Open access article DNA profiling of Hungarian King Béla III and other skeletal remains originating from the Royal Basilica of Székesfehérvár, Olasz, J., Seidenberg, V., Hummel, S. et al. Archaeol Anthropol Sci (2018).
Abstract
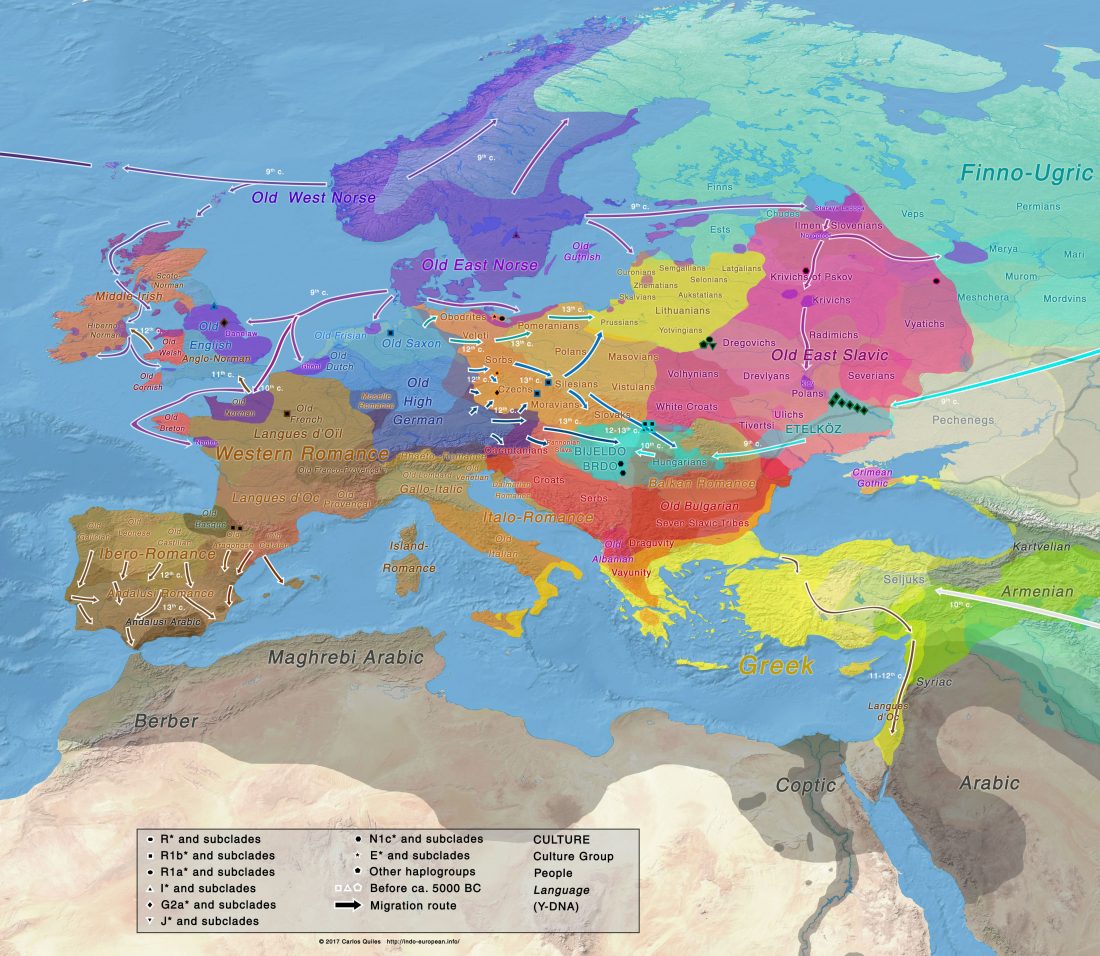
