Recent paper First encounters in the north: cultural diversity and gene flow in Early Mesolithic Scandinavia, by Manninen et al. Antiquity (2021).
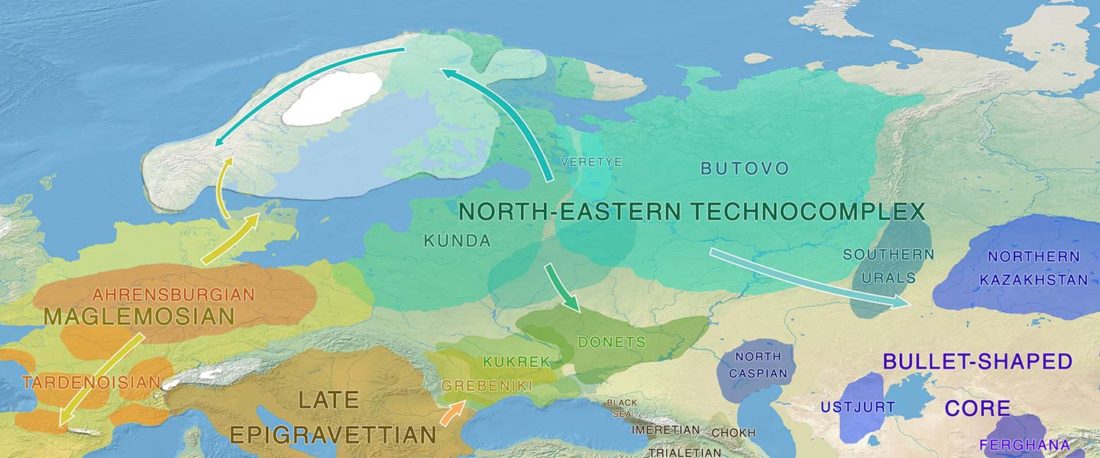
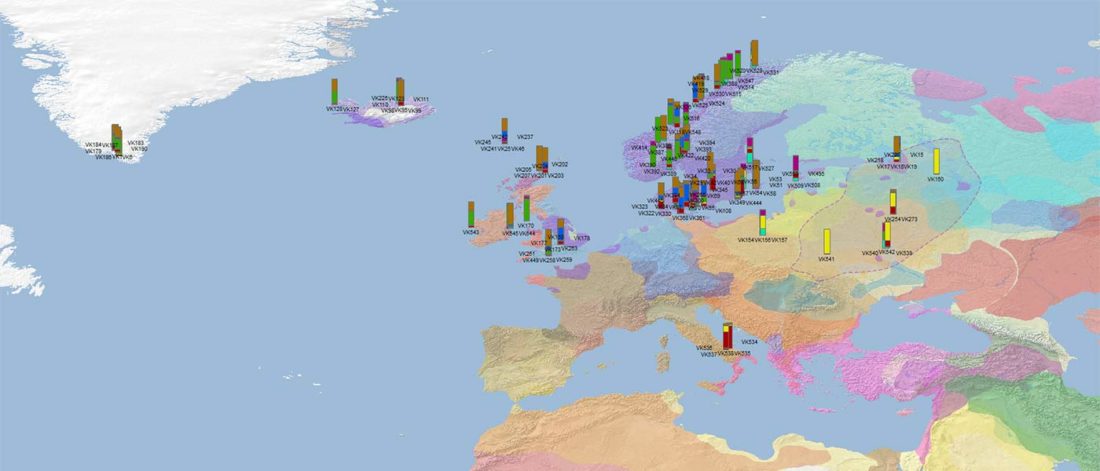
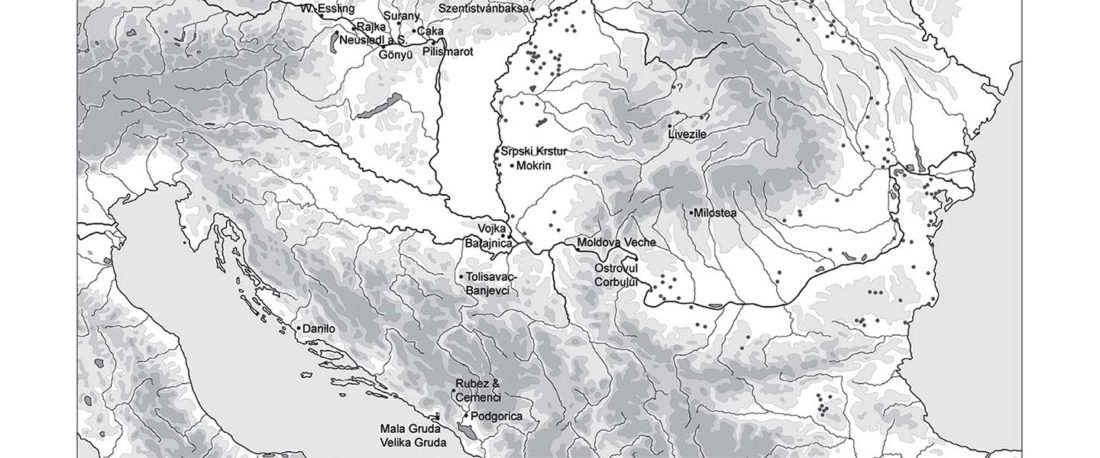
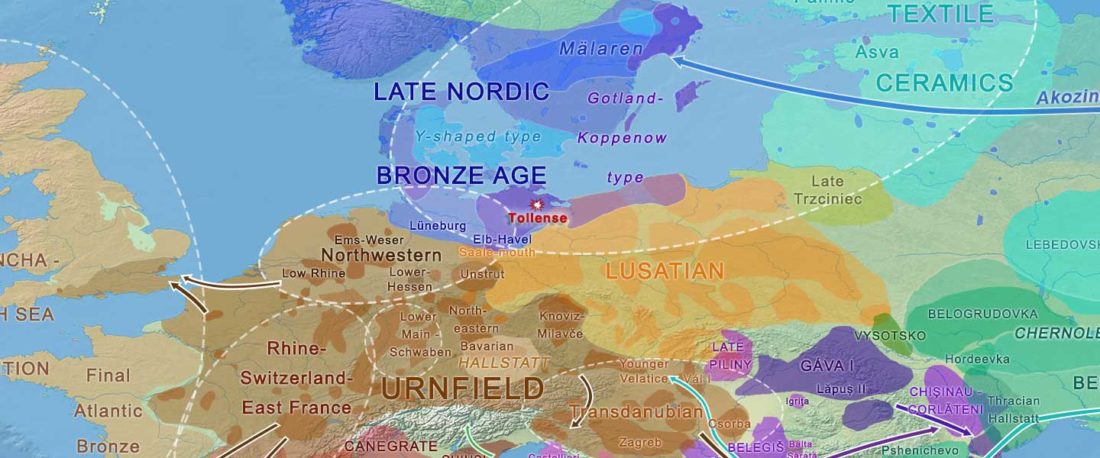
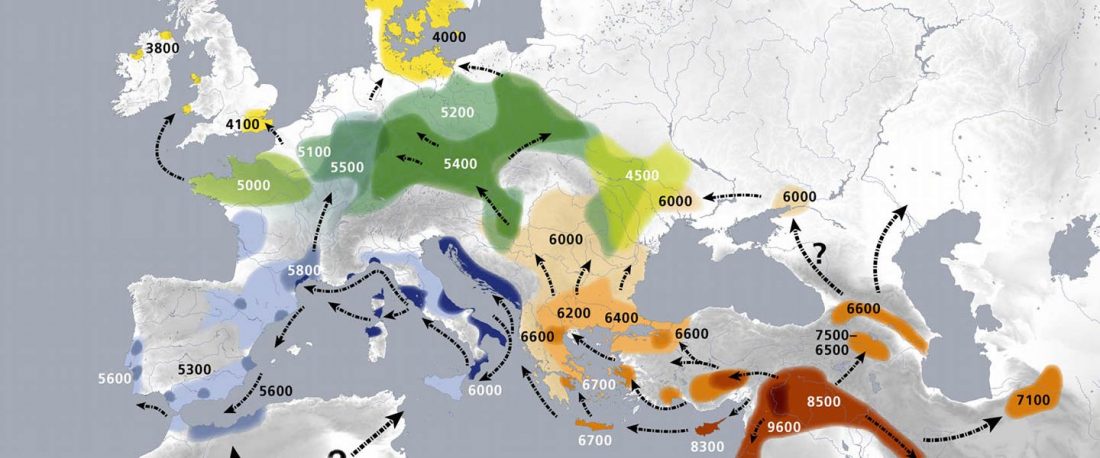
