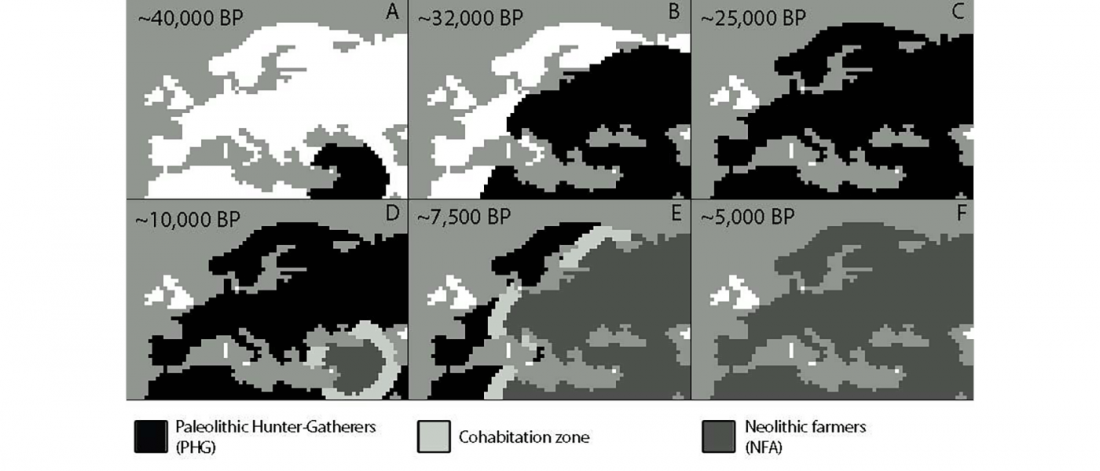
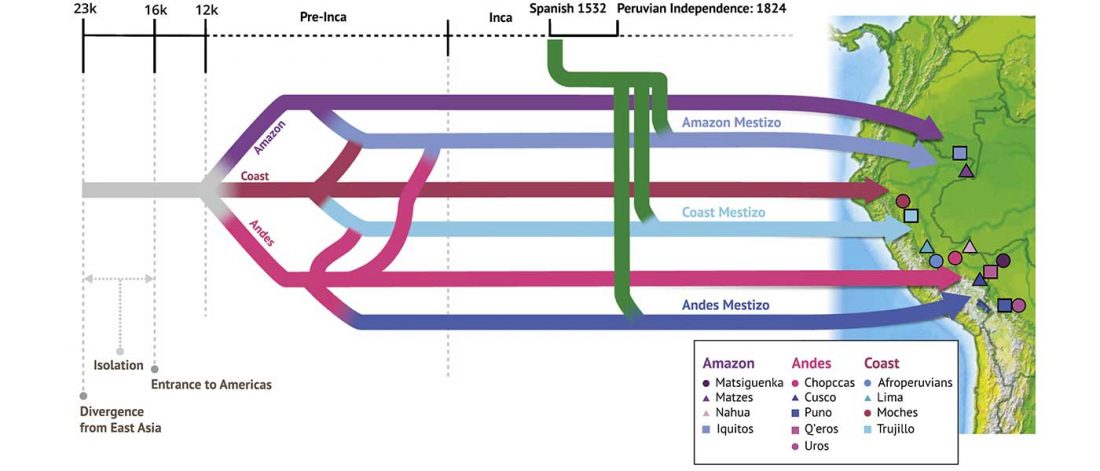
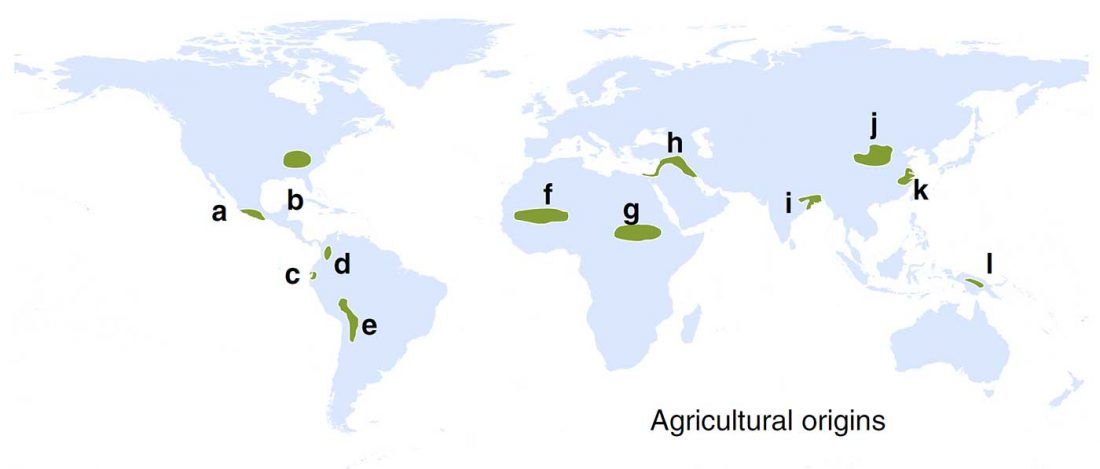
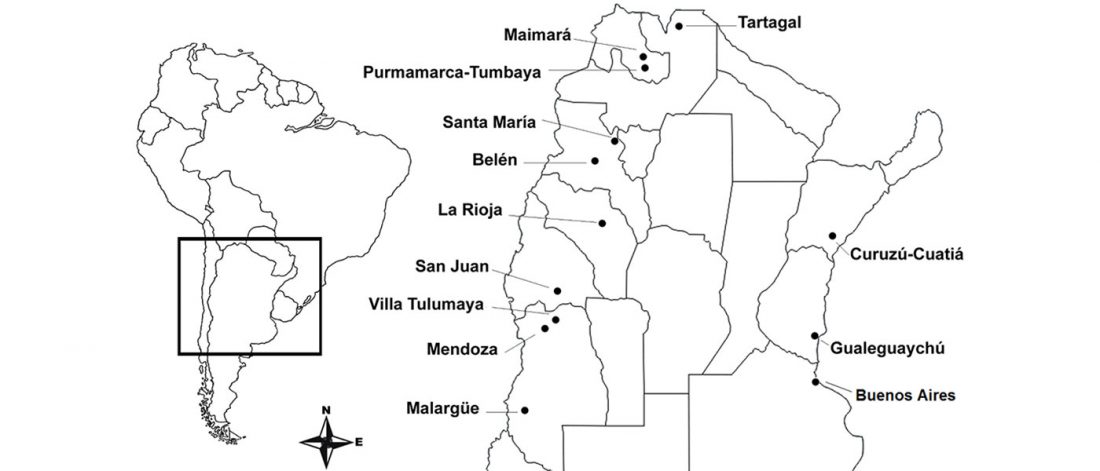
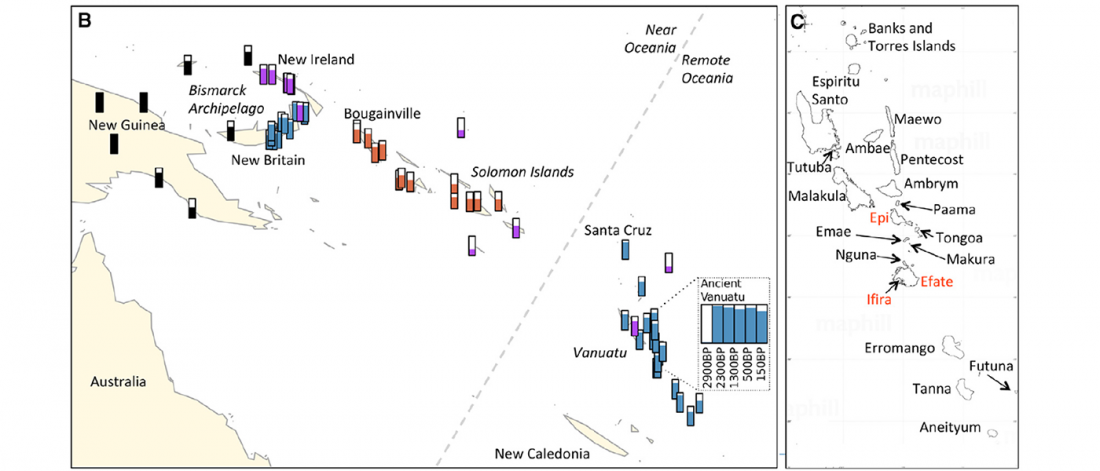
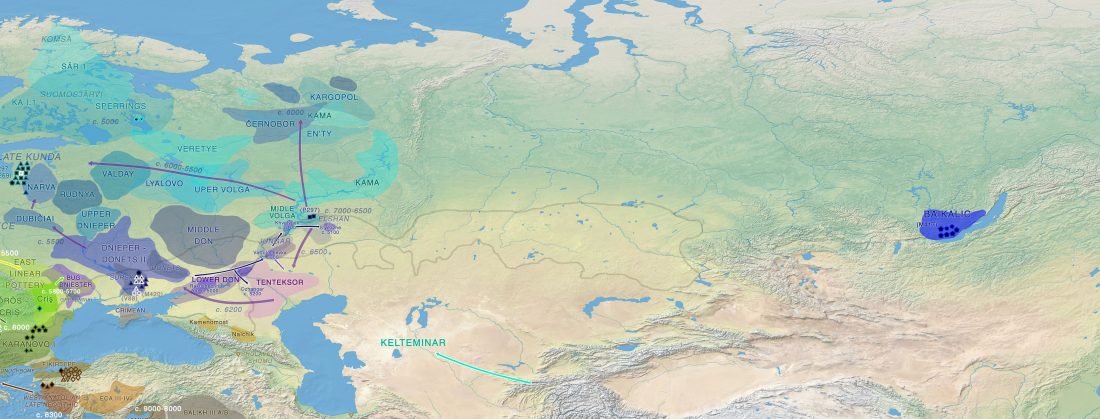
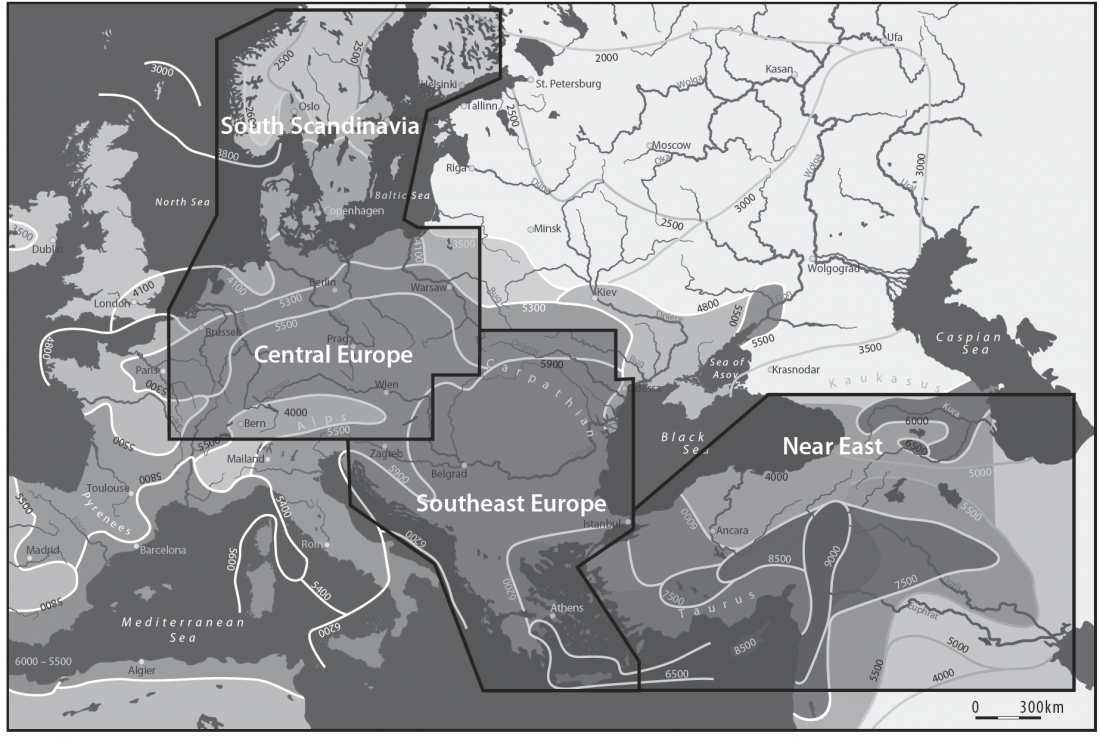
