About two months ago I stumbled upon a gem in archaeological studies related to Proto-Indo-Europeans, the book О скипетрах, о лошадях, о войне: этюды в защиту миграционной концепции М.Гимбутас (On sceptres, on horses, on war: Studies in defence of M. Gimbutas’ migration concepts), 2007, by V. A. Dergachev, from the Institute of Cultural Heritage of the Moldavian Republic.
About two months ago I stumbled upon a gem in archaeological studies related to Proto-Indo-Europeans, the book О скипетрах, о лошадях, о войне: этюды в защиту миграционной концепции М.Гимбутас (On sceptres, on horses, on war: Studies in defence of M. Gimbutas’ migration concepts), 2007, by V. A. Dergachev, from the Institute of Cultural Heritage of the Moldavian Republic.
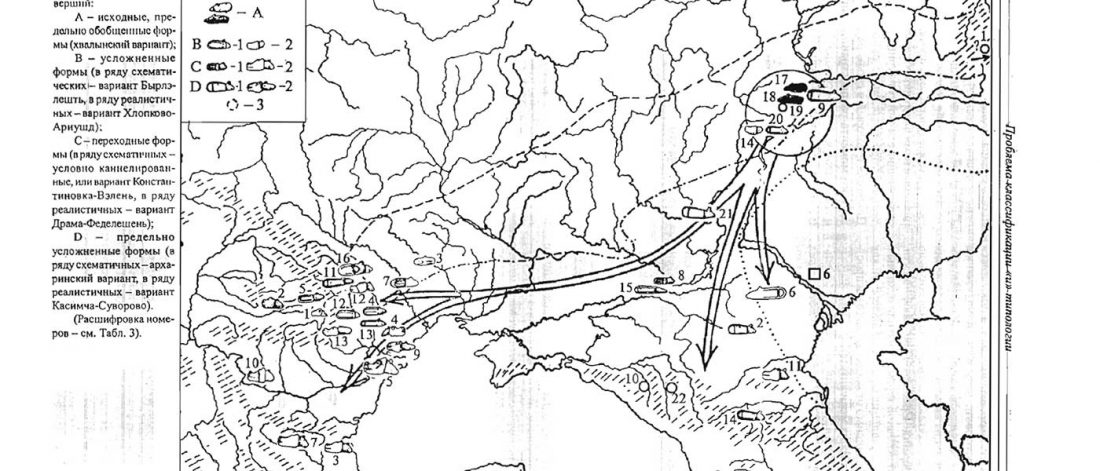
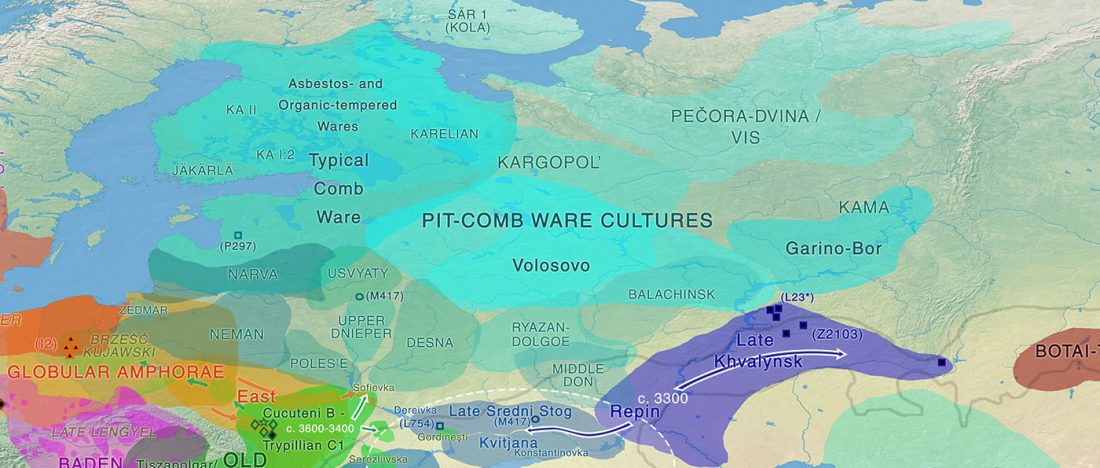
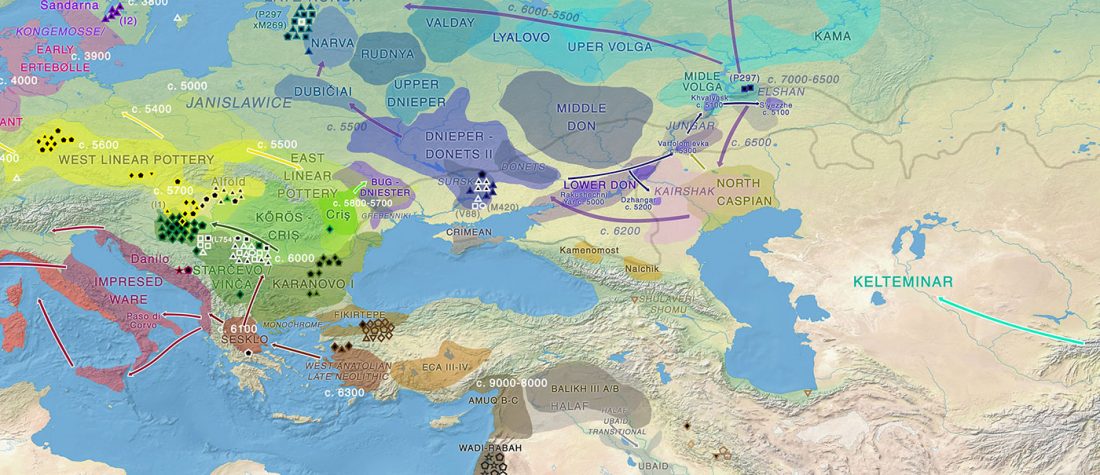
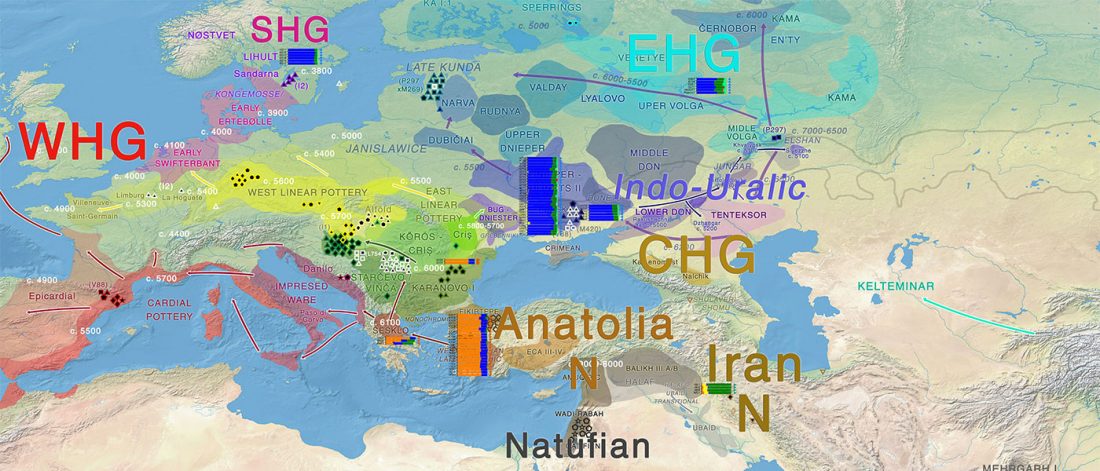
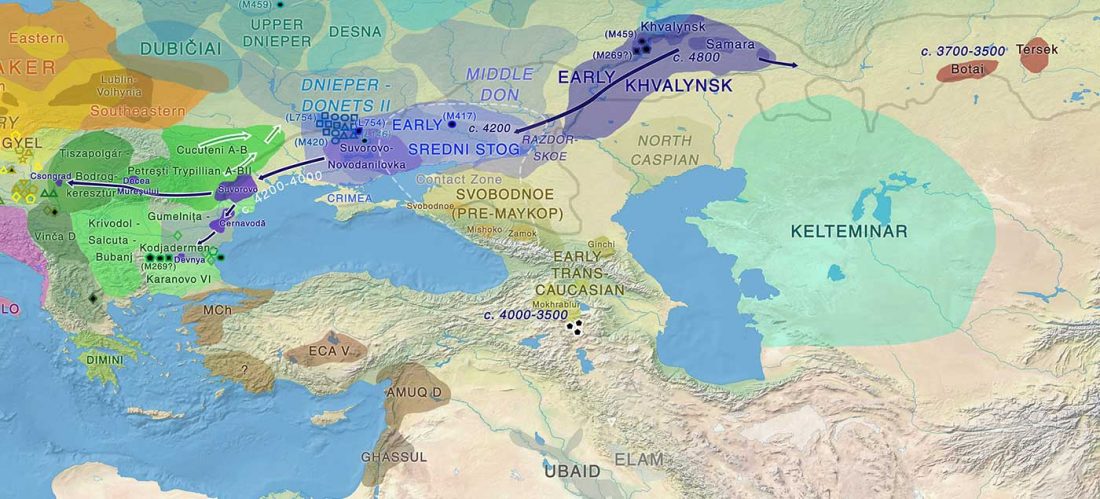
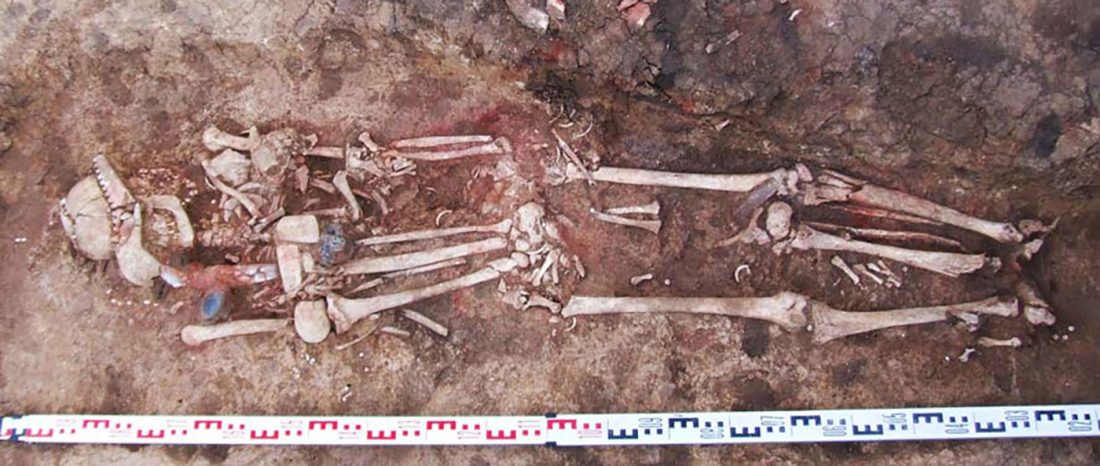
