This is mainly a reread of from Book Two: A Game of Clans of the series A Song of Sheep and Horses: chapters iii.5. Early Indo-Europeans and Uralians, iv.3. Early Uralians, v.6. Late Uralians and vi.3. Disintegrating Uralians.
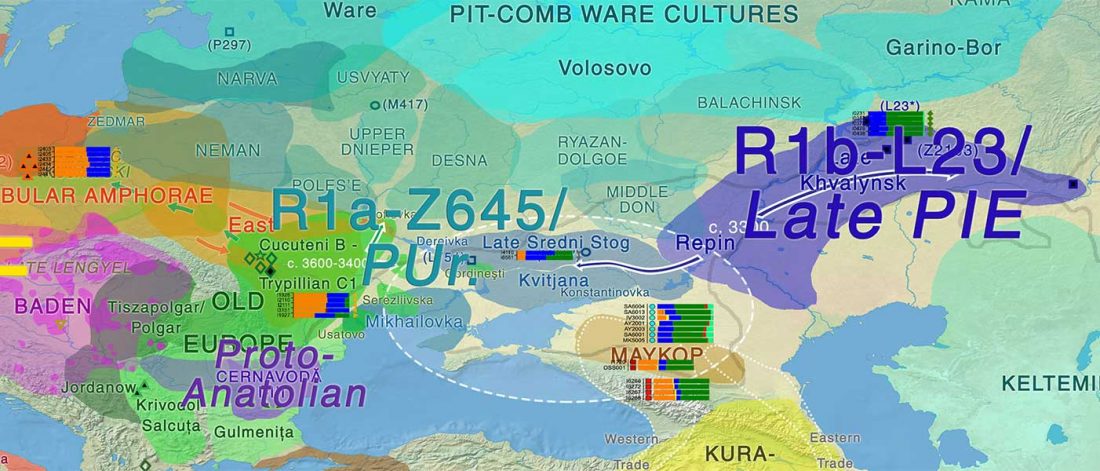
“Sredni Stog”
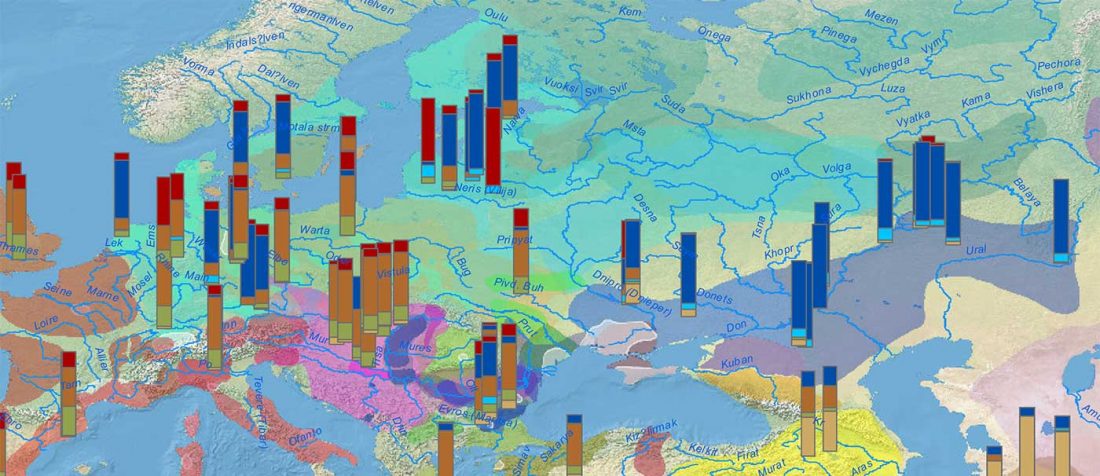
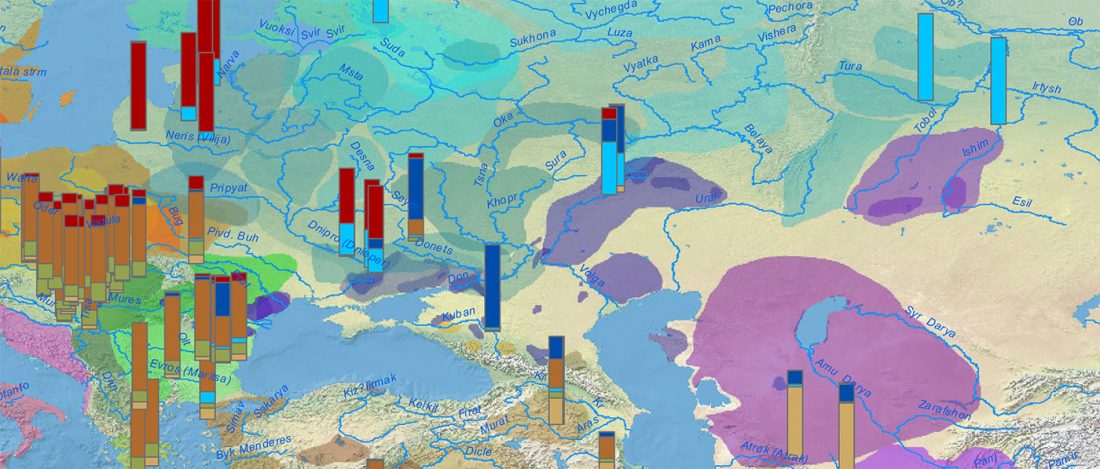
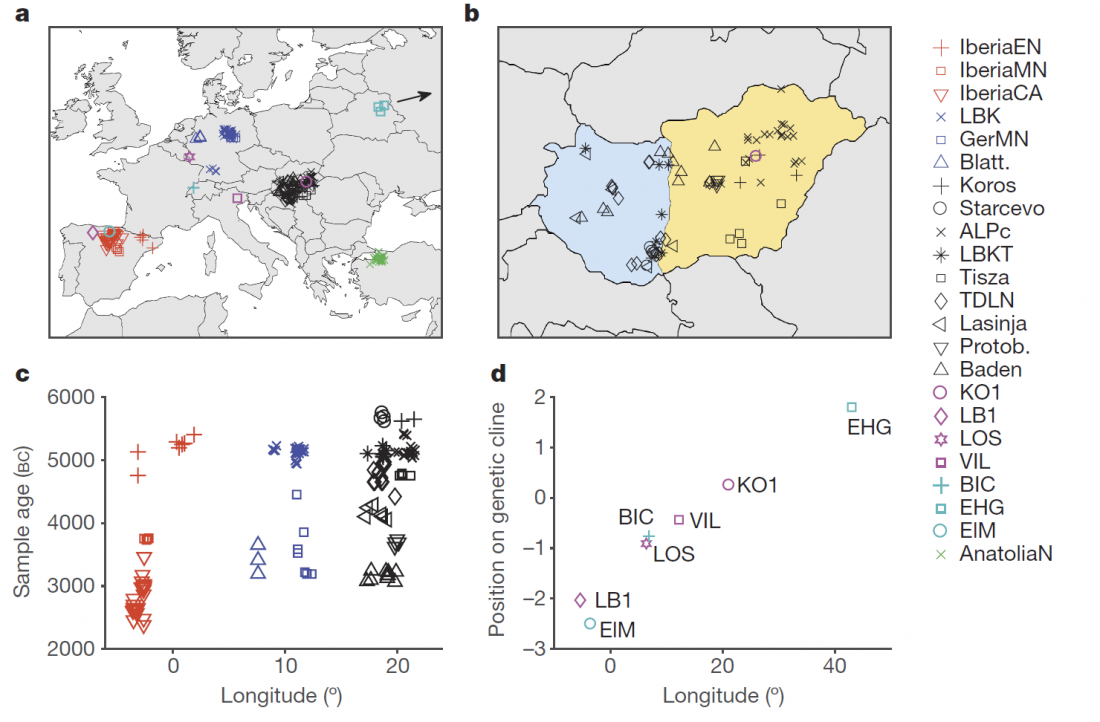
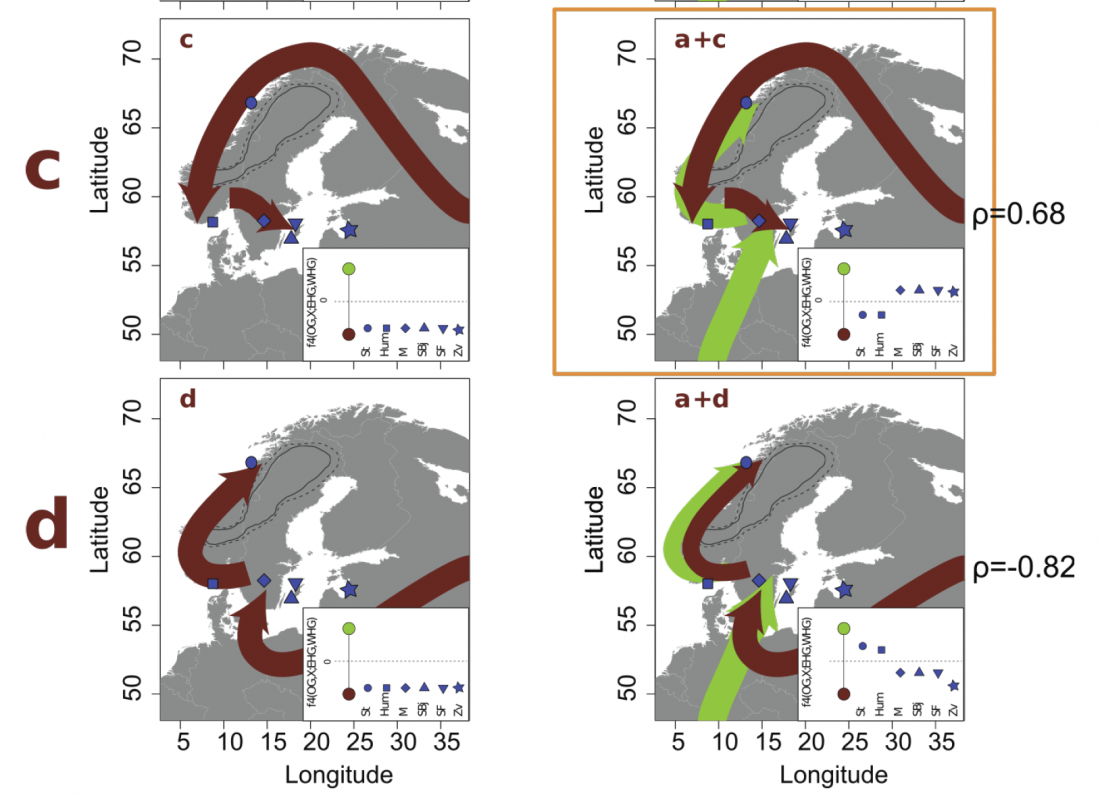
While the true source of R1a-M417 – the main haplogroup eventually associated with Corded Ware, and thus Uralic speakers – is still not known with precision, due to the lack of R1a-M198 in ancient samples, we already know that the Pontic-Caspian steppes were probably not it.
We have many samples from the north Pontic area since … Read the rest “ASoSaH Reread (II): Y-DNA haplogroups among Uralians (apart from R1a-M417)”