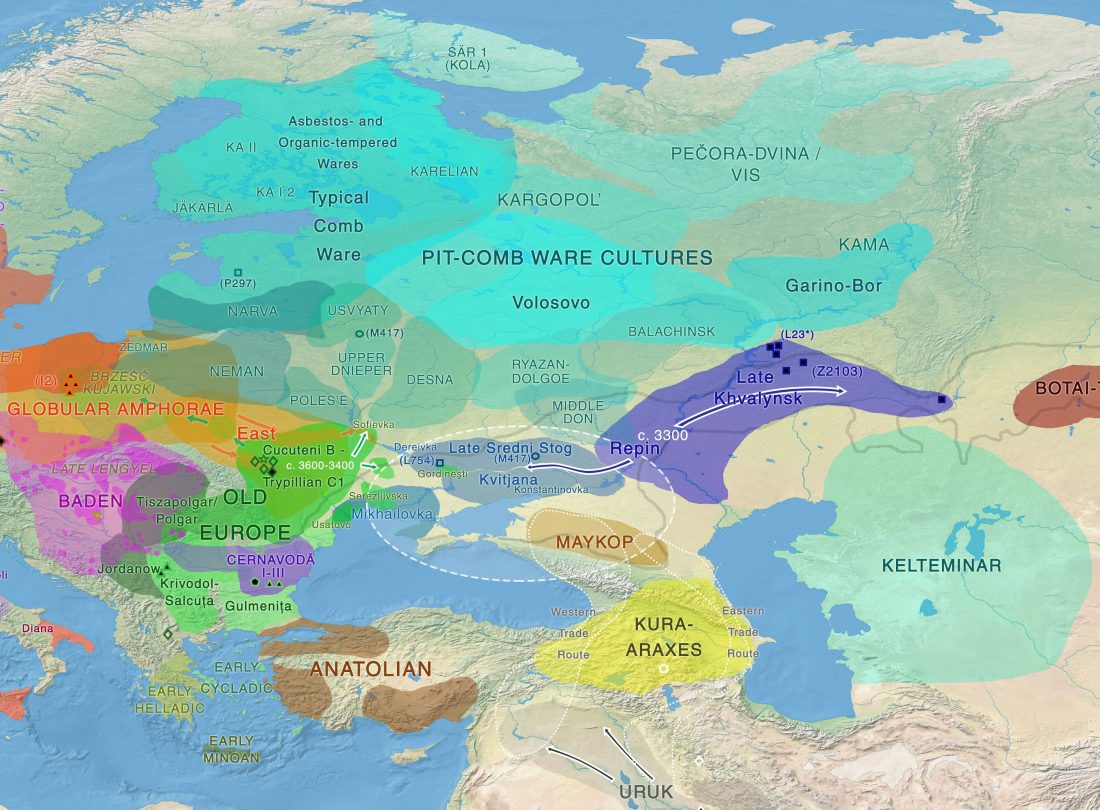
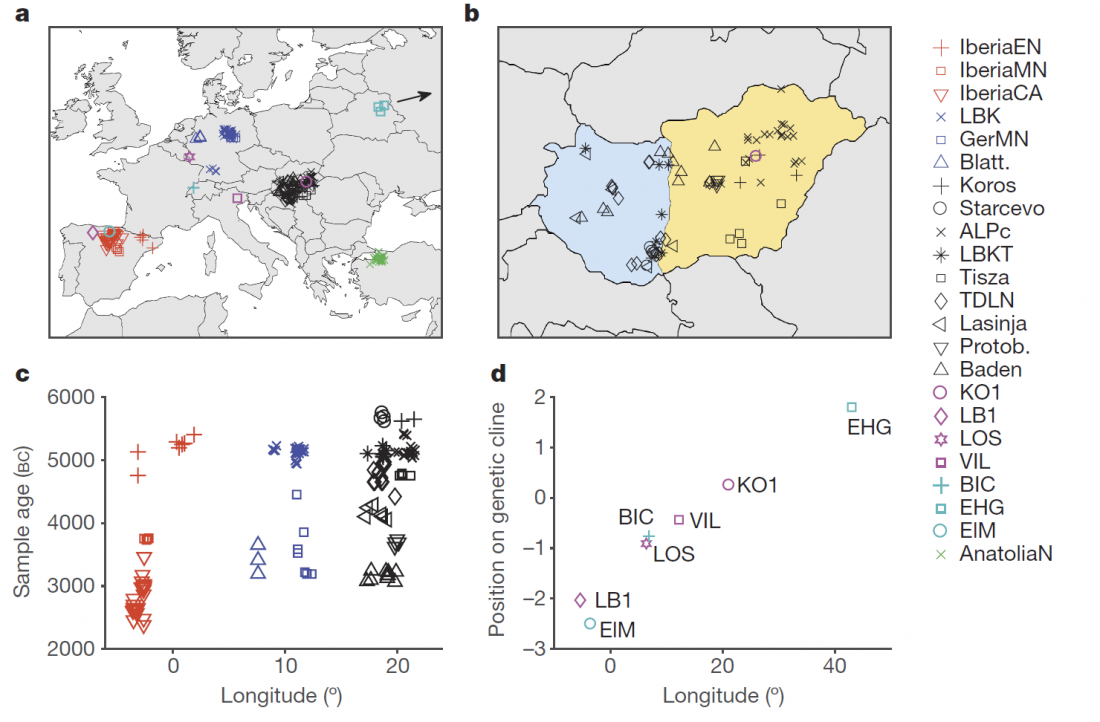
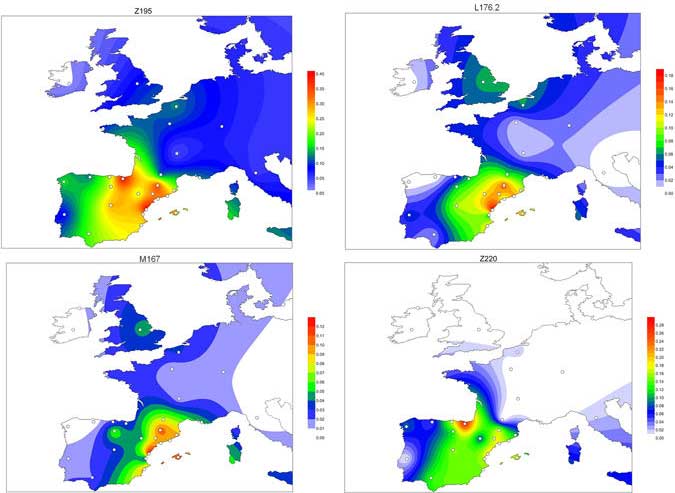
Open access research highlight A history of male migration in and out of the Green Sahara, by Yali Xue, Genome Biology (2018) 19:30, on the recent paper by D’Atanasio et al.
Insights from the Green Saharan Y-chromosomal findings (emphasis mine):
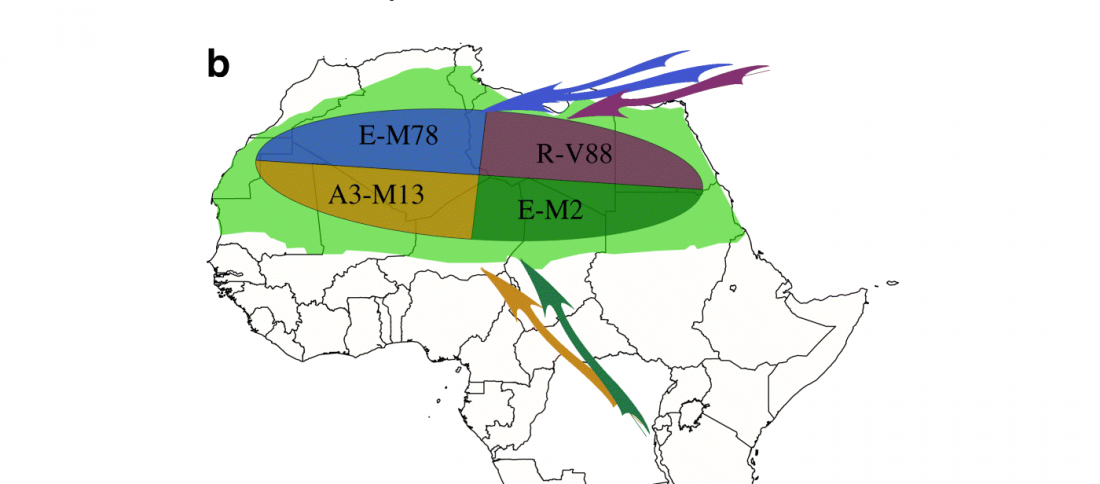
… Read the rest “A history of male migration in and out of the Green Sahara”It is widely accepted that sub-Saharan Y chromosomes are dominated by E-M2 lineages carried by Bantu-speaking farmers as they expanded from West Africa starting < 5 kya, reaching South Africa within recent centuries [4]. The E-M2-Bantu lineages lie phylogenetically within the E-M2-Green Sahara lineage and show at least three explosive lineage expansions beginning 4.9–5.3 kya [5] (Fig. 1a). These events of