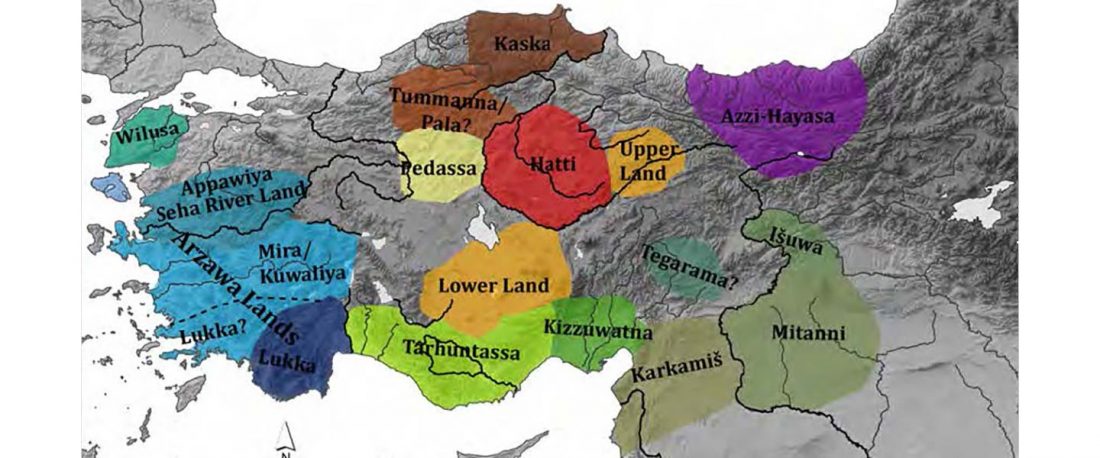
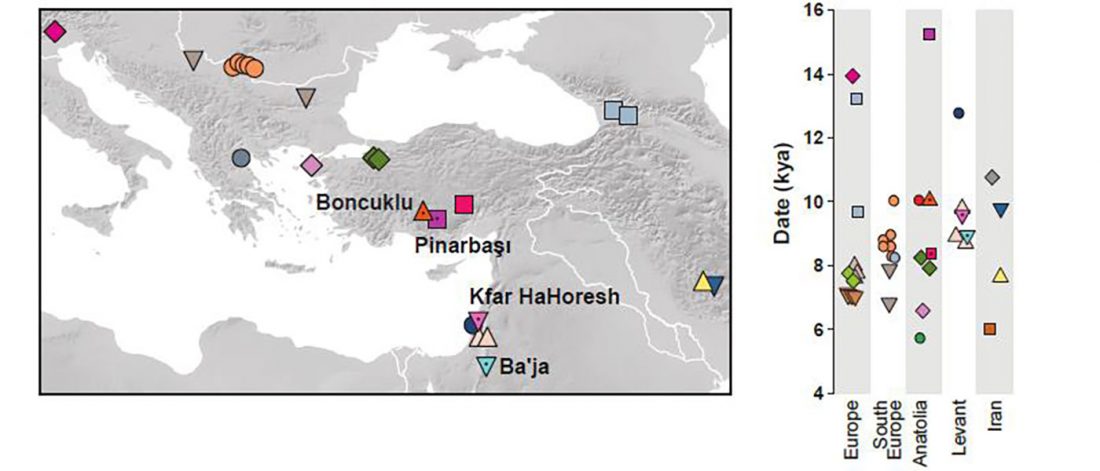
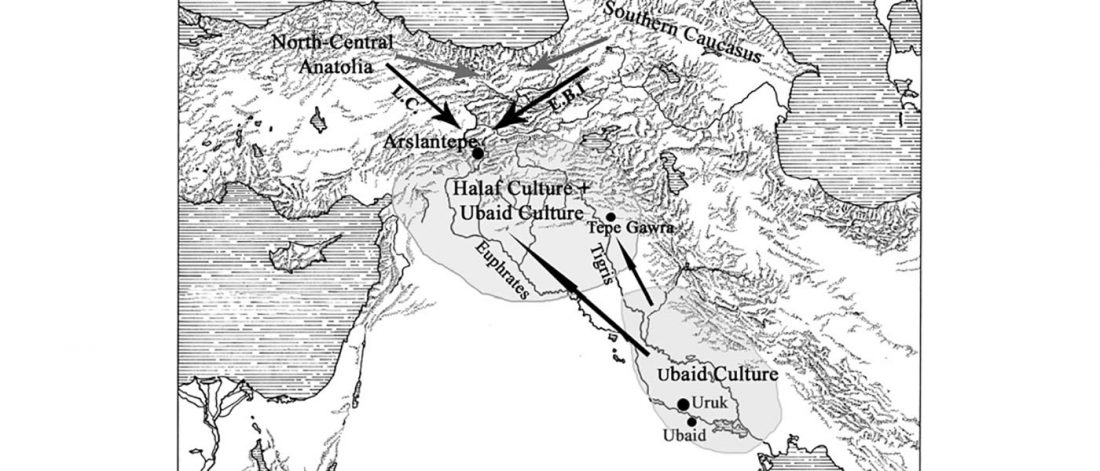
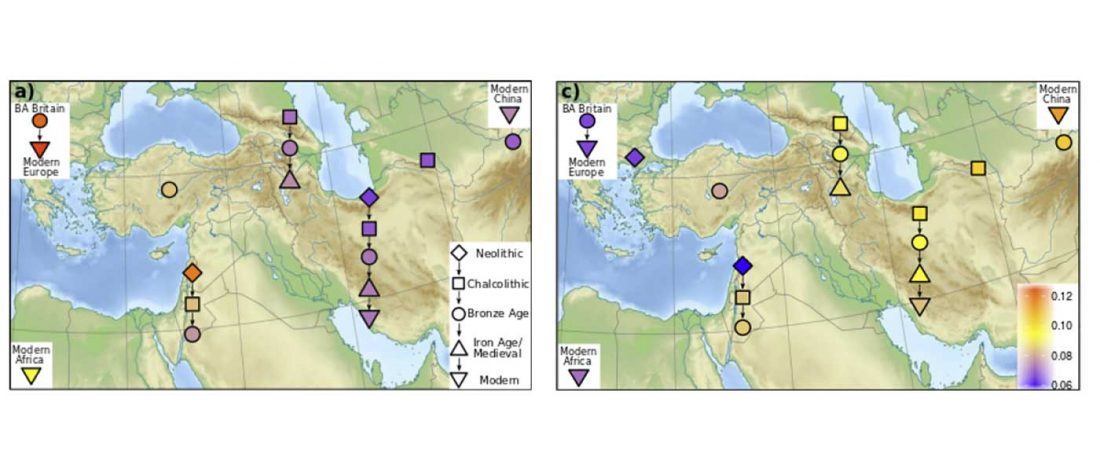
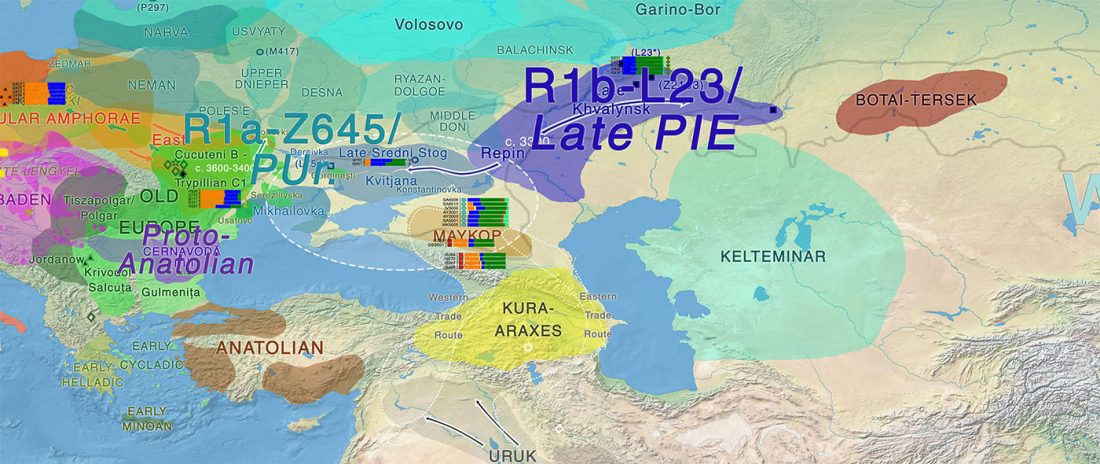
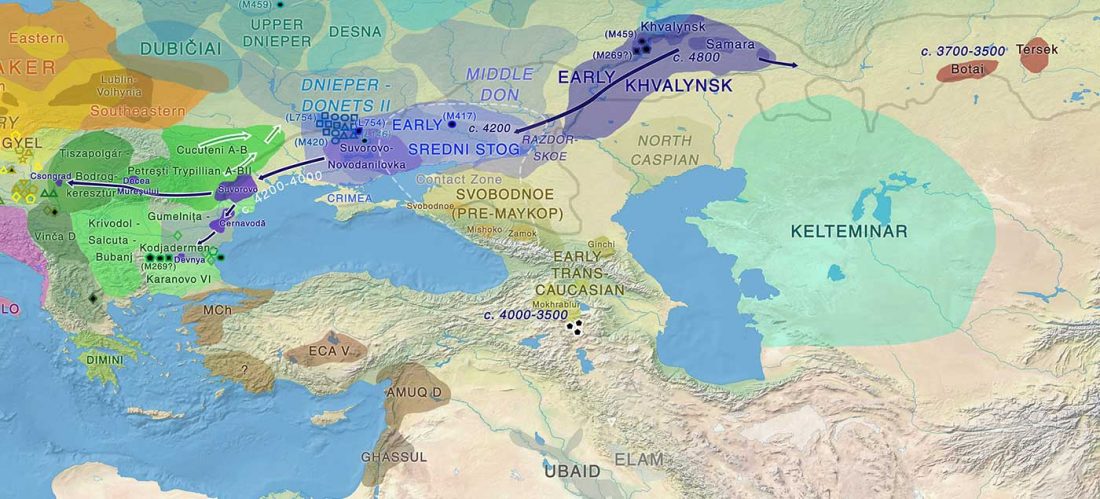
