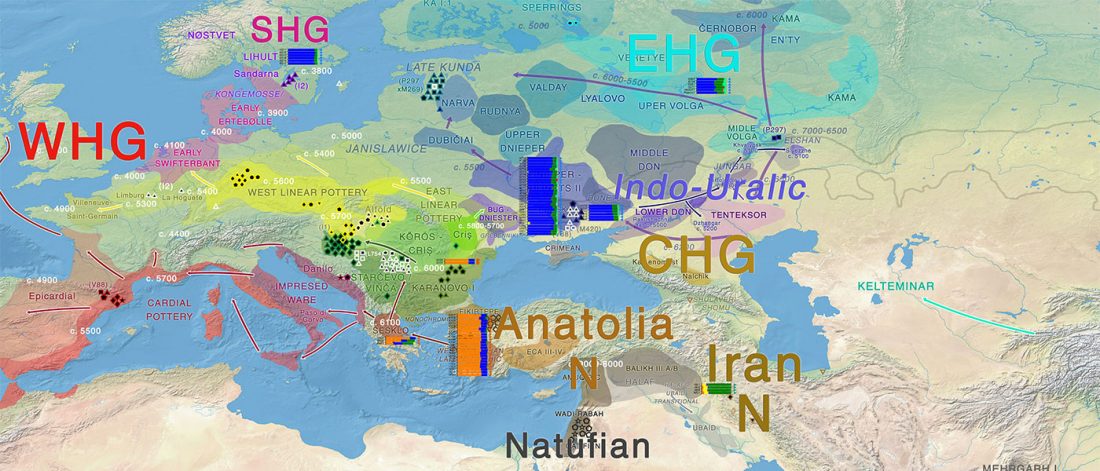
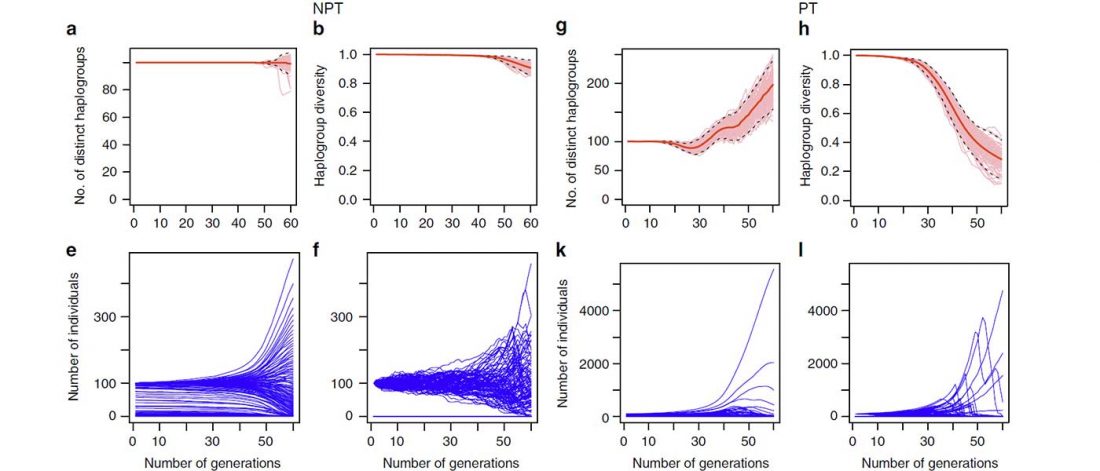
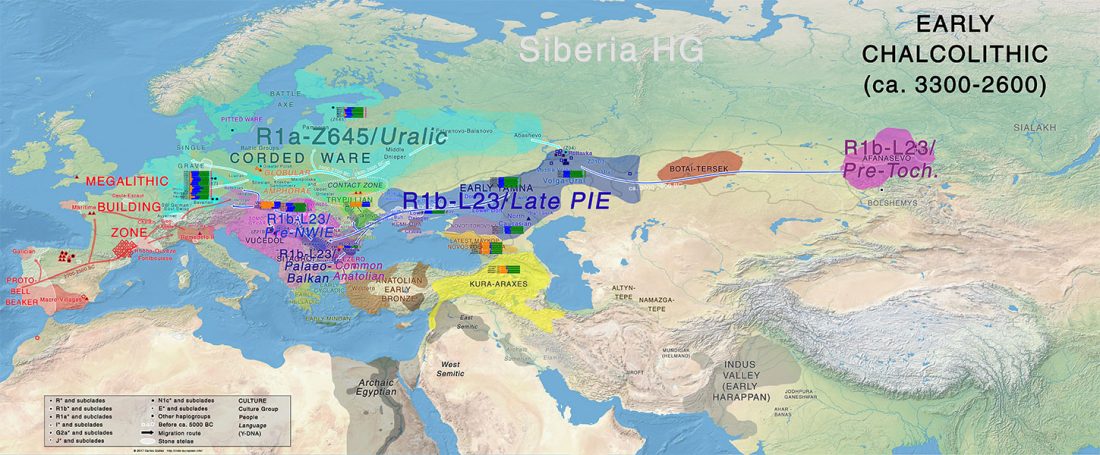
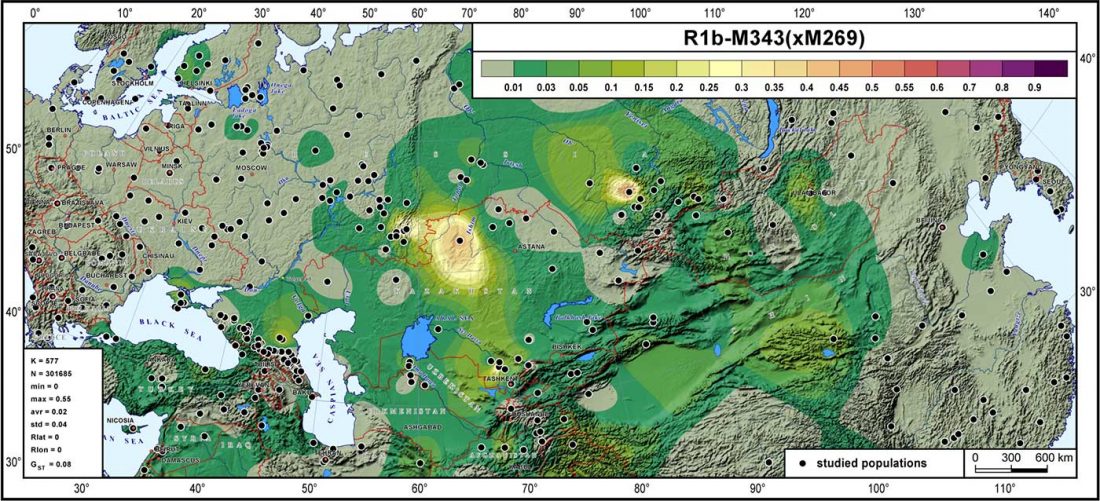
Steppe and Caucasus Eneolithic: the new keystones of the EHG-CHG-ANE ancestry in steppe groups
Some interesting excerpts from Wang et al. (2018):
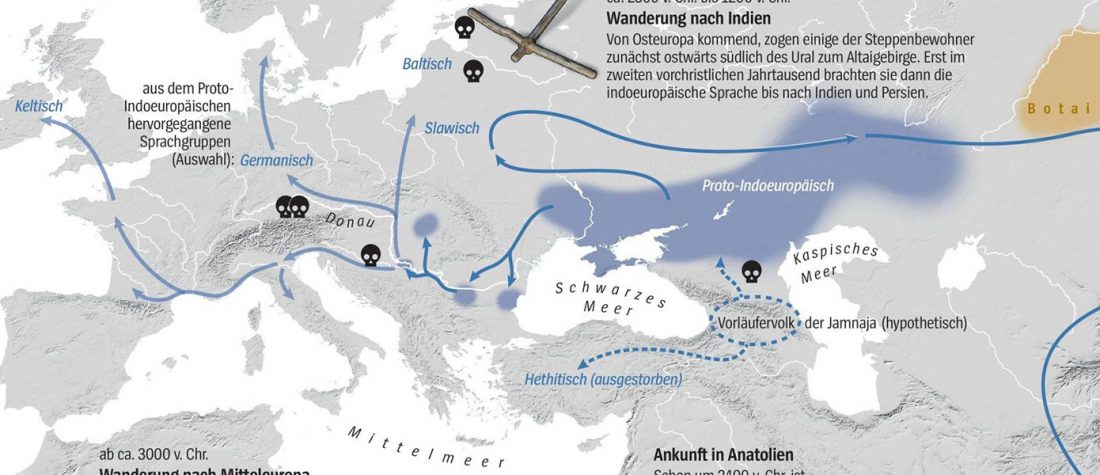
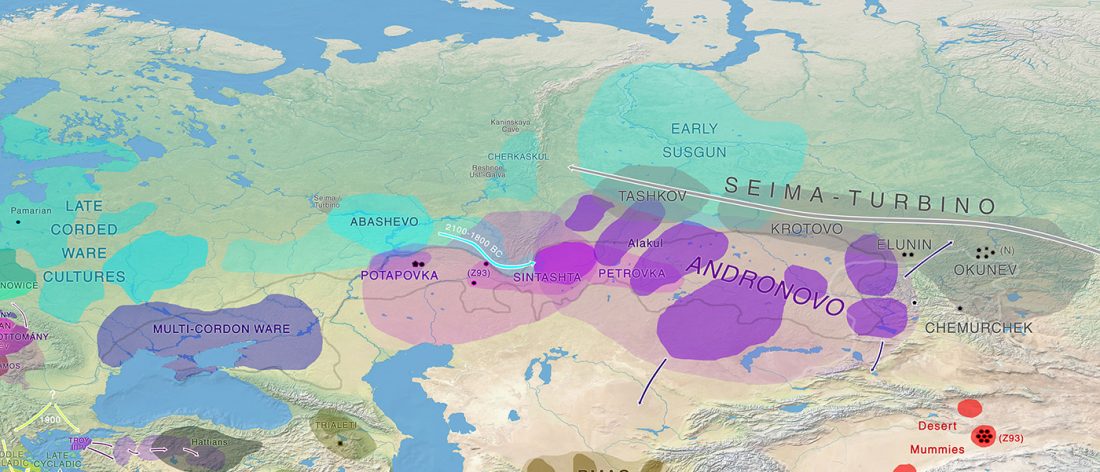
