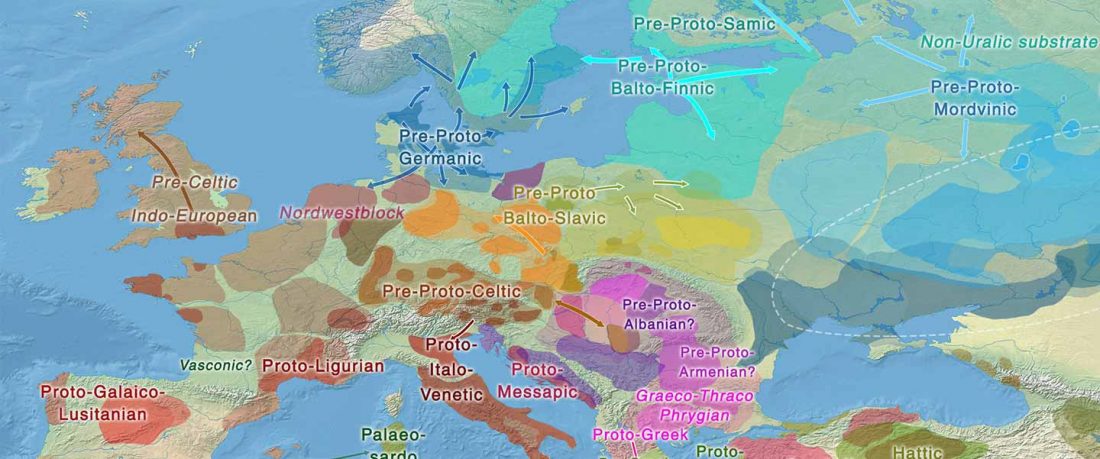
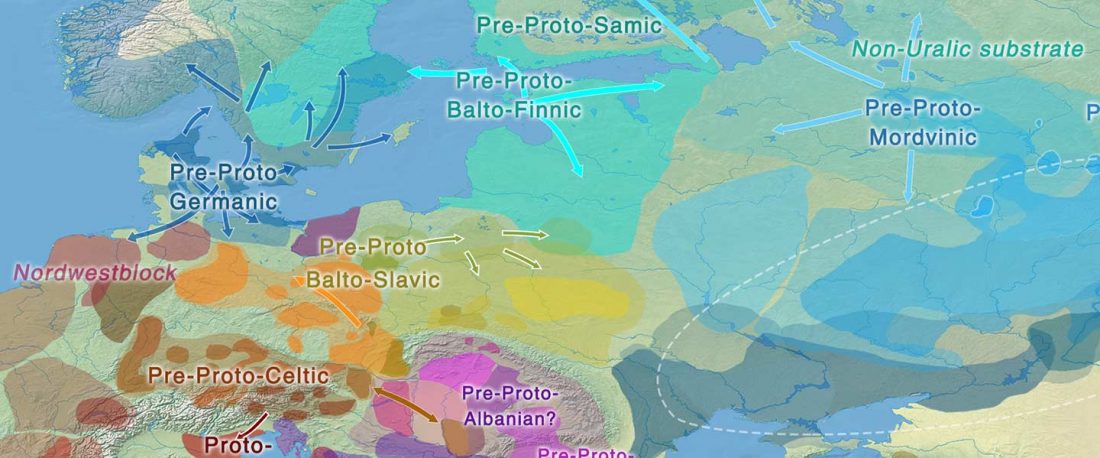
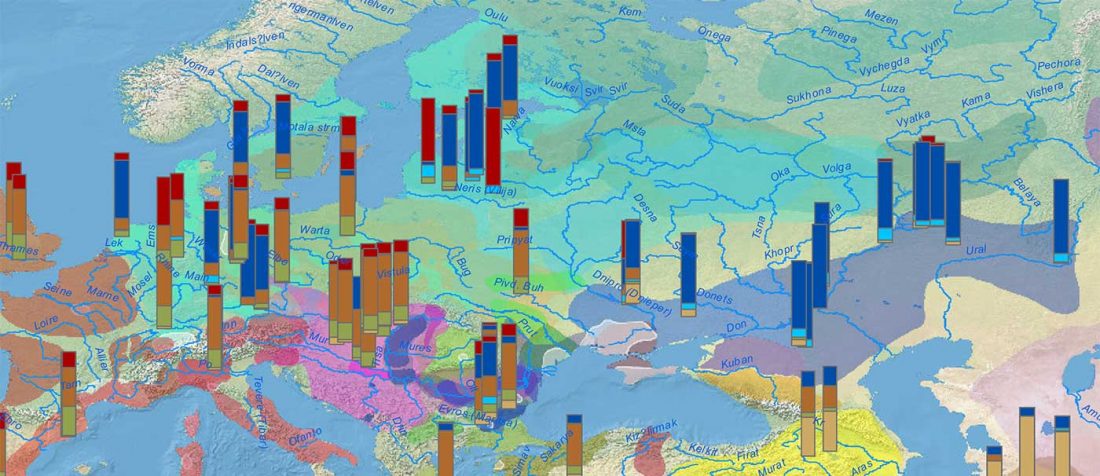
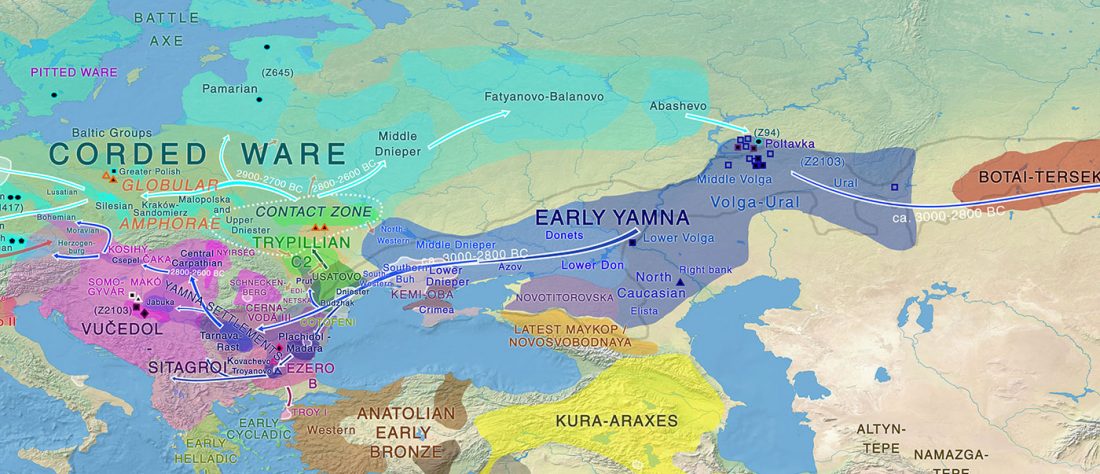
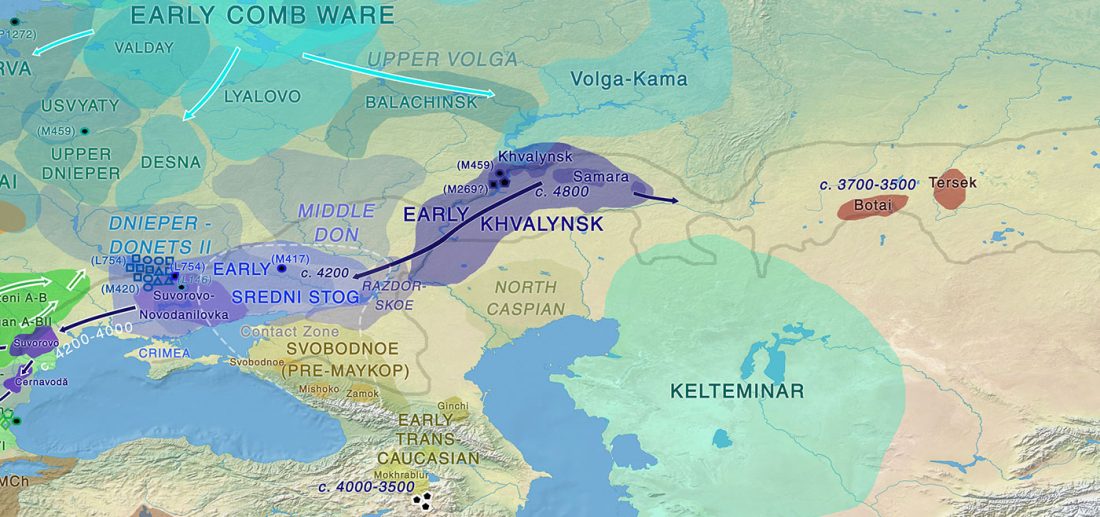
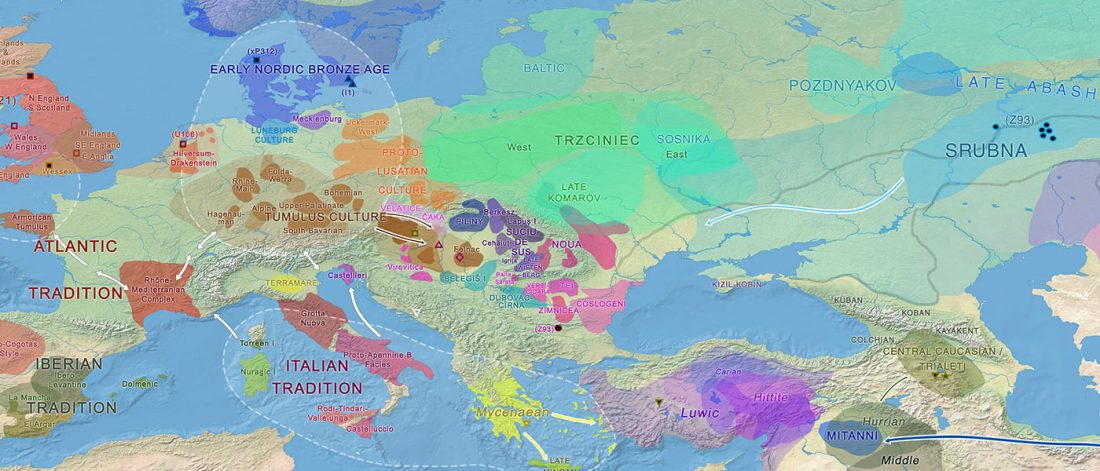
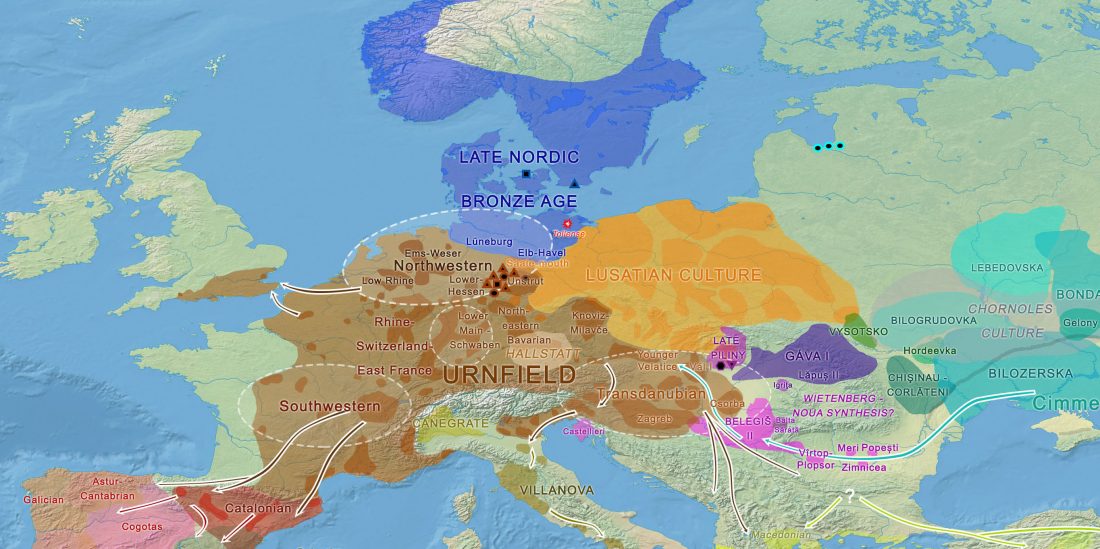
New archaeological paper (behind paywall) New evidence on the southeast Baltic Late Bronze Age agrarian intensification and the earliest AMS dates of Lens culinaris and Vicia faba, by Minkevičius et al. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany (2019).
Interesting excerpts (emphasis mine):
Arrival of farming in the south-east Baltic
… Read the rest “The Lusatian culture, the most likely vector of Balto-Slavic expansions”The current state of research reveals no firm evidence of crop cultivation in the region before the LBA (Piličiauskas et al. 2017b; Grikpėdis and Motuzaitė-Matuzevičiūtė 2018). Current archaeobotanical data firmly suggest the adoption of farming during the EBA to LBA transition. (…) By comparison, in other parts of N Europe subsistence economy