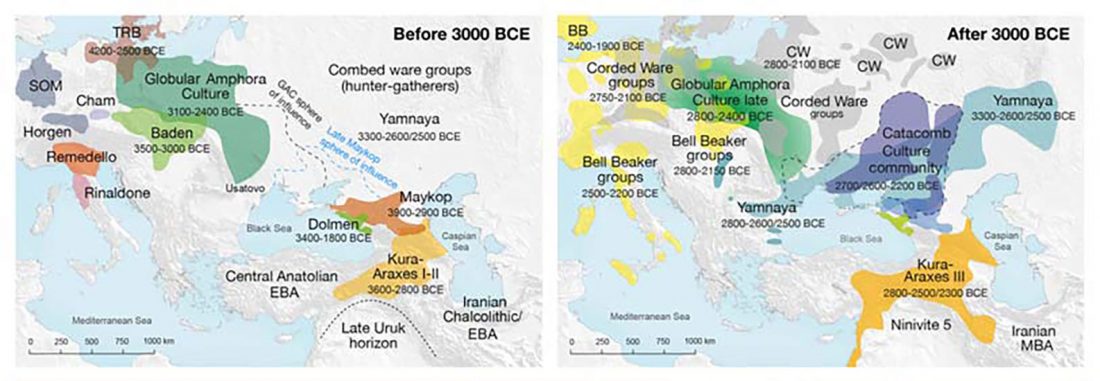
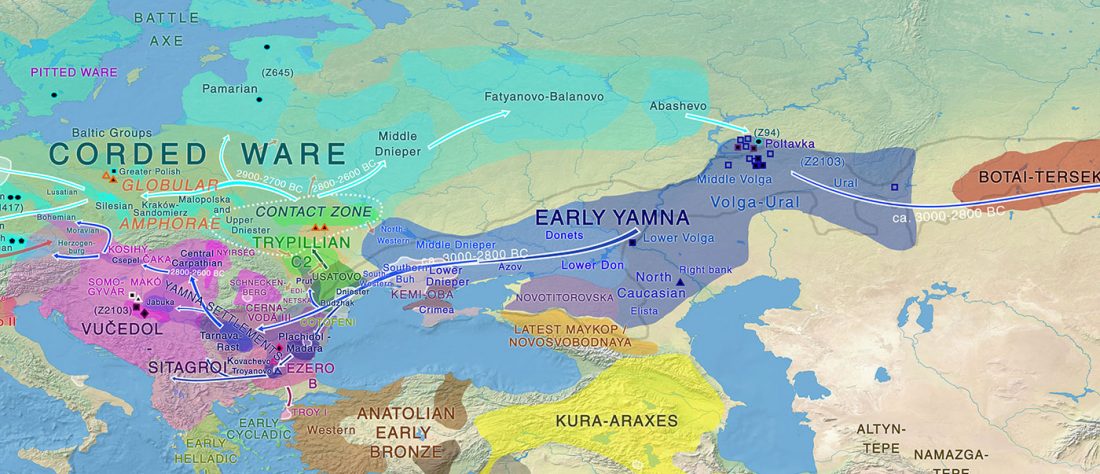
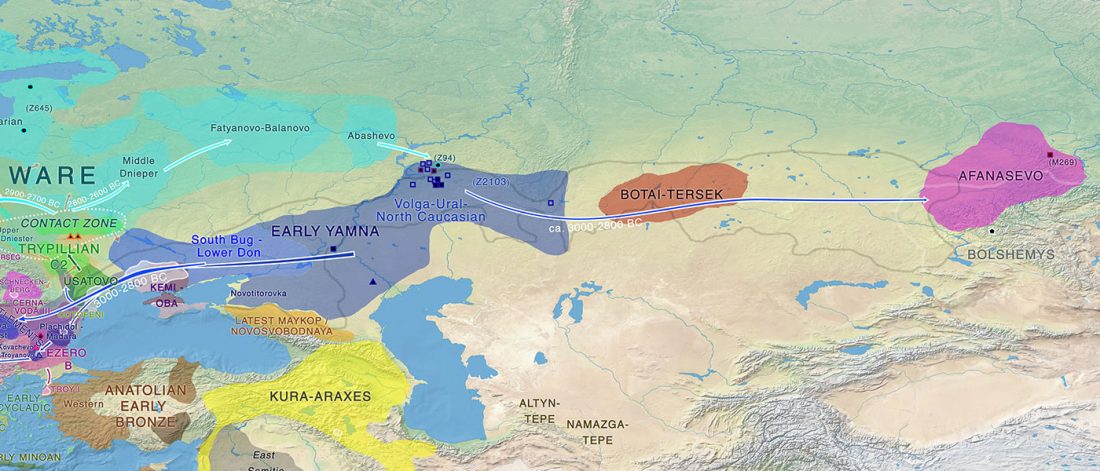
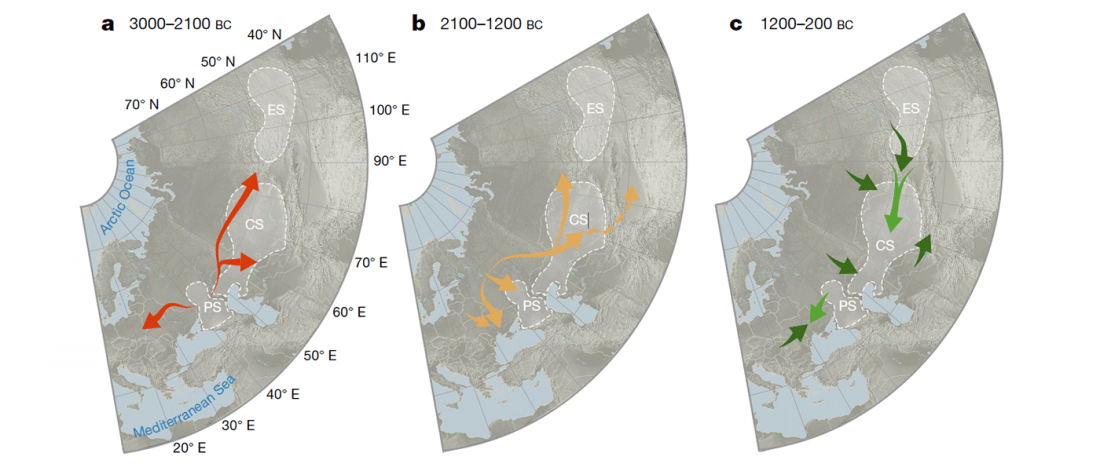
Open access The genetic prehistory of the Greater Caucasus, by Wang et al. bioRxiv (2018).
