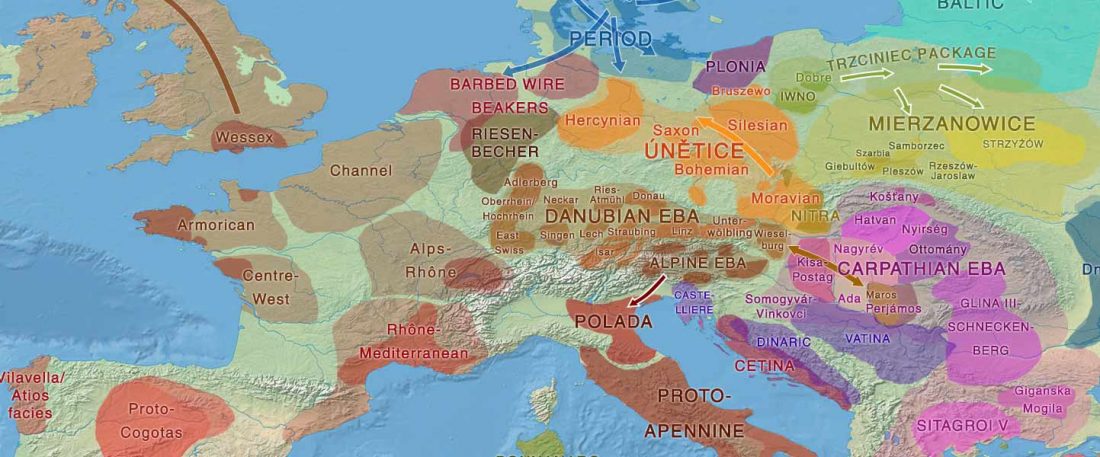
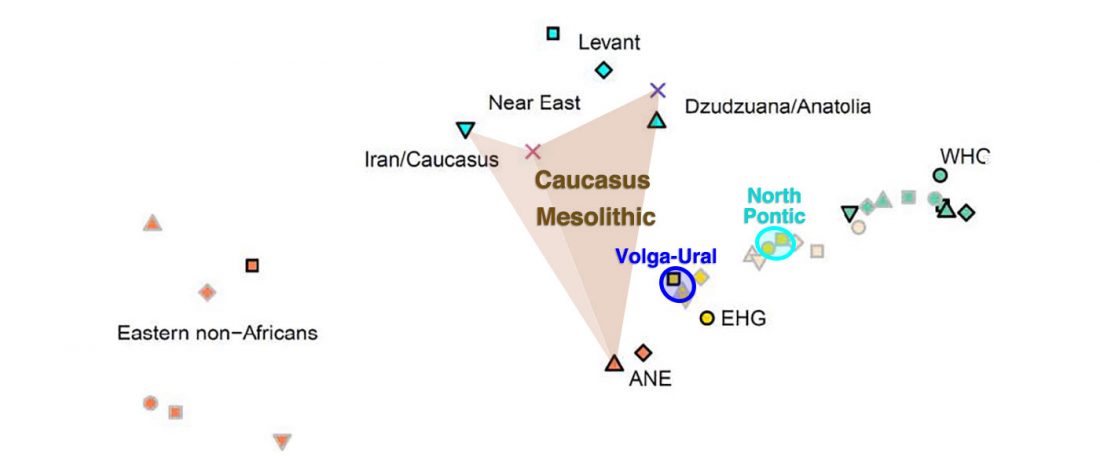
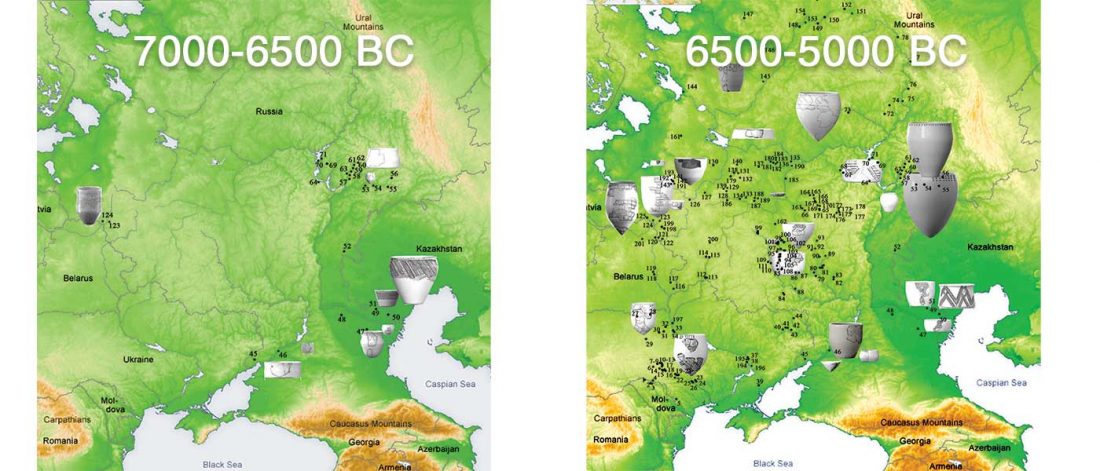
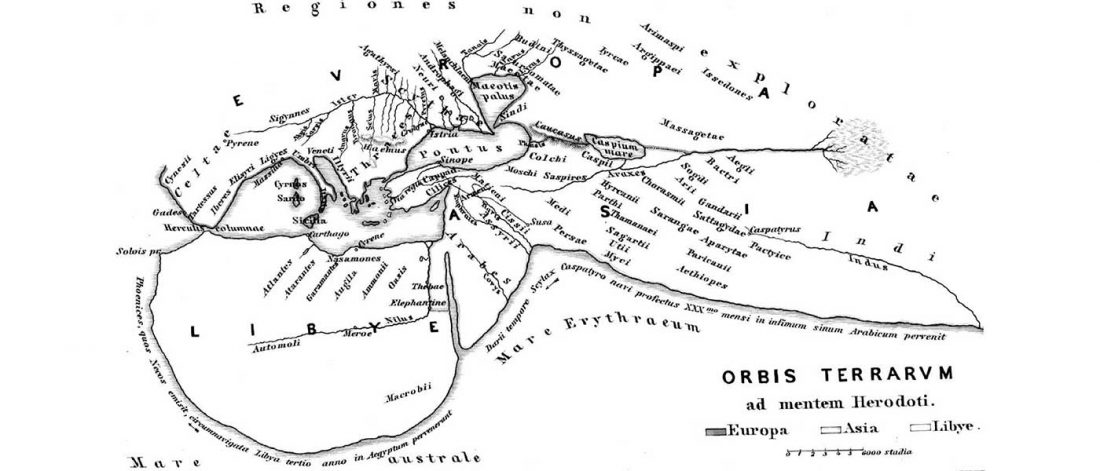
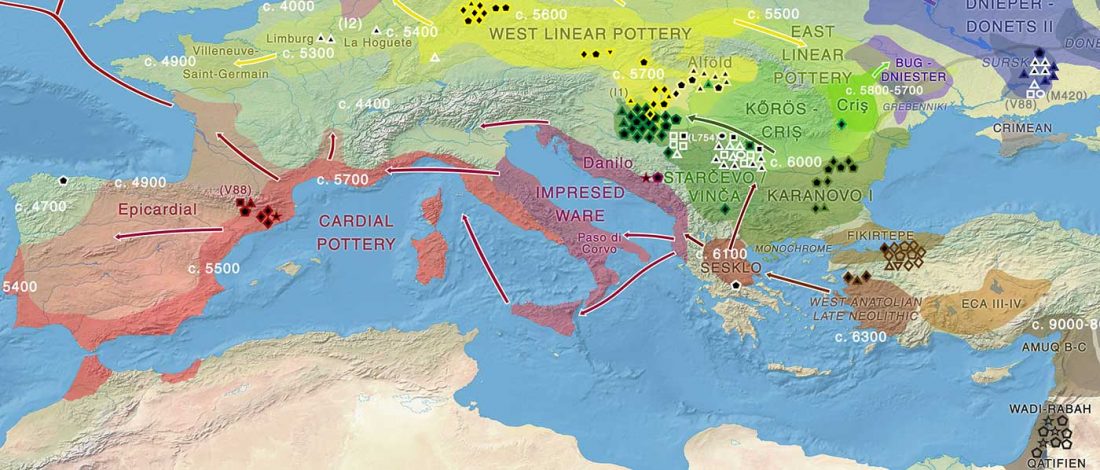
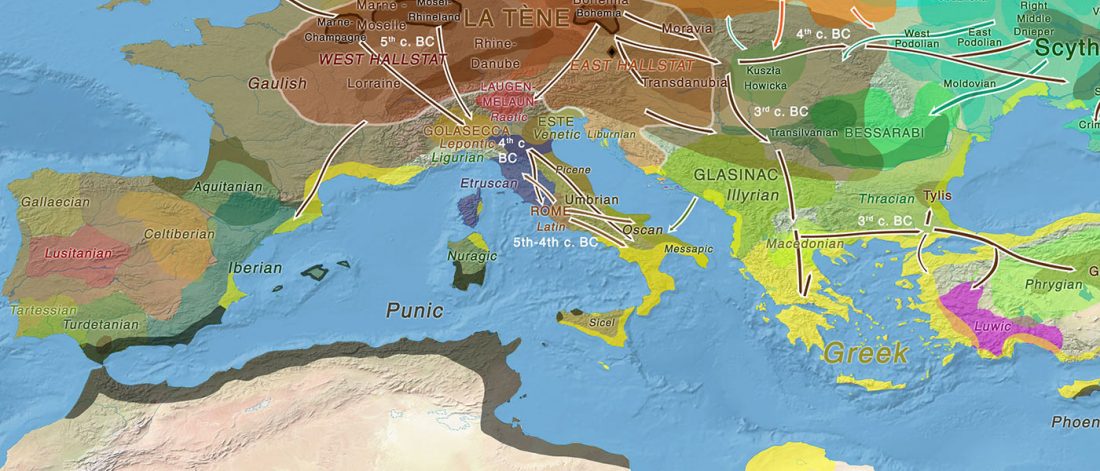