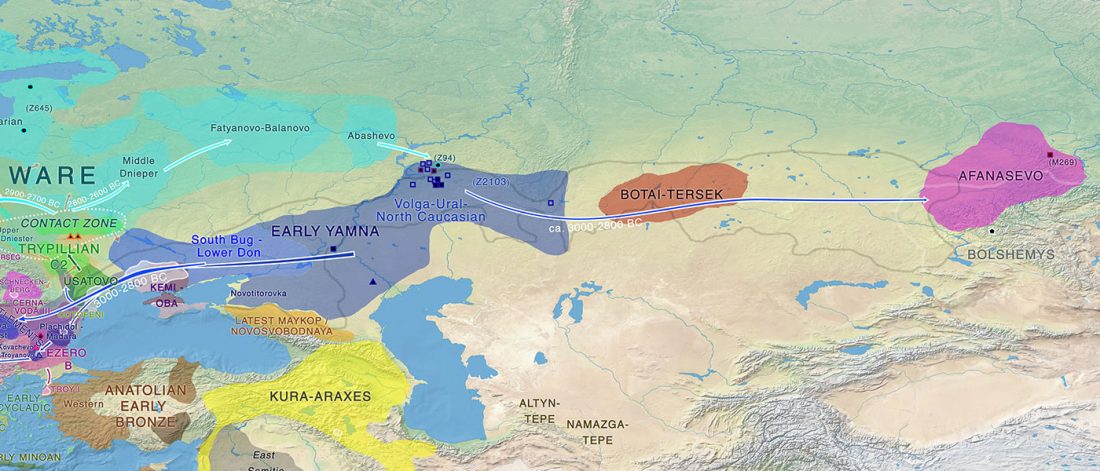
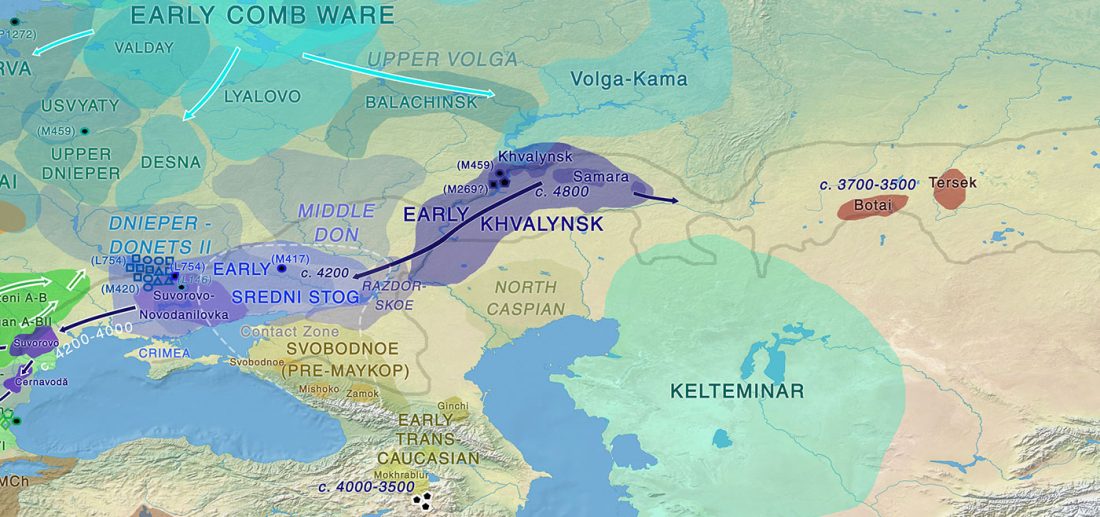
Dergachev’s work dedicates 488 pages to a very specific Final Neolithic-Eneolithic period in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, and the most relevant parts of the book concern the nature and expansion of horses and horse domestication, horse-head scepters, and other horse-related symbology… Read the rest “About Scepters, Horses, and War: on Khvalynsk migrants in the Caucasus and the Danube”