The Caucasus Mountains as a prehistoric barrier
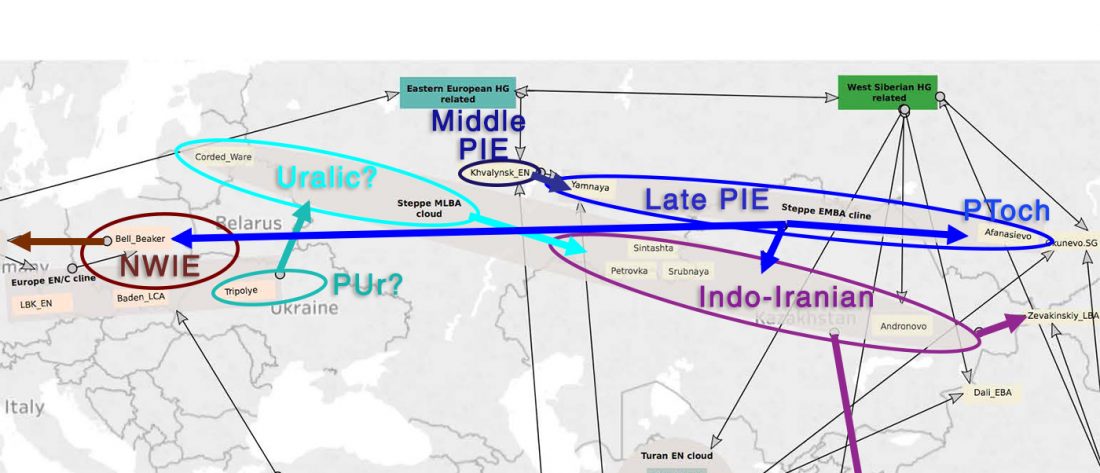
I think the essential message we can extract from the paper is that the Caucasus was a long-lasting cultural and genetic barrier, although (obviously) it was not insurmontable.