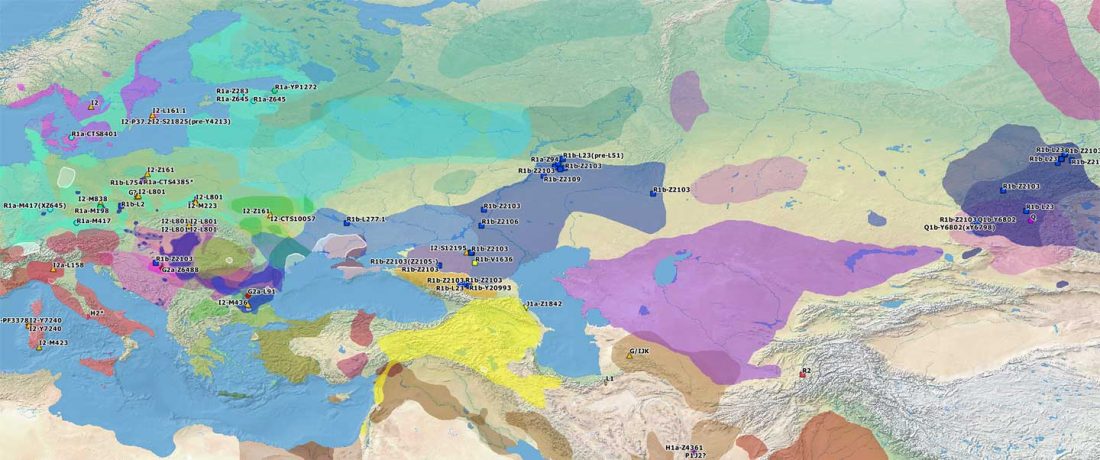
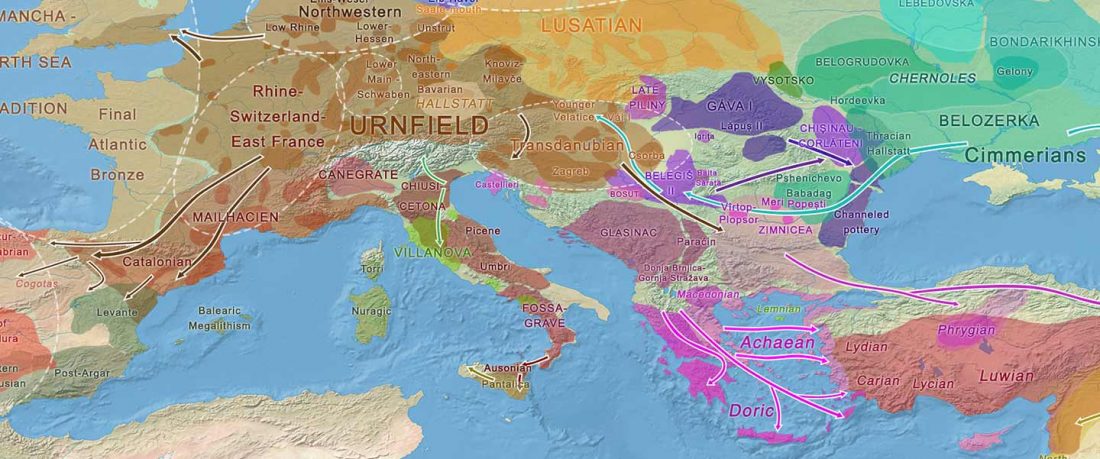
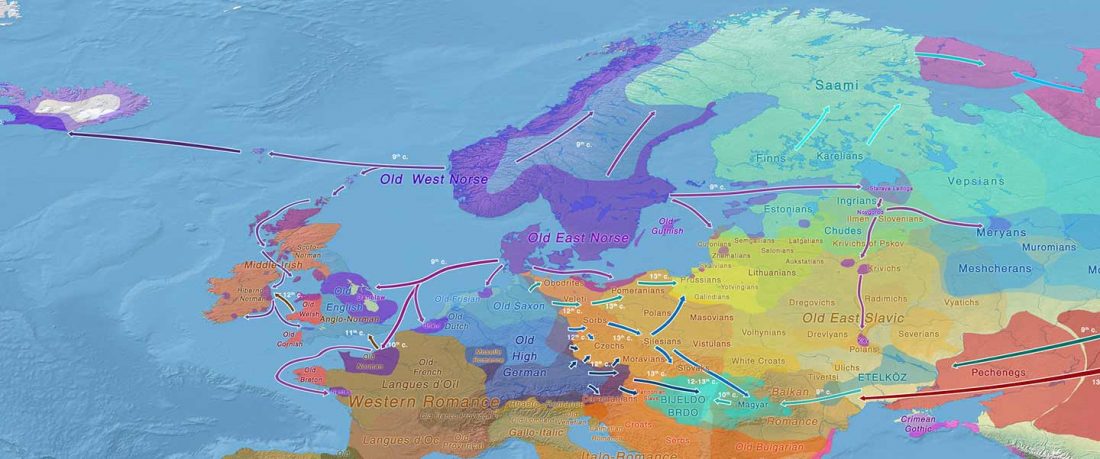
The authors criticize the model laid out in Günther et al. (2018), whereby the origin of the previously defined Mesolithic Scandinavian hunter-gatherer genetic group (SHG) was defined as an admixture between genetically defined WHG and EHG populations that migrated into Scandinavia from two separate Ice Age refugia: the south (WHG) and north (EHG). This dualistic model was further associated with two specific lithic blade technologies present in Early Mesolithic Scandinavia (Sørensen et al. 2013), as summarized … Read the rest “The importance of archaeology before population genomics”