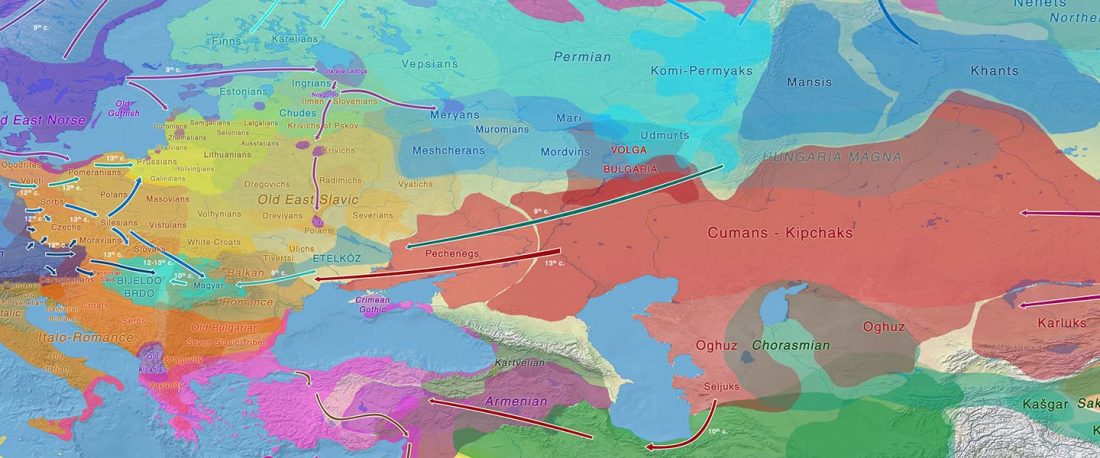
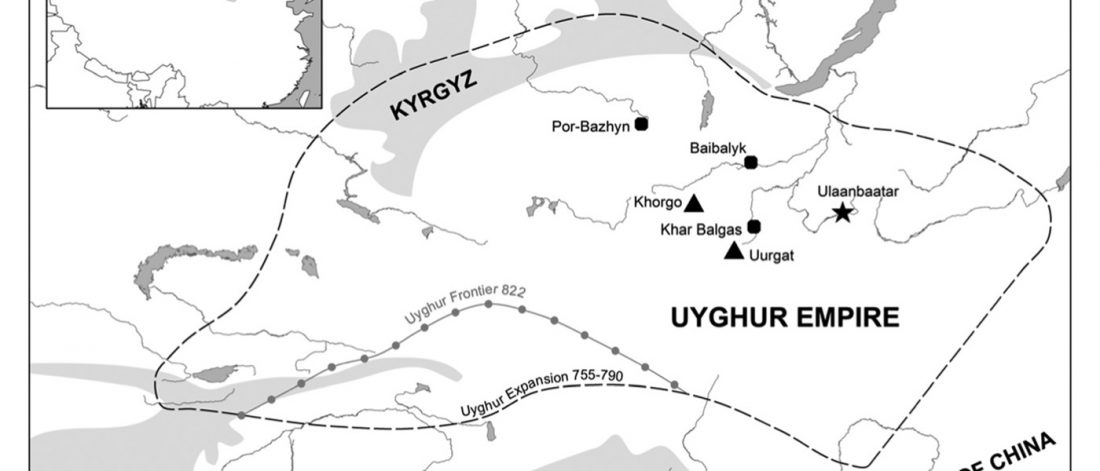
As I said 6 months ago, 2019 is a tough year to write a blog, because this was going to be a complex regional election year and therefore a time of political promises, hence tenure offers too. Now the preliminary offers have been made, elections have passed, but the timing has slightly shifted toward 2020. So I may have the time, but not really any benefit of dedicating too much effort to the blog, and a lot of potential benefit of dedicating any time to evaluable scientific work.
On the other hand, I saw some potential benefit for … Read the rest “A Song of Sheep and Horses, revised edition, now available as printed books”