New preprint by the Jena-Reich labs, The Genomic Formation of Human Populations in East Asia, by Wang et al. bioRxiv (2020).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
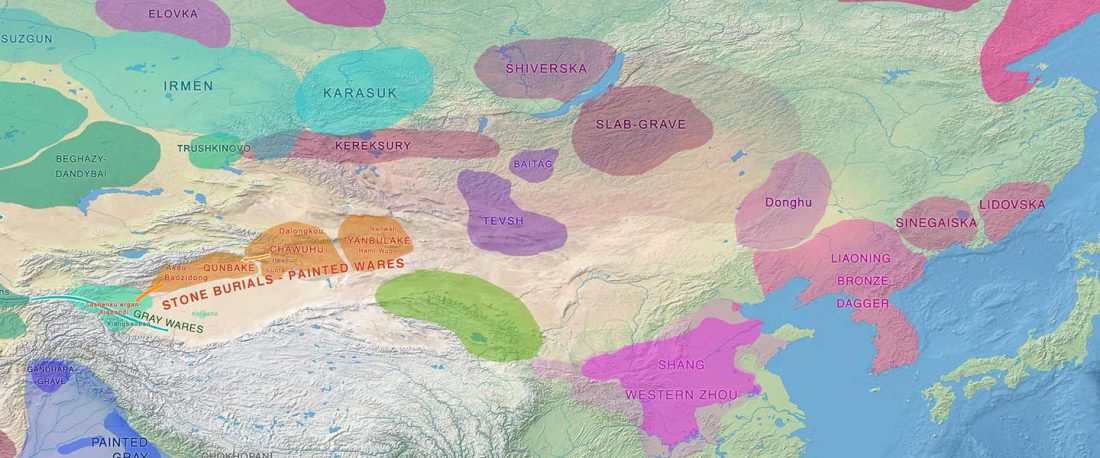
Mongolia Neolithic cluster
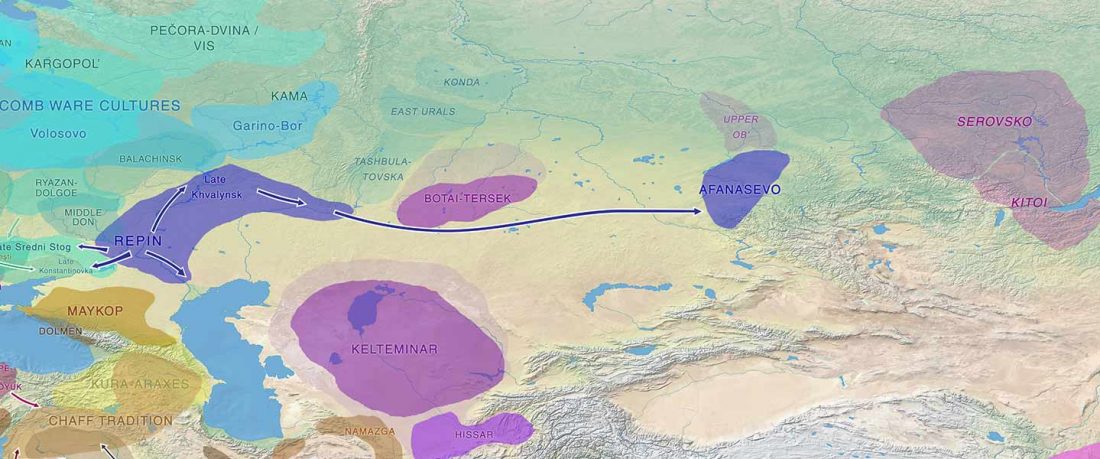
… Read the rest “Yamnaya-like Chemurchek links Afanasievo with Iron Age Tocharians”The three most ancient individuals of the Mongolia ‘East’ cluster are from the Kherlen River region of eastern Mongolia (Tamsag-Bulag culture) and date to 6000-4300 BCE (this places them in the Early Neolithic period, which in Northeast Asia is defined by the use of pottery and not by agriculture). These individuals are genetically similar to previously reported Neolithic individuals from the cis-Baikal region and have minimal evidence of West Eurasian-related admixture