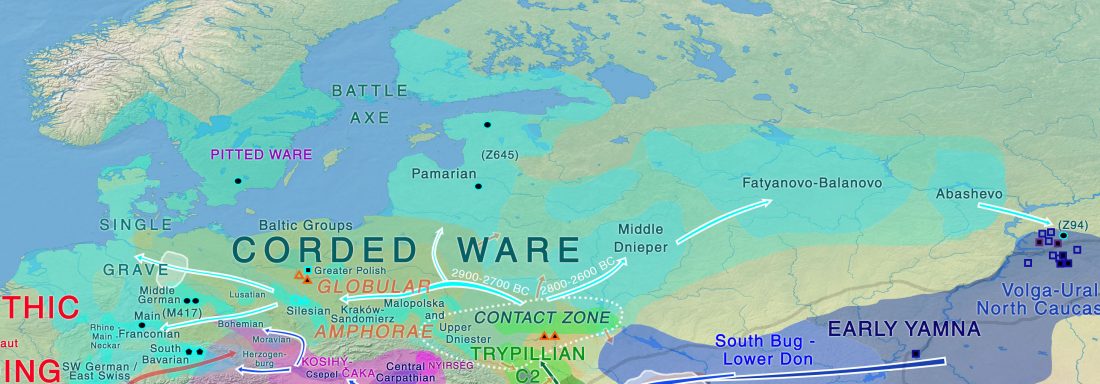
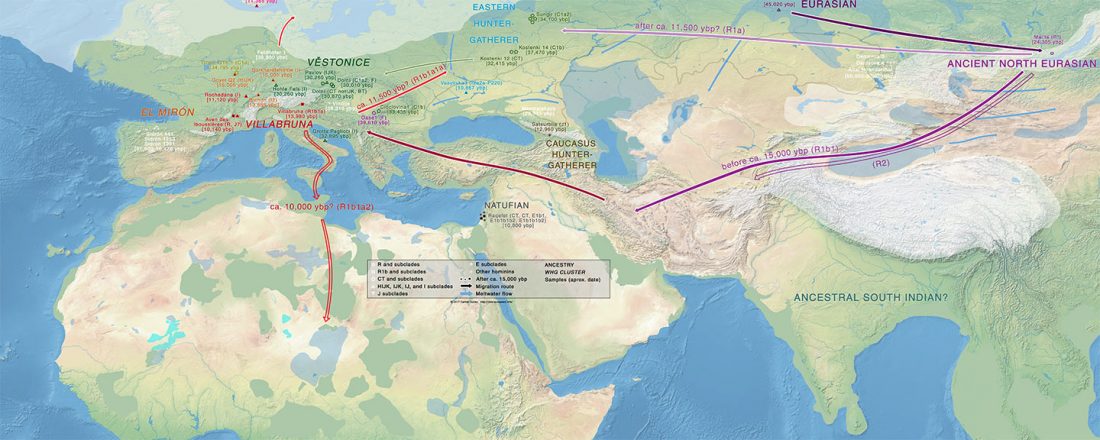
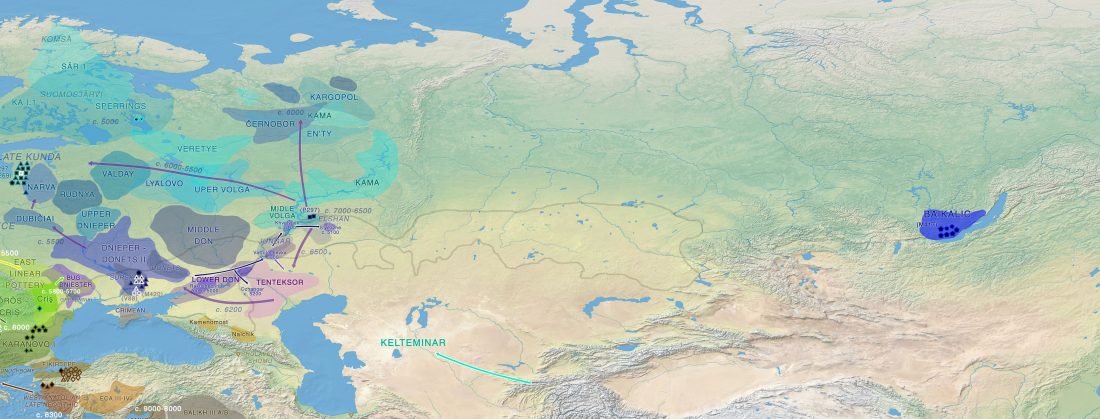
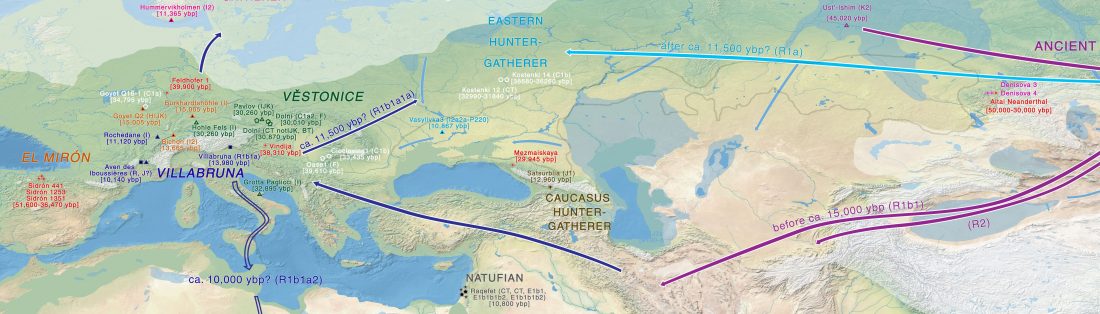
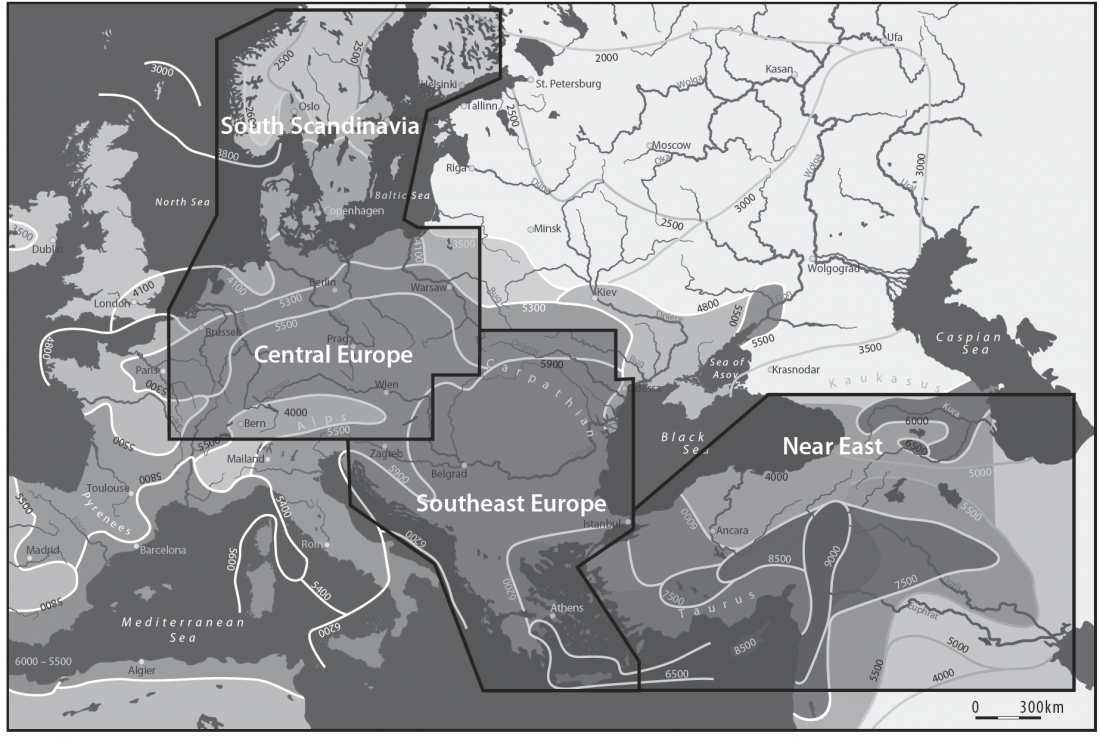
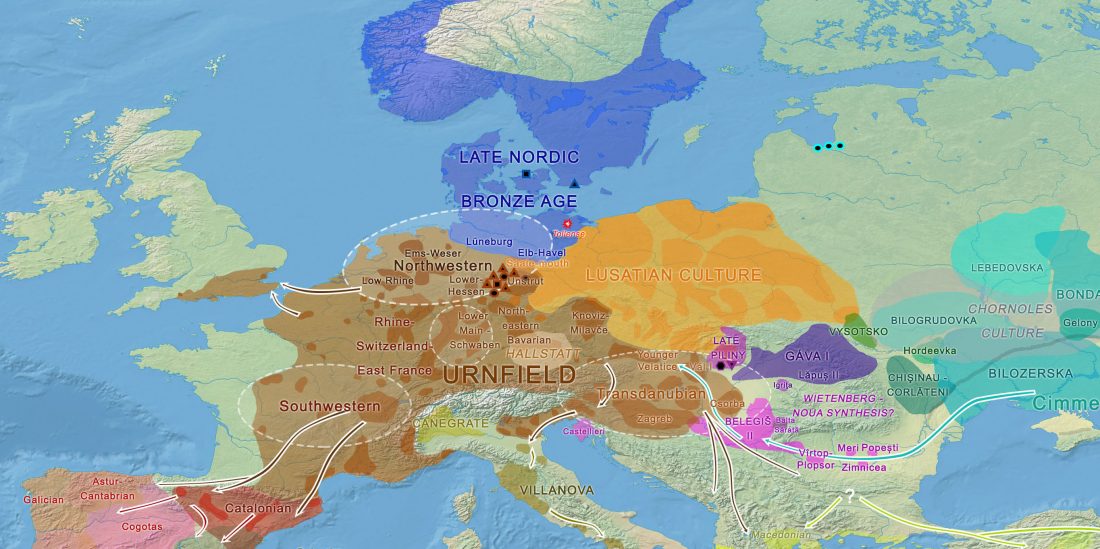