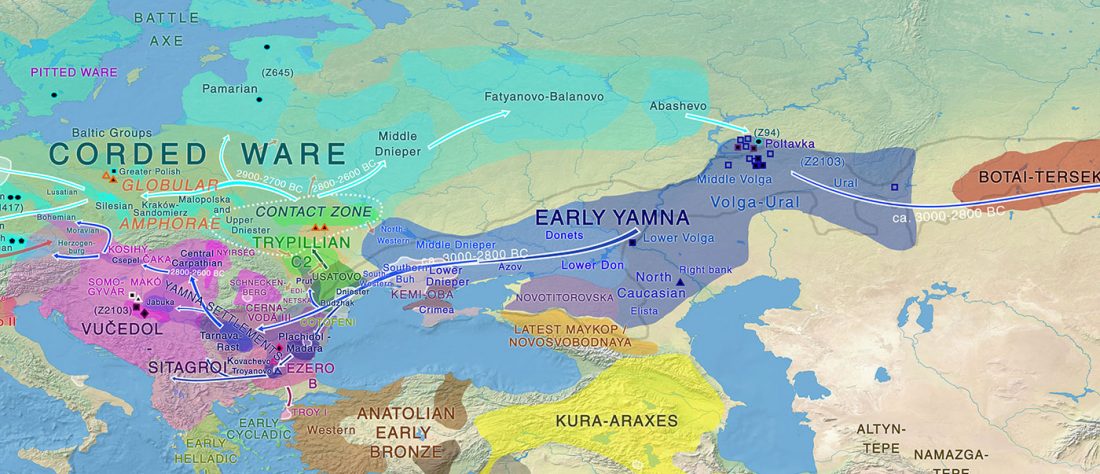
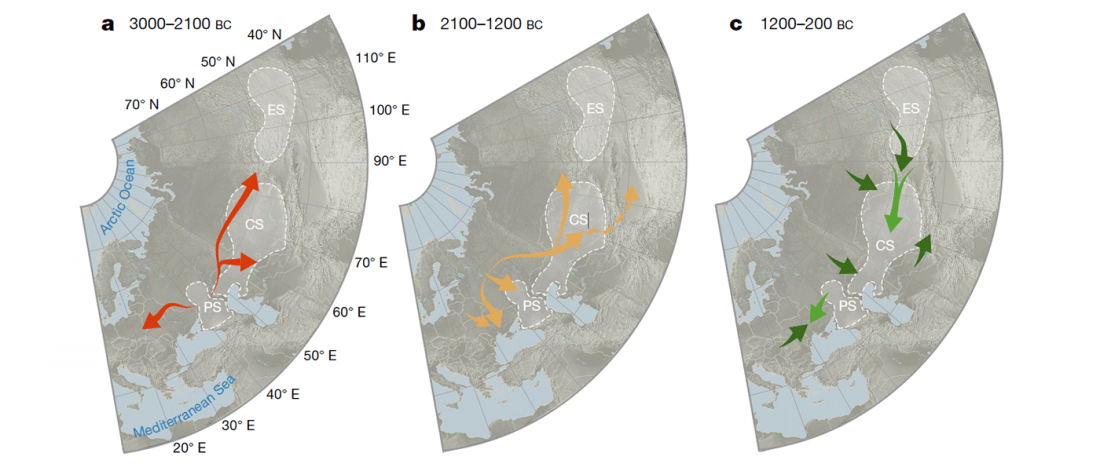
… Read the rest “Steppe and Caucasus Eneolithic: the new keystones of the EHG-CHG-ANE ancestry in steppe groups”An interesting observation is that steppe zone individuals directly north of the Caucasus (Eneolithic Samara and Eneolithic steppe) had initially not received any gene flow from Anatolian farmers. Instead, the ancestry profile in Eneolithic steppe individuals shows an even mixture of EHG and CHG ancestry, which argues for an effective cultural and genetic border between the contemporaneous Eneolithic populations in the North Caucasus, notably Steppe and Caucasus. Due to the temporal limitations of our dataset, we currently cannot determine whether this ancestry is stemming from an existing natural genetic