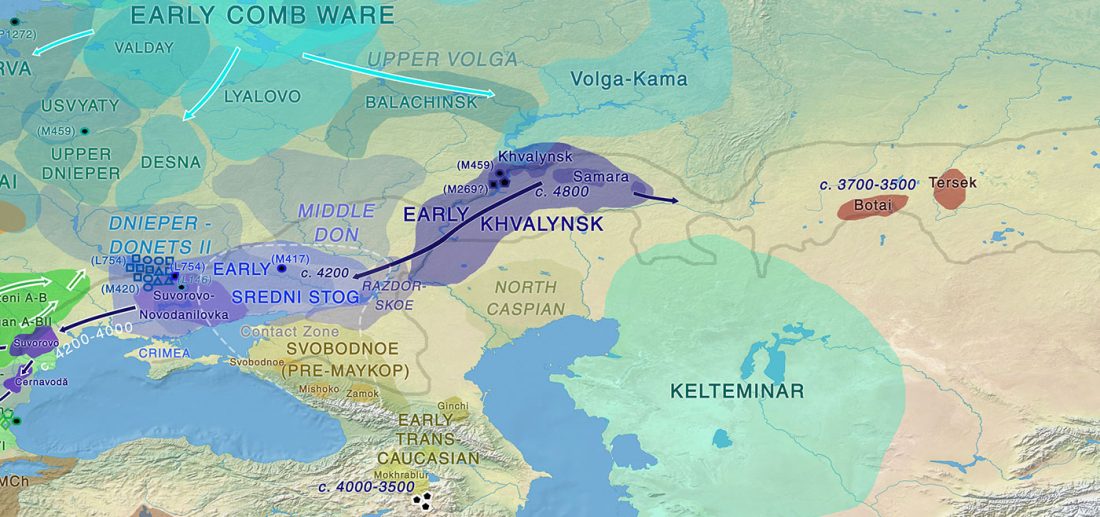
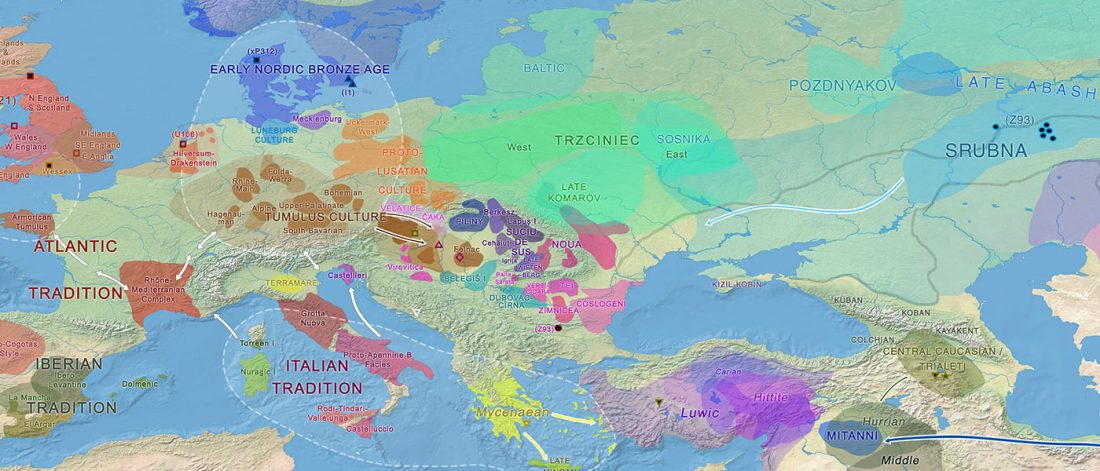
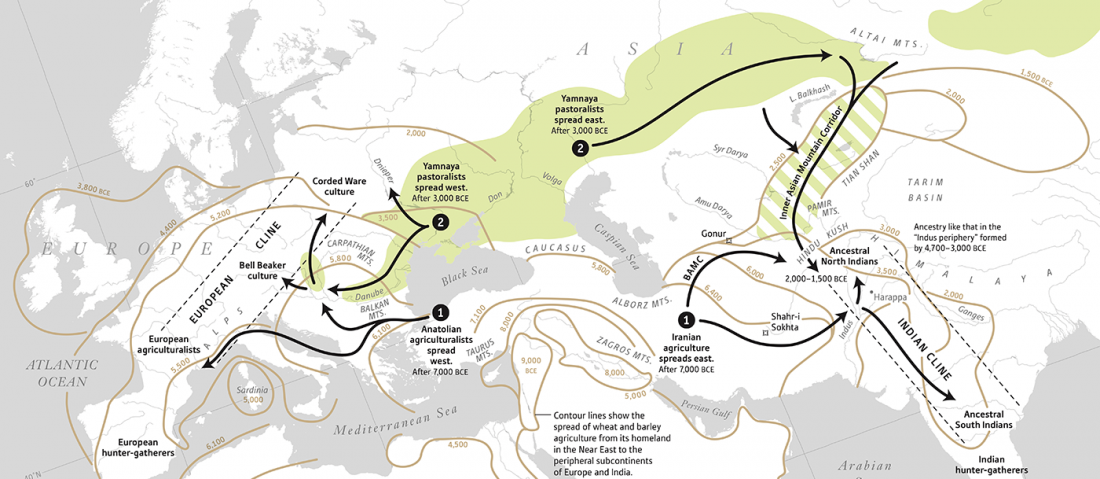
… Read the rest “The Caucasus a genetic and cultural barrier; Yamna dominated by R1b-M269; Yamna settlers in Hungary cluster with Yamna”Our results show that at the time of the eponymous grave mound of Maykop, the North Caucasus piedmont region was genetically connected to the south. Even without direct ancient DNA data from northern Mesopotamia, the new genetic evidence suggests an increased assimilation of Chalcolithic individuals from Iran, Anatolia