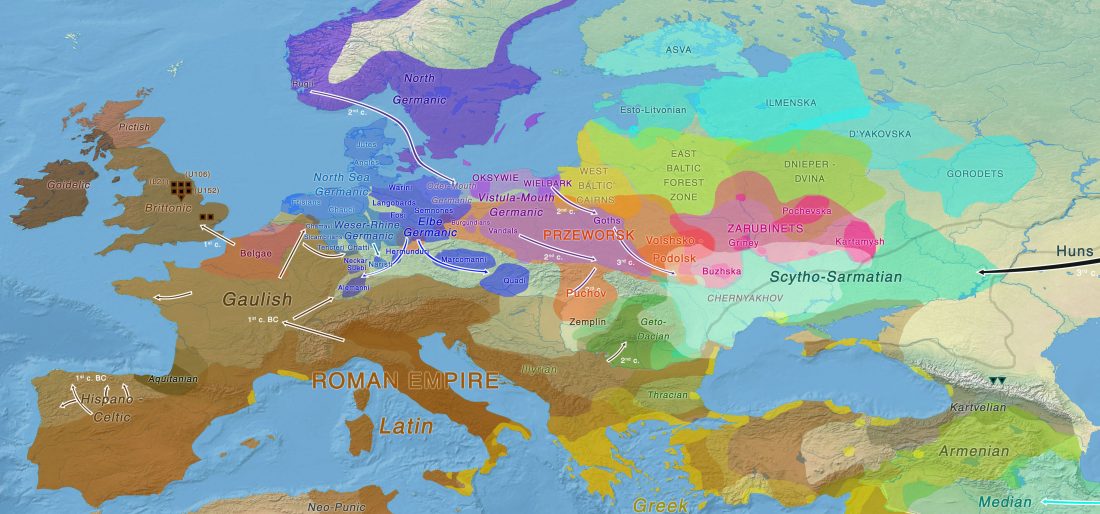
… Read the rest “First Hungarian ruling dynasty, the Árpáds, of Y-DNA haplogroup R1a”A few decades after the collapse of the Avar Khaganate (c. 822 AD), Hungarian invaders conquered the Carpathian Basin (c. 862–895 AD). The first Hungarian ruling dynasty, the Árpáds played an important role in European history during the Middle Ages. King Béla III (1172–1196) was one of the most significant rulers of the dynasty. He also consolidated Hungarian dominance over the Northern Balkans. The