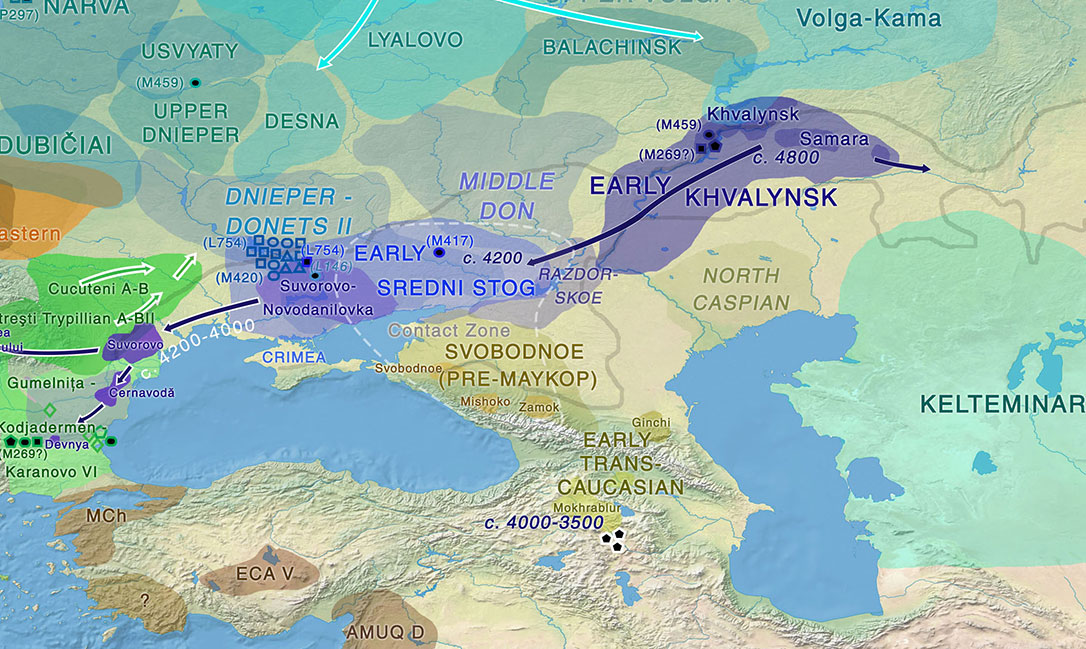
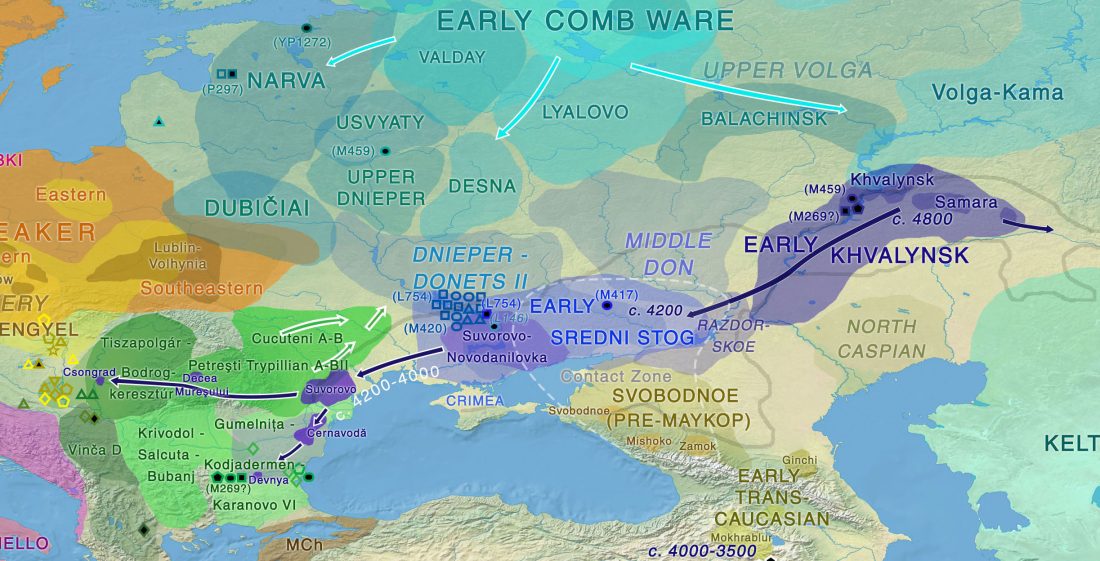
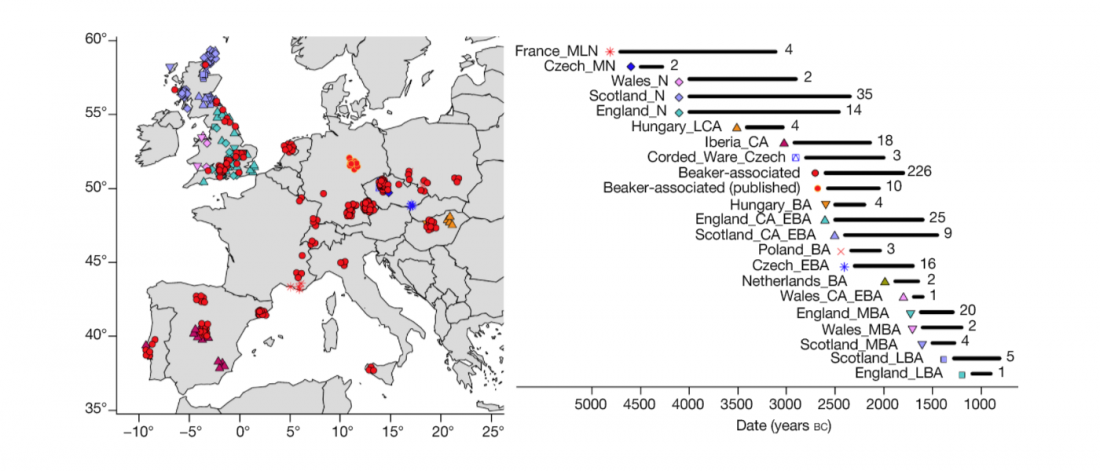
Two new interesting papers concerning Corded Ware and Bell Beaker peoples appeared last week, supporting yet again what is already well-known since 2015 about West Uralic and North-West Indo-European speakers and their expansion.
Below are relevant excerpts (emphasis mine) and comments.
#UPDATE (27 OCT 2019): I have updated Y-DNA and mtDNA maps of Corded Ware, Bell Beaker, EBA, MBA, and LBA migrations. I have also updated PCA plots, which now include the newly reported samples and those from the Tollense valley, and I have tried some qpAdm models (see below).