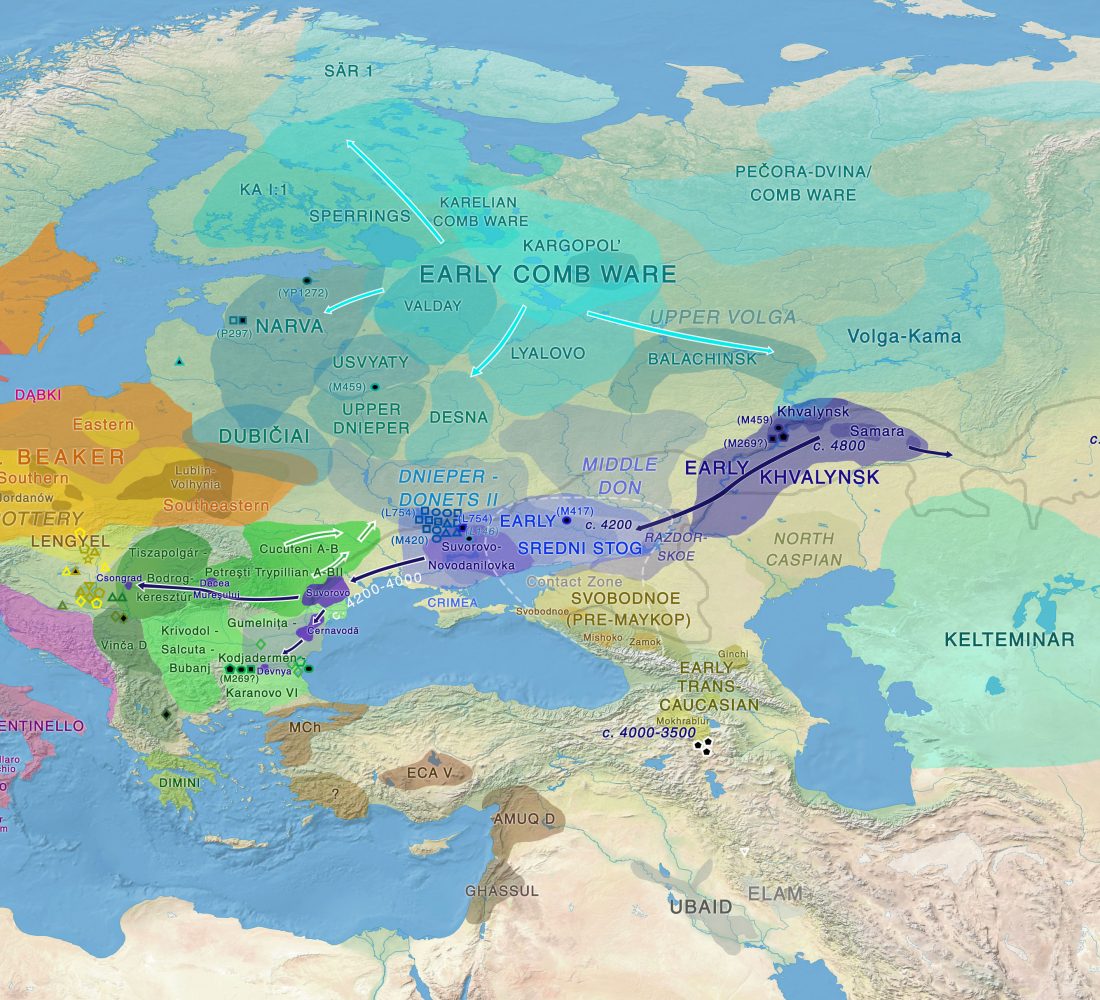
Open access Evolutionary genomic dynamics of Peruvians before, during, and after the Inca Empire by Harris et al., PNAS (2018) 201720798 (published ahead of print).
Abstract (emphasis mine):
… Read the rest “Inca and Spanish Empires had a profound impact on Peruvian demography”Native Americans from the Amazon, Andes, and coastal geographic regions of South America have a rich cultural heritage but are genetically understudied, therefore leading to gaps in our knowledge of their genomic architecture and demographic history. In this study, we sequence 150 genomes to high coverage combined with an additional 130 genotype array samples from Native American and mestizo populations in Peru. The majority of our samples possess greater than 90% Native