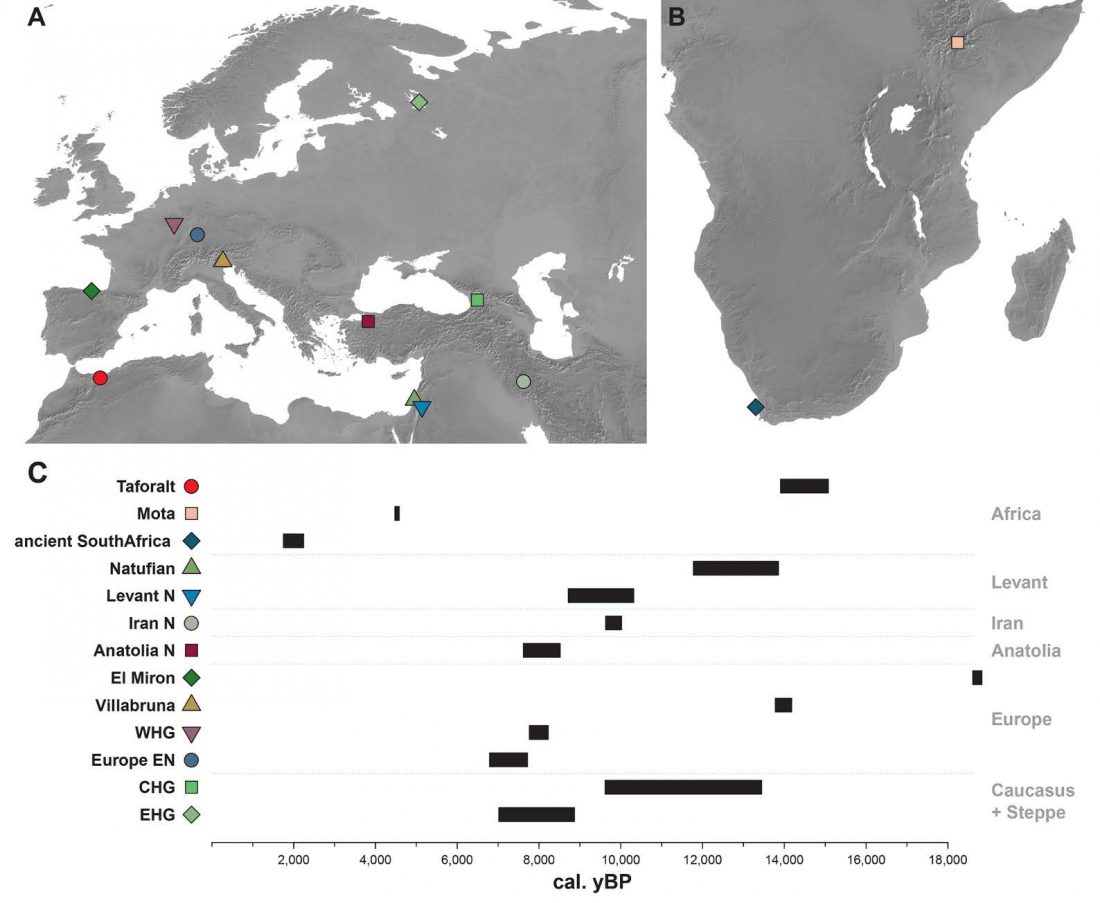
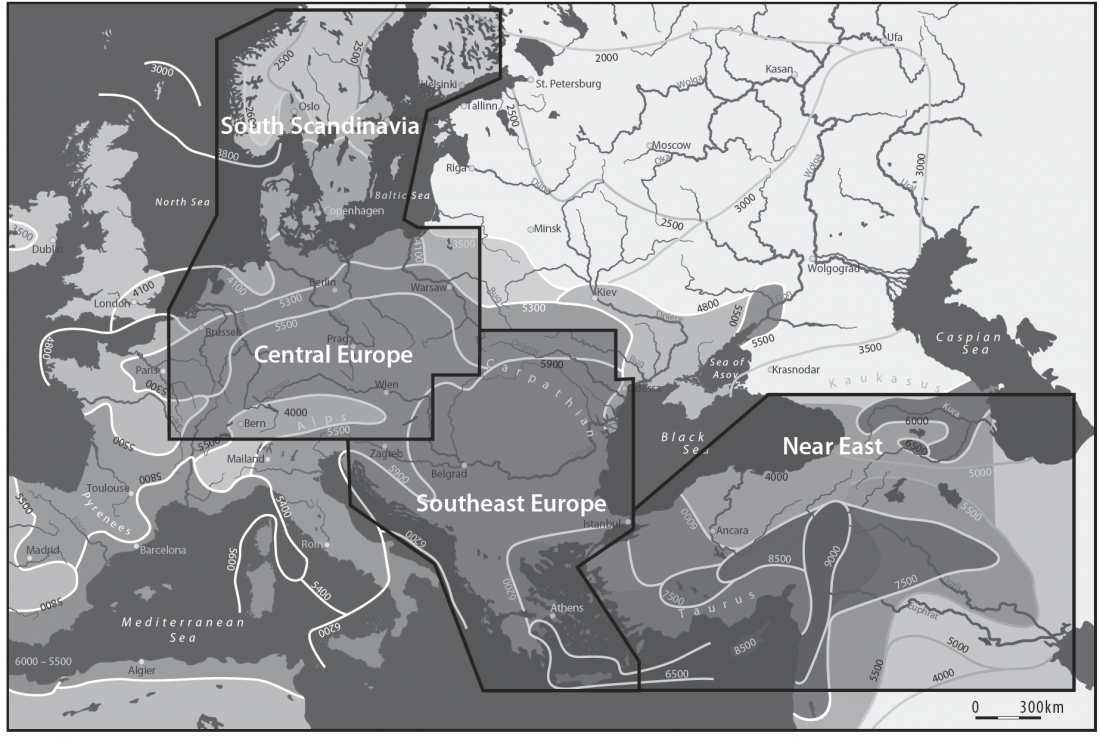
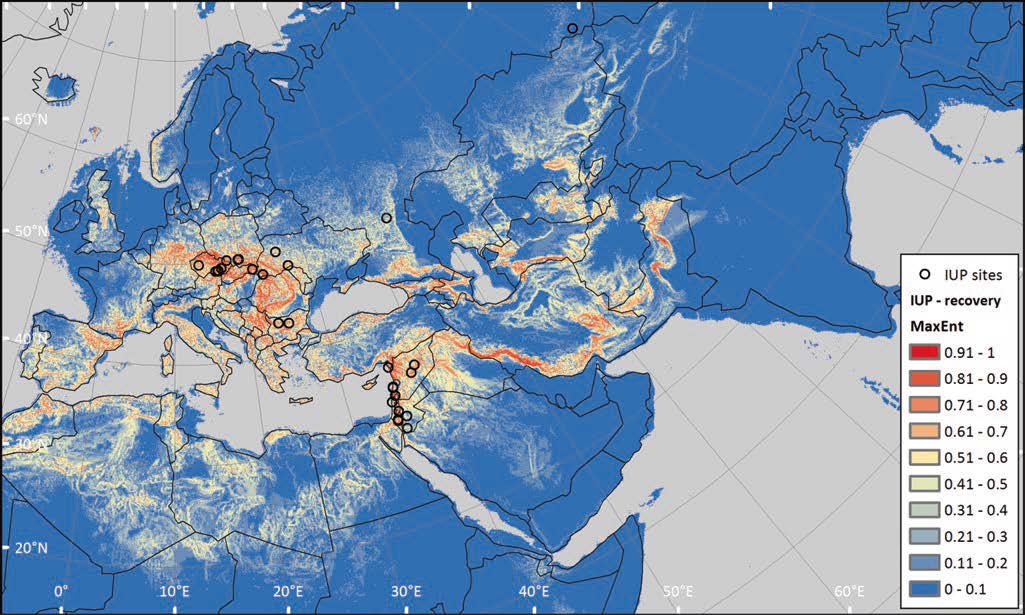
There has been some renewed interest lately in the origin of Proto-Anatolians, because of the recent lecture by Petra Goedegebuure, associate professor of Hittitology at the University of Chicago: Anatolians on the Move: From Kurgans to Kanesh, given at the Oriental Institute (Feb 5 2020).
I will try to comment on her lecture with a critical view of some of her ideas, keeping in mind reasons for one or the other potential routes, which we can for the moment simplify as Gimbutas’ (1965, 1993) eastern route through the Caucasus vs. Anthony’s (2007, 2015) … Read the rest “Proto-Anatolians: from the Southern Caucasus or